Appendix B GSS-API Reference
This appendix includes the following sections:
-
GSS-API Functions provides a table of GSS-API functions.
-
GSS-API Status Codes discusses status codes returned by GSS-API functions, and provides a list of those status codes.
-
GSS-API Data Types and Values discusses the various data types used by GSS-API.
-
Implementation-Specific Features in GSS-API covers features that are unique to the Sun implementation of GSS-API.
-
Kerberos v5 Status Codes lists the status codes that can be returned by the Kerberos v5 mechanism.
Additional GSS-API definitions can be found in the file gssapi.h.
GSS-API Functions
The Oracle Solaris software implements the GSS-API functions. For more information on each function, see its man page. See also Functions From Previous Versions of GSS-API.
- gss_acquire_cred()
-
Assume a global identity by obtaining a GSS-API credential handle for preexisting credentials
- gss_add_cred()
- gss_inquire_cred()
- gss_inquire_cred_by_mech()
- gss_release_cred()
- gss_init_sec_context()
- gss_accept_sec_context()
- gss_delete_sec_context()
- gss_process_context_token()
-
Process a token on a security context from a peer application
- gss_context_time()
- gss_inquire_context()
- gss_wrap_size_limit()
- gss_export_sec_context()
- gss_import_sec_context()
- gss_get_mic()
-
Calculate a cryptographic message integrity code (MIC) for a message
- gss_verify_mic()
-
Check a MIC against a message to verify integrity of a received message
- gss_wrap()
-
Attach a MIC to a message, and optionally encrypt the message content
- gss_unwrap()
-
Verify a message with attached MIC. Decrypt message content if necessary
- gss_import_name()
- gss_display_name()
- gss_compare_name()
- gss_release_name()
- gss_inquire_names_for_mech()
- gss_inquire_mechs_for_name()
- gss_canonicalize_name()
- gss_export_name()
- gss_duplicate_name()
- gss_add_oid_set_member()
- gss_display_status()
- gss_indicate_mechs()
- gss_release_buffer()
- gss_release_oid_set()
- gss_create_empty_oid_set()
- gss_test_oid_set_member()
Functions From Previous Versions of GSS-API
This section explains functions that were included in previous versions of the GSS-API.
Functions for Manipulating OIDs
The Sun implementation of GSS-API provides the following functions for convenience and for backward compatibility. However, these functions might not be supported by other implementations of GSS-API.
Although a mechanism's name can be converted from a string to an OID, programmers should use the default GSS-API mechanism if at all possible.
Renamed Functions
The following functions have been supplanted by newer functions. In each case, the new function is the functional equivalent of the older function. Although the old functions are supported, developers should replace these functions with the newer functions whenever possible.
GSS-API Status Codes
Major status codes are encoded in the OM_uint32 as shown in the following figure.
Figure B–1 Major-Status Encoding
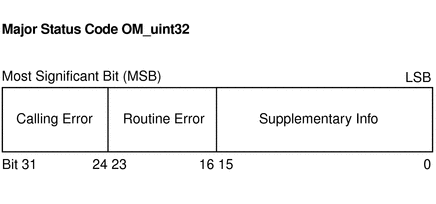
If a GSS-API routine returns a GSS status code whose upper 16 bits contain a nonzero value, the call has failed. If the calling error field is nonzero, the application's call of the routine was erroneous. The calling errors are listed in Table B–1. If the routine error field is nonzero, the routine failed because of a routine-specific error, as listed in Table B–2. The bits in the supplementary information field of the status code can be set whether the upper 16 bits indicate a failure or a success. The meaning of individual bits is listed in Table B–3.
GSS-API Major Status Code Values
The following tables list the calling errors that are returned by GSS-API. These errors are specific to a particular language-binding, which is C in this case.
Table B–1 GSS-API Calling Errors|
Error |
Value in Field |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_CALL_INACCESSIBLE_READ |
1 |
An input parameter that is required could not be read |
|
GSS_S_CALL_INACCESSIBLE_WRITE |
2 |
A required output parameter could not be written |
|
GSS_S_CALL_BAD_STRUCTURE |
3 |
A parameter was malformed |
The following table lists the GSS-API routine errors, generic errors that are returned by GSS-API functions.
