Chapter 2 About NLI
The Solstice X.25 Network Layer Interface (NLI) provides acces to the X.25 Packet Layer Protocol (PLP). The NLI defines the format that STREAMS messages must take when interfacing to the network layer. This allows for the easy construction of user level library software, and means that applications map conveniently onto the STREAMS format.
2.1 NLI Overview
The Solstice X.25 Network Layer Interface provides access to the X.25 Packet Layer Protocol (PLP). The NLI defines the format that STREAMS messages must take when interfacing to the network layer. This allows for the easy construction of user level library software, and means that applications map conveniently onto the STREAMS format.
Solstice X.25 applications use the putmsg and getmsg system calls to interact with the PLP driver.
Figure 2-1 NLI and STREAMS
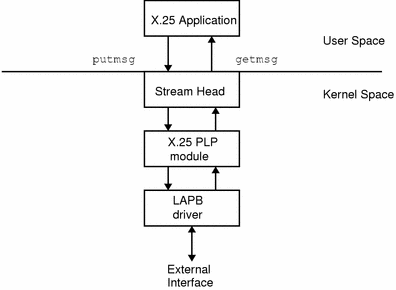
Messages passed using NLI have both a control and a data part. Primitives and associated parameters are passed to the X.25 driver using the control part of the message. Data, if there is any, is contained in the data part of the message.
Figure 2-2 NLI Message Format
Solstice X.25 NLI provides the following:
-
NLI messages
These determine the format of the control parts of putmsg and getmsg, and are used to communicate with the network.
-
A series of ioctls
These communicate with the Solstice X.25 code, rather than with the network.
-
A series of library functions
These are not part of the NLI, but can be used along with it.
2.2 NLI Commands
Solstice X.25 NLI provides a series of NLI commands contained within C structures. These determine the format of the control parts of putmsg and getmsg. The NLI commands correspond to X.25 packet types, and are used to communicate with the network. For example, when an application passes down the NLI command N_CI to a stream using putmsg, this is translated into an X.25 Call Connect by the PLP module. When the PLP module receives a Connect Indication, it translates it into an N_CI command which is passed up to the application using a getmsg system call.
Table 2-1 summarizes the structures and their corresponding Packet Types and NLI Commands. Refer to the sections indicated for detailed information.
Table 2-1 NLI Commands and Structures|
NLI Command |
X.25 Packet |
NLI Structure |
See section |
|---|---|---|---|
|
N_DC | |||
|
xdiscf |
"6.4.7 N_DI--Clear Request/Indication ""6.4.13 N_RI--Reset Request/Indication" |
||
|
N_EAck | |||
The following commands and structures are also provided. They do not correspond to X.25 packet types:
Table 2-2 PVC and Listening Commands and Structures|
NLI Command |
NLI Structure |
Description |
See section |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Specify X.25 service to use with PVC | |||
|
Specify X.25 service to stop using with PVC | |||
|
xcanlisf |
Cancel listening | ||
|
Listen for incoming calls |
2.3 NLI ioctls
Solstice X.25 NLI provides a series of ioctls. These are used to communicate with the Solstice X.25 code itself, rather than with the network. For example, ioctls are used to gather statistics about a link, or to set the parameters to be used on a link. This distinguishes them from the NLI Commands given in Table 2-1. To use them together, you might use an ioctl to set the parameters to be used on a link and then use an NLI command to initiate a call over the link. The NLI ioctls can be used for the following purposes:
-
Operating on the Network User Identifiers mapping table
-
Reading and resetting statistics
-
Getting status information
-
Operating on the X.25 Routing Table
-
Overriding settings made using x25tool
2.4 Support Functions
Solstice X.25 also includes a library of Sun-specific support functions that you can use when writing applications. These are not part of the NLI, but can be used in NLI applications.
2.5 Support for OSI Connection-Mode Network Service (OSI CONS)
The Solstice X.25 NLI can support applications which use the OSI Connection-Mode Network Service, as defined in X.223 and ISO 8878. To be consistent with these documents, this service is referred to as OSI CONS in this guide. This service provides the mapping between the OSI CONS primitives and the elements of the X.25 Packet Layer Protocol.
2.6 Addressing
When making straightforward X.25 calls, you need to work with DTE and LSAP addresses. When making OSI CONS calls, you use NSAP and LSAP addresses. See "6.3.1 xaddrf--Define Addressing" for more information.
2.7 Facilities and QOS Parameters
The X.25 Recommendations allow service providers to offer a number of optional facilities, that affect the way that calls are made and handled.
-
Non-OSI extended addressing
-
X.25 fast select request/indication with no restriction on response
-
X.25 fast select request/indication with restriction on response
-
X.25 reverse charging
-
X.25 packet size negotiation
-
X.25 window size negotiation
-
X.25 network user identification
-
X.25 Recognized Private Operating Agency selection
-
X.25 Closed User Groups
-
X.25 programmable facilities
-
X.25 call deflection.
The following Quality of Service (QOS) parameters are available when writing OSI CONS applications:
-
Throughput Class
-
Minimum Throughput Class
-
Target Transit Delay
-
Maximum Acceptable Transit Delay
-
Use of Expedited Data
-
Protection
-
Priority
-
Receipt Acknowledgment
2.8 Operating System Support
Solstice X.25 9.2 will run on Solaris 7 or Solaris 8. It is not compatible with earlier versions of the Solaris operating system.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
