Hardware Components
You can provide the three required elements of mail configuration in the same system or have separate systems provide these elements.
When users are to communicate with networks outside your domain, you must also add a fourth element, a mail gateway. For more information, refer to Mail Gateway. The following sections describe each hardware component.
Mail Host
A mail host is the machine that you designate as the main mail machine on your network. A mail host is the machine to which other systems at the site forward mail that cannot be delivered. You designate a system as a mail host in the hosts database by adding the word mailhost to the right of the IP address in the local /etc/hosts file. Alternately, you can add the word mailhost similarly to the hosts file in the name service. For detailed task information, refer to How to Set Up a Mail Host in Chapter 13, Mail Services (Tasks).
A good candidate for a mail host is a system that is configured as a router from your network to the Internet global network. For more information, refer to Chapter 15, Solaris PPP 4.0 (Overview), Chapter 24, UUCP (Overview), and Configuring an IPv4 Router in System Administration Guide: IP Services. If no systems on your local network have a modem, designate a system as the mail host.
Some sites use standalone machines that are not networked in a time-sharing configuration. Specifically, the standalone machine serves terminals that are attached to its serial ports. You can set up electronic mail for this configuration by designating the standalone system as the mail host of a single-system network. Overview of the Hardware Components in Chapter 12, Mail Services (Overview) provides a figure that shows a typical email configuration.
Mail Server
A mailbox is a single file that contains email for a particular user. Mail is delivered to the system where the user's mailbox resides, which can be on a local machine or a remote server. A mail server is any system that maintains user mailboxes in its /var/mail directory. For task information, refer to How to Set Up a Mail Server in Chapter 13, Mail Services (Tasks).
The mail server routes all mail from a client. When a client sends mail, the mail server puts the mail in a queue for delivery. After the mail is in the queue, a user can reboot or turn off the client without losing those mail messages. When the recipient gets mail from a client, the path in the From line of the message contains the name of the mail server. If the recipient responds, the response goes to the user's mailbox. Good candidates for mail servers are systems that provide a home directory for users or systems that are backed up regularly.
If the mail server is not the user's local system, users in configurations that use NFS software can mount the /var/mail directory by using the /etc/vfstab file, if they have root access. Otherwise, users can use the automounter. If NFS support is not available, users can log in to the server to read their mail.
If users on your network send other types of mail, such as audio files or files from desktop publishing systems, you need to allocate more space on the mail server for mailboxes.
By establishing a mail server for all mailboxes, you can simplify your process of doing backups. Backups can be difficult to do when mail is spread over many systems. The disadvantage of storing many mailboxes on one server is that the server can be a single point of failure for many users. However, the advantages of providing good backups usually make the risk worthwhile.
Mail Client
A mail client is a user of mail services with a mailbox on a mail server. Additionally, the mail client has a mail alias in the /etc/mail/aliases file that points to the location of the mailbox. For task information, refer to How to Set Up a Mail Client in Chapter 13, Mail Services (Tasks).
Mail Gateway
The mail gateway is a machine that handles connections between networks that run different communications protocols or communications between different networks that use the same protocol. For example, a mail gateway might connect a TCP/IP network to a network that runs the Systems Network Architecture (SNA) protocol suite.
The simplest mail gateway to set up is the mail gateway that connects two networks that use the same protocol or mailer. This system handles mail with an address for which sendmail cannot find a recipient in your domain. If a mail gateway exists, sendmail uses the gateway to send and receive mail outside your domain.
You can set up a mail gateway between two networks that use unmatched mailers, as shown in the next figure. To support this configuration, you must customize the sendmail.cf file on the mail gateway system, which can be a difficult and time-consuming process.
Figure 14–1 Gateway Between Different Communications Protocols
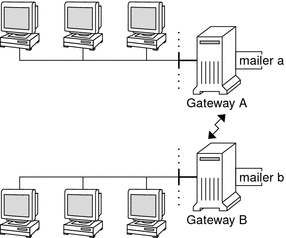
If you have a machine that provides connections to the Internet, you can configure that machine as the mail gateway. Carefully consider your site's security needs before you configure a mail gateway. You might need to create a firewall gateway between your corporate network and other networks, and set up that gateway as the mail gateway. For task information, refer to How to Set Up a Mail Gateway in Chapter 13, Mail Services (Tasks).
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