Table B–2 GSS-API Routine Errors|
Error |
Value in Field |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_BAD_MECH |
1 |
An unsupported mechanism was requested. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_NAME |
2 |
An invalid name was supplied. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_NAMETYPE |
3 |
A supplied name was of an unsupported type. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_BINDINGS |
4 |
Incorrect channel bindings were supplied. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_STATUS |
5 |
An invalid status code was supplied. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_MIC, GSS_S_BAD_SIG |
6 |
A token had an invalid MIC. |
|
GSS_S_NO_CRED |
7 |
The credentials were unavailable, inaccessible, or not supplied. |
|
GSS_S_NO_CONTEXT |
8 |
No context has been established. |
|
GSS_S_DEFECTIVE_TOKEN |
9 |
A token was invalid. |
|
GSS_S_DEFECTIVE_CREDENTIAL |
10 |
A credential was invalid. |
|
GSS_S_CREDENTIALS_EXPIRED |
11 |
The referenced credentials have expired. |
|
GSS_S_CONTEXT_EXPIRED |
12 |
The context has expired. |
|
GSS_S_FAILURE |
13 |
Miscellaneous failure. The underlying mechanism detected an error for which no specific GSS–API status code is defined. The mechanism-specific status code, that is, the minor-status code, provides more details about the error. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_QOP |
14 |
The quality-of-protection that was requested could not be provided. |
|
GSS_S_UNAUTHORIZED |
15 |
The operation is forbidden by local security policy. |
|
GSS_S_UNAVAILABLE |
16 |
The operation or option is unavailable. |
|
GSS_S_DUPLICATE_ELEMENT |
17 |
The requested credential element already exists. |
|
GSS_S_NAME_NOT_MN |
18 |
The provided name was not a mechanism name (MN). |
The name GSS_S_COMPLETE, which is a zero value, indicates an absence of any API errors or supplementary information bits.
The following table lists the supplementary information values returned by GSS-API functions.
Table B–3 GSS-API Supplementary Information Codes|
Code |
Bit Number |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_CONTINUE_NEEDED |
0 (LSB) |
Returned only by gss_init_sec_context() or gss_accept_sec_context(). The routine must be called again to complete its function. |
|
GSS_S_DUPLICATE_TOKEN |
1 |
The token was a duplicate of an earlier token. |
|
GSS_S_OLD_TOKEN |
2 |
The token's validity period has expired. |
|
GSS_S_UNSEQ_TOKEN |
3 |
A later token has already been processed. |
|
GSS_S_GAP_TOKEN |
4 |
An expected per-message token was not received. |
For more on status codes, see GSS-API Status Codes.
Displaying Status Codes
The function gss_display_status() translates GSS-API status codes into text format. This format allows the codes to be displayed to a user or put in a text log. gss_display_status() only displays one status code at a time, and some functions can return multiple status conditions. Accordingly, gss_display_status() should be called as part of a loop. When gss_display_status() indicates a non-zero status code, another status code is available for the function to fetch.
Example B–1 Displaying Status Codes with gss_display_status()
OM_uint32 message_context;
OM_uint32 status_code;
OM_uint32 maj_status;
OM_uint32 min_status;
gss_buffer_desc status_string;
...
message_context = 0;
do {
maj_status = gss_display_status(
&min_status,
status_code,
GSS_C_GSS_CODE,
GSS_C_NO_OID,
&message_context,
&status_string);
fprintf(stderr, "%.*s\n", \
(int)status_string.length, \
(char *)status_string.value);
gss_release_buffer(&min_status, &status_string,);
} while (message_context != 0);
Status Code Macros
The macros, GSS_CALLING_ERROR(), GSS_ROUTINE_ERROR() and GSS_SUPPLEMENTARY_INFO(), take a GSS status code. These macros remove all information except for the relevant field. For example, the GSS_ROUTINE_ERROR() can be applied to a status code to remove the calling errors and supplementary information fields. This operation leaves the routine errors field only. The values delivered by these macros can be directly compared with a GSS_S_xxx symbol of the appropriate type. The macro GSS_ERROR() returns a non-zero value if a status code indicates a calling or routine error, and a zero value otherwise. All macros that are defined by GSS-API evaluate the arguments exactly once.
GSS-API Data Types and Values
This section describes various types of GSS-API data types and values. Some data types, such as gss_cred_id_t or gss_name_t, are opaque to the user. These data types do not need to be discussed. This section explains the following topics:
-
Basic GSS-API Data Types – Shows the definitions of the
OM_uint32, gss_buffer_desc, gss_OID_desc, gss_OID_set_desc_struct, and gss_channel_bindings_struct data types. -
Name Types – Shows the various name formats recognized by the GSS-API for specifying names.
-
Address Types for Channel Bindings – Shows the various values that can be used as the initiator_addrtype and acceptor_addrtype fields of the gss_channel_bindings_t structure.
Basic GSS-API Data Types
This section describes data types that are used by GSS-API.
OM_uint32
The OM_uint32 is a platform-independent 32–bit unsigned
integer.
gss_buffer_desc
The definition of the gss_buffer_desc with
the gss_buffer_t pointer takes the following form:
typedef struct gss_buffer_desc_struct {
size_t length;
void *value;
} gss_buffer_desc, *gss_buffer_t;
gss_OID_desc
The definition of the gss_OID_desc with the gss_OID pointer takes the following form:
typedef struct gss_OID_desc_struct {
OM_uint32 length;
void*elements;
} gss_OID_desc, *gss_OID;
gss_OID_set_desc
The definition of the gss_OID_set_desc with
the gss_OID_set pointer takes the following form:
typedef struct gss_OID_set_desc_struct {
size_t count;
gss_OID elements;
} gss_OID_set_desc, *gss_OID_set;
gss_channel_bindings_struct
The definition of the gss_channel_bindings_struct structure and the gss_channel_bindings_t pointer has the following form:
typedef struct gss_channel_bindings_struct {
OM_uint32 initiator_addrtype;
gss_buffer_desc initiator_address;
OM_uint32 acceptor_addrtype;
gss_buffer_desc acceptor_address;
gss_buffer_desc application_data;
} *gss_channel_bindings_t;
Name Types
A name type indicates the format of the associated name. See Names in GSS-API and GSS-API OIDs for more on names and name types. The GSS-API supports the gss_OID name types in the following table.
- GSS_C_NO_NAME
-
The symbolic name GSS_C_NO_NAME is recommended as a parameter value to indicate that no value is supplied in the transfer of names.
- GSS_C_NO_OID
-
This value corresponds to a null input value instead of an actual object identifier. Where specified, the value indicates interpretation of an associated name that is based on a mechanism-specific default printable syntax.
- GSS_C_NT_ANONYMOUS
-
A means to identify anonymous names. This value can be compared with to determine in a mechanism-independent fashion whether a name refers to an anonymous principal.
- GSS_C_NT_EXPORT_NAME
-
A name that has been exported with the gss_export_name() function.
- GSS_C_NT_HOSTBASED_SERVICE
-
Used to represent services that are associated with host computers. This name form is constructed using two elements, service and hostname, as follows: service@hostname.
- GSS_C_NT_MACHINE_UID_NAME
-
Used to indicate a numeric user identifier corresponding to a user on a local system. The interpretation of this value is OS-specific. The gss_import_name() function resolves this UID into a user name, which is then treated as the User Name Form.
- GSS_C_NT_STRING_STRING_UID_NAME
-
Used to indicate a string of digits that represents the numeric user identifier of a user on a local system. The interpretation of this value is OS-specific. This name type is similar to the Machine UID Form, except that the buffer contains a string that represents the user ID.
- GSS_C_NT_USER_NAME
-
A named user on a local system. The interpretation of this value is OS-specific. The value takes the form: username.
Address Types for Channel Bindings
The following table shows the possible values for the initiator_addrtype and acceptor_addrtype fields of the gss_channel_bindings_struct structure. These fields indicate the format that a name can take, for example, ARPAnet IMP address or AppleTalk address. Channel bindings are discussed in Using Channel Bindings in GSS-API.
Table B–4 Channel Binding Address Types|
Field |
Value (Decimal) |
Address Type |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_C_AF_UNSPEC |
0 |
Unspecified address type |
|
GSS_C_AF_LOCAL |
1 |
Host-local |
|
GSS_C_AF_INET |
2 |
Internet address type, for example, IP |
|
GSS_C_AF_IMPLINK |
3 |
ARPAnet IMP |
|
GSS_C_AF_PUP |
4 |
pup protocols, for example, BSP |
|
GSS_C_AF_CHAOS |
5 |
MIT CHAOS protocol |
|
GSS_C_AF_NS |
6 |
XEROX NS |
|
GSS_C_AF_NBS |
7 |
nbs |
|
GSS_C_AF_ECMA |
8 |
ECMA |
|
GSS_C_AF_DATAKIT |
9 |
Datakit protocols |
|
GSS_C_AF_CCITT |
10 |
CCITT |
|
GSS_C_AF_SNA |
11 |
IBM SNA |
|
GSS_C_AF_DECnet |
12 |
DECnet |
|
GSS_C_AF_DLI |
13 |
Direct data link interface |
|
GSS_C_AF_LAT |
14 |
LAT |
|
GSS_C_AF_HYLINK |
15 |
NSC Hyperchannel |
|
GSS_C_AF_APPLETALK |
16 |
AppleTalk |
|
GSS_C_AF_BSC |
17 |
BISYNC |
|
GSS_C_AF_DSS |
18 |
Distributed system services |
|
GSS_C_AF_OSI |
19 |
OSI TP4 |
|
GSS_C_AF_X25 |
21 |
X.25 |
|
GSS_C_AF_NULLADDR |
255 |
No address specified |
Implementation-Specific Features in GSS-API
Some aspects of the GSS-API can differ between implementations of the API. In most cases, differences in implementations have only minimal effect on programs. In all cases, developers can maximize portability by not relying on any behavior that is specific to a given implementation, including the Sun implementation.
Sun-Specific Functions
The Sun implementation does not have customized GSS-API functions.
Human-Readable Name Syntax
Implementations of GSS-API can differ in the printable syntax that corresponds to names. For portability, applications should not compare names that use human-readable, that is, printable, forms. Instead, such applications should use gss_compare_name() to determine whether an internal-format name matches any other name.
The Sun implementation of gss_display_name() displays names as follows. If the input_nameargument denotes a user principal, the gss_display_name() returns user_principal@realm as the output_name_buffer and the gss_OID value as the output_name_type. If Kerberos v5 is the underlying mechanism, gss_OID is 1.2.840.11354.1.2.2.
If gss_display_name() receives a name that was created by gss_import_name() with the GSS_C_NO_OID name type, gss_display_name() returns GSS_C_NO_OID in the output_name_type parameter.
Format of Anonymous Names
The gss_display_name() function outputs the string
'<anonymous>' to indicate an anonymous GSS-API principal.
The name type OID associated with this name is GSS_C_NT_ANONYMOUS.
No other valid printable names supported by the Sun implementation should
be surrounded by angle brackets (<>).
Implementations of Selected Data Types
The following data types have been implemented as pointers, although
some implementations might specify these types as arithmetic types: gss_cred_t, gss_ctx_id_t, and gss_name_t.
Deletion of Contexts and Stored Data
When context establishment fails, the Sun implementation does not automatically delete partially built contexts. Applications should therefore handle this event by deleting the contexts with gss_delete_sec_context().
The Sun implementation automatically releases stored data, such as internal names, through memory management. However, applications should still call appropriate functions, such as gss_release_name(), when data elements are no longer needed.
Protection of Channel-Binding Information
Support for channel bindings varies by mechanism. Both the Diffie-Hellman mechanism and the Kerberos v5 mechanism support channel bindings.
Developers should assume that channel bindings data do not have confidentiality protection. Although the Kerberos v5 mechanism provides this protection, confidentiality for channel-bindings data is not available with the Diffie-Hellman mechanism.
Context Exportation and Interprocess Tokens
The Sun implementation detects and rejects attempted multiple imports of the same context.
Types of Credentials Supported
The Sun implementation of the GSS-API supports the acquisition of GSS_C_INITIATE, GSS_C_ACCEPT, and GSS_C_BOTH credentials through gss_acquire_cred().
Credential Expiration
The Sun implementation of the GSS-API supports credential expiration. Therefore, programmers can use parameters that relate to credential lifetime in functions such as gss_acquire_cred() and gss_add_cred().
Context Expiration
The Sun implementation of the GSS-API supports context expiration. Therefore, programmers can use parameters that relate to context lifetime in functions such as gss_init_sec_context() and gss_inquire_context().
Wrap Size Limits and QOP Values
The Sun implementation of the GSS-API, as opposed to any underlying mechanism, does not impose a maximum size for messages to be processed by gss_wrap(). Applications can determine the maximum message size with gss_wrap_size_limit().
The Sun implementation of the GSS-API detects invalid QOP values when gss_wrap_size_limit() is called.
Use of minor_status Parameter
In the Sun implementation of the GSS-API, functions return only mechanism-specific information in the minor_status parameter. Other implementations might include implementation-specific return values as part of the returned minor-status code.
Kerberos v5 Status Codes
Each GSS-API function returns two status codes: a major status code and a minor status code. Major status codes relate to the behavior of GSS-API. For example, if an application attempts to transmit a message after a security context has expired, GSS-API returns a major status code of GSS_S_CONTEXT_EXPIRED. Major status codes are listed in GSS-API Status Codes.
Minor status codes are returned by the underlying security mechanisms supported by a given implementation of GSS-API. Every GSS-API function takes as the first argument a minor_status or minor_stat parameter. An application can examine this parameter when the function returns, successfully or not, to see the status that is returned by the underlying mechanism.
The following tables list the status messages that can be returned by Kerberos v5 in the minor_status argument. For more on GSS-API status codes, see GSS-API Status Codes.
Messages Returned in Kerberos v5 for Status Code 1
The following table lists the minor status messages that are returned in Kerberos v5 for status code 1.
Table B–5 Kerberos v5 Status Codes 1|
Minor Status |
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_NONE |
-1765328384L |
No error |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_NAME_EXP |
-1765328383L |
Client's entry in database has expired |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_SERVICE_EXP |
-1765328382L |
Server's entry in database has expired |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_BAD_PVNO |
-1765328381L |
Requested protocol version not supported |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_C_OLD_MAST_KVNO |
-1765328380L |
Client's key is encrypted in an old master key |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_S_OLD_MAST_KVNO |
-1765328379L |
Server's key is encrypted in an old master key |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_C_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN |
-1765328378L |
Client not found in Kerberos database |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_S_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN |
-1765328377L |
Server not found in Kerberos database |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_PRINCIPAL_NOT_UNIQUE |
-1765328376L |
Principal has multiple entries in Kerberos database |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_NULL_KEY |
-1765328375L |
Client or server has a null key |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_CANNOT_POSTDATE |
-1765328374L |
Ticket is ineligible for postdating |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_NEVER_VALID |
-1765328373L |
Requested effective lifetime is negative or too short |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_POLICY |
-1765328372L |
KDC policy rejects request |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_BADOPTION |
-1765328371L |
KDC can't fulfill requested option |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_ETYPE_NOSUPP |
-1765328370L |
KDC has no support for encryption type |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_SUMTYPE_NOSUPP |
-1765328369L |
KDC has no support for checksum type |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_PADATA_TYPE_NOSUPP |
-1765328368L |
KDC has no support for padata type |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_TRTYPE_NOSUPP |
-1765328367L |
KDC has no support for transited type |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_CLIENT_REVOKED |
-1765328366L |
Client's credentials have been revoked |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_SERVICE_REVOKED |
-1765328365L |
Credentials for server have been revoked |
Messages Returned in Kerberos v5 for Status Code 2
The following table lists the minor status messages that are returned in Kerberos v5 for status code 2.
Table B–6 Kerberos v5 Status Codes 2|
Minor Status |
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_TGT_REVOKED |
-1765328364L |
TGT has been revoked |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_CLIENT_NOTYET |
-1765328363L |
Client not yet valid, try again later |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_SERVICE_NOTYET |
-1765328362L |
Server not yet valid, try again later |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_KEY_EXP |
-1765328361L |
Password has expired |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_PREAUTH_FAILED |
-1765328360L |
Preauthentication failed |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_PREAUTH_REQUIRED |
-1765328359L |
Additional preauthentication required |
|
KRB5KDC_ERR_SERVER_NOMATCH |
-1765328358L |
Requested server and ticket don't match |
|
KRB5PLACEHOLD_27 through KRB5PLACEHOLD_30 |
-1765328357L through -1765328354L |
KRB5 error codes 27 through 30 (reserved) |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_BAD_INTEGRITY |
-1765328353L |
Decrypt integrity check failed |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_TKT_EXPIRED |
-1765328352L |
Ticket expired |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_TKT_NYV |
-1765328351L |
Ticket not yet valid |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_REPEAT |
-1765328350L |
Request is a replay |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_NOT_US |
-1765328349L |
The ticket isn't for us |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_BADMATCH |
-1765328348L |
Ticket/authenticator do not match |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW |
-1765328347L |
Clock skew too great |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_BADADDR |
-1765328346L |
Incorrect net address |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_BADVERSION |
-1765328345L |
Protocol version mismatch |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_MSG_TYPE |
-1765328344L |
Invalid message type |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED |
-1765328343L |
Message stream modified |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_BADORDER |
-1765328342L |
Message out of order |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_ILL_CR_TKT |
-1765328341L |
Illegal cross-realm ticket |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_BADKEYVER |
-1765328340L |
Key version is not available |
Messages Returned in Kerberos v5 for Status Code 3
The following table lists the minor status messages that are returned in Kerberos v5 for status code 3.
Table B–7 Kerberos v5 Status Codes 3|
Minor Status |
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_NOKEY |
-1765328339L |
Service key not available |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_MUT_FAIL |
-1765328338L |
Mutual authentication failed |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_BADDIRECTION |
-1765328337L |
Incorrect message direction |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_METHOD |
-1765328336L |
Alternative authentication method required |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_BADSEQ |
-1765328335L |
Incorrect sequence number in message |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_INAPP_CKSUM |
-1765328334L |
Inappropriate type of checksum in message |
|
KRB5PLACEHOLD_51 throughKRB5PLACEHOLD_59 |
-1765328333L through -1765328325L |
KRB5 error codes 51 through 59 (reserved) |
|
KRB5KRB_ERR_GENERIC |
-1765328324L |
Generic error |
|
KRB5KRB_ERR_FIELD_TOOLONG |
-1765328323L |
Field is too long for this implementation |
|
KRB5PLACEHOLD_62 through KRB5PLACEHOLD_127 |
-1765328322L through -1765328257L |
KRB5 error codes 62 through 127 (reserved) |
|
value not returned |
-1765328256L |
For internal use only |
|
KRB5_LIBOS_BADLOCKFLAG |
-1765328255L |
Invalid flag for file lock mode |
|
KRB5_LIBOS_CANTREADPWD |
-1765328254L |
Cannot read password |
|
KRB5_LIBOS_BADPWDMATCH |
-1765328253L |
Password mismatch |
|
KRB5_LIBOS_PWDINTR |
-1765328252L |
Password read interrupted |
|
KRB5_PARSE_ILLCHAR |
-1765328251L |
Illegal character in component name |
|
KRB5_PARSE_MALFORMED |
-1765328250L |
Malformed representation of principal |
|
KRB5_CONFIG_CANTOPEN |
-1765328249L |
Can't open/find Kerberos /etc/krb5/krb5 configuration file |
|
KRB5_CONFIG_BADFORMAT |
-1765328248L |
Improper format of Kerberos /etc/krb5/krb5 configuration file |
|
KRB5_CONFIG_NOTENUFSPACE |
-1765328247L |
Insufficient space to return complete information |
|
KRB5_BADMSGTYPE |
-1765328246L |
Invalid message type has been specified for encoding |
|
KRB5_CC_BADNAME |
-1765328245L |
Credential cache name malformed |
Messages Returned in Kerberos v5 for Status Code 4
The following table lists the minor status messages that are returned in Kerberos v5 for status code 4.
Table B–8 Kerberos v5 Status Codes 4|
Minor Status |
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
KRB5_CC_UNKNOWN_TYPE |
-1765328244L |
Unknown credential cache type |
|
KRB5_CC_NOTFOUND |
-1765328243L |
No matching credential has been found |
|
KRB5_CC_END |
-1765328242L |
End of credential cache reached |
|
KRB5_NO_TKT_SUPPLIED |
-1765328241L |
Request did not supply a ticket |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_WRONG_PRINC |
-1765328240L |
Wrong principal in request |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_TKT_INVALID |
-1765328239L |
Ticket has invalid flag set |
|
KRB5_PRINC_NOMATCH |
-1765328238L |
Requested principal and ticket don't match |
|
KRB5_KDCREP_MODIFIED |
-1765328237L |
KDC reply did not match expectations |
|
KRB5_KDCREP_SKEW |
-1765328236L |
Clock skew too great in KDC reply |
|
KRB5_IN_TKT_REALM_MISMATCH |
-1765328235L |
Client/server realm mismatch in initial ticket request |
|
KRB5_PROG_ETYPE_NOSUPP |
-1765328234L |
Program lacks support for encryption type |
|
KRB5_PROG_KEYTYPE_NOSUPP |
-1765328233L |
Program lacks support for key type |
|
KRB5_WRONG_ETYPE |
-1765328232L |
Requested encryption type not used in message |
|
KRB5_PROG_SUMTYPE_NOSUPP |
-1765328231L |
Program lacks support for checksum type |
|
KRB5_REALM_UNKNOWN |
-1765328230L |
Cannot find KDC for requested realm |
|
KRB5_SERVICE_UNKNOWN |
-1765328229L |
Kerberos service unknown |
|
KRB5_KDC_UNREACH |
-1765328228L |
Cannot contact any KDC for requested realm |
|
KRB5_NO_LOCALNAME |
-1765328227L |
No local name found for principal name |
|
KRB5_MUTUAL_FAILED |
-1765328226L |
Mutual authentication failed |
|
KRB5_RC_TYPE_EXISTS |
-1765328225L |
Replay cache type is already registered |
|
KRB5_RC_MALLOC |
-1765328224L |
No more memory to allocate in replay cache code |
|
KRB5_RC_TYPE_NOTFOUND |
-1765328223L |
Replay cache type is unknown |
Messages Returned in Kerberos v5 for Status Code 5
The following table lists the minor status messages that are returned in Kerberos v5 for status code 5
Table B–9 Kerberos v5 Status Codes 5|
Minor Status |
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
KRB5_RC_UNKNOWN |
-1765328222L |
Generic unknown RC error |
|
KRB5_RC_REPLAY |
-1765328221L |
Message is a replay |
|
KRB5_RC_IO |
-1765328220L |
Replay I/O operation failed |
|
KRB5_RC_NOIO |
-1765328219L |
Replay cache type does not support non-volatile storage |
|
KRB5_RC_PARSE |
-1765328218L |
Replay cache name parse and format error |
|
KRB5_RC_IO_EOF |
-1765328217L |
End-of-file on replay cache I/O |
|
KRB5_RC_IO_MALLOC |
-1765328216L |
No more memory to allocate in replay cache I/O code |
|
KRB5_RC_IO_PERM |
-1765328215L |
Permission denied in replay cache code |
|
KRB5_RC_IO_IO |
-1765328214L |
I/O error in replay cache i/o code |
|
KRB5_RC_IO_UNKNOWN |
-1765328213L |
Generic unknown RC/IO error |
|
KRB5_RC_IO_SPACE |
-1765328212L |
Insufficient system space to store replay information |
|
KRB5_TRANS_CANTOPEN |
-1765328211L |
Can't open/find realm translation file |
|
KRB5_TRANS_BADFORMAT |
-1765328210L |
Improper format of realm translation file |
|
KRB5_LNAME_CANTOPEN |
-1765328209L |
Can't open or find lname translation database |
|
KRB5_LNAME_NOTRANS |
-1765328208L |
No translation is available for requested principal |
|
KRB5_LNAME_BADFORMAT |
-1765328207L |
Improper format of translation database entry |
|
KRB5_CRYPTO_INTERNAL |
-1765328206L |
Cryptosystem internal error |
|
KRB5_KT_BADNAME |
-1765328205L |
Key table name malformed |
|
KRB5_KT_UNKNOWN_TYPE |
-1765328204L |
Unknown Key table type |
|
KRB5_KT_NOTFOUND |
-1765328203L |
Key table entry not found |
|
KRB5_KT_END |
-1765328202L |
End of key table reached |
|
KRB5_KT_NOWRITE |
-1765328201L |
Cannot write to specified key table |
Messages Returned in Kerberos v5 for Status Code 6
The following table lists the minor status messages that are returned in Kerberos v5 for status code 6.
Table B–10 Kerberos v5 Status Codes 6|
Minor Status |
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
KRB5_KT_IOERR |
-1765328200L |
Error writing to key table |
|
KRB5_NO_TKT_IN_RLM |
-1765328199L |
Cannot find ticket for requested realm |
|
KRB5DES_BAD_KEYPAR |
-1765328198L |
DES key has bad parity |
|
KRB5DES_WEAK_KEY |
-1765328197L |
DES key is a weak key |
|
KRB5_BAD_ENCTYPE |
-1765328196L |
Bad encryption type |
|
KRB5_BAD_KEYSIZE |
-1765328195L |
Key size is incompatible with encryption type |
|
KRB5_BAD_MSIZE |
-1765328194L |
Message size is incompatible with encryption type |
|
KRB5_CC_TYPE_EXISTS |
-1765328193L |
Credentials cache type is already registered |
|
KRB5_KT_TYPE_EXISTS |
-1765328192L |
Key table type is already registered |
|
KRB5_CC_IO |
-1765328191L |
Credentials cache I/O operation failed |
|
KRB5_FCC_PERM |
-1765328190L |
Credentials cache file permissions incorrect |
|
KRB5_FCC_NOFILE |
-1765328189L |
No credentials cache file found |
|
KRB5_FCC_INTERNAL |
-1765328188L |
Internal file credentials cache error |
|
KRB5_CC_WRITE |
-1765328187L |
Error writing to credentials cache file |
|
KRB5_CC_NOMEM |
-1765328186L |
No more memory to allocate in credentials cache code |
|
KRB5_CC_FORMAT |
-1765328185L |
Bad format in credentials cache |
|
KRB5_INVALID_FLAGS |
-1765328184L |
Invalid KDC option combination, which is an internal library error |
|
KRB5_NO_2ND_TKT |
-1765328183L |
Request missing second ticket |
|
KRB5_NOCREDS_SUPPLIED |
-1765328182L |
No credentials supplied to library routine |
|
KRB5_SENDAUTH_BADAUTHVERS |
-1765328181L |
Bad sendauth version was sent |
|
KRB5_SENDAUTH_BADAPPLVERS |
-1765328180L |
Bad application version was sent by sendauth |
|
KRB5_SENDAUTH_BADRESPONSE |
-1765328179L |
Bad response during sendauth exchange |
|
KRB5_SENDAUTH_REJECTED |
-1765328178L |
Server rejected authentication during sendauth exchange |
Messages Returned in Kerberos v5 for Status Code 7
The following table lists the minor status messages that are returned in Kerberos v5 for status code 7.
Table B–11 Kerberos v5 Status Codes 7|
Minor Status |
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
KRB5_PREAUTH_BAD_TYPE |
-1765328177L |
Unsupported preauthentication type |
|
KRB5_PREAUTH_NO_KEY |
-1765328176L |
Required preauthentication key not supplied |
|
KRB5_PREAUTH_FAILED |
-1765328175L |
Generic preauthentication failure |
|
KRB5_RCACHE_BADVNO |
-1765328174L |
Unsupported format version number for replay cache |
|
KRB5_CCACHE_BADVNO |
-1765328173L |
Unsupported credentials cache format version number |
|
KRB5_KEYTAB_BADVNO |
-1765328172L |
Unsupported version number for key table format |
|
KRB5_PROG_ATYPE_NOSUPP |
-1765328171L |
Program lacks support for address type |
|
KRB5_RC_REQUIRED |
-1765328170L |
Message replay detection requires rcache parameter |
|
KRB5_ERR_BAD_HOSTNAME |
-1765328169L |
Host name cannot be canonicalized |
|
KRB5_ERR_HOST_REALM_UNKNOWN |
-1765328168L |
Cannot determine realm for host |
|
KRB5_SNAME_UNSUPP_NAMETYPE |
-1765328167L |
Conversion to service principal is undefined for name type |
|
KRB5KRB_AP_ERR_V4_REPLY |
-1765328166L |
Initial Ticket response appears to be Version 4 error |
|
KRB5_REALM_CANT_RESOLVE |
-1765328165L |
Cannot resolve KDC for requested realm |
|
KRB5_TKT_NOT_FORWARDABLE |
-1765328164L |
The requesting ticket cannot get forwardable tickets |
|
KRB5_FWD_BAD_PRINCIPAL |
-1765328163L |
Bad principal name while trying to forward credentials |
|
KRB5_GET_IN_TKT_LOOP |
-1765328162L |
Looping detected inside krb5_get_in_tkt |
|
KRB5_CONFIG_NODEFREALM |
-1765328161L |
Configuration file /etc/krb5/krb5.conf does not specify default realm |
|
KRB5_SAM_UNSUPPORTED |
-1765328160L |
Bad SAM flags in obtain_sam_padata |
|
KRB5_KT_NAME_TOOLONG |
-1765328159L |
Keytab name too long |
|
KRB5_KT_KVNONOTFOUND |
-1765328158L |
Key version number for principal in key table is incorrect |
|
KRB5_CONF_NOT_CONFIGURED |
-1765328157L |
Kerberos /etc/krb5/krb5.conf configuration file not configured |
|
ERROR_TABLE_BASE_krb5 |
-1765328384L |
default |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
