Parts of the IPv6 Address
An IPv6 address is 128 bits in length and consists of eight, 16-bit fields, with each field bounded by a colon. Each field must contain a hexadecimal number, in contrast to the dotted-decimal notation of IPv4 addresses. In the next figure, the x's represent hexadecimal numbers.
Figure 3–2 Basic IPv6 Address Format
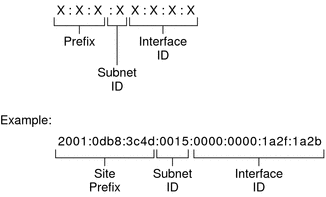
The leftmost three fields (48 bits) contain the site prefix. The prefix describes the public topology that is usually allocated to your site by an ISP or Regional Internet Registry (RIR).
The next field is the 16-bit subnet ID, which you (or another administrator) allocate for your site. The subnet ID describes the private topology, also known as the site topology, because it is internal to your site.
The rightmost four fields (64 bits) contain the interface ID, also referred to as a token. The interface ID is either automatically configured from the interface's MAC address or manually configured in EUI-64 format.
Consider again the address in Figure 3–2:
2001:0db8:3c4d:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:1a2b
This example shows all 128 bits of an IPv6 address. The first 48 bits, 2001:0db8:3c4d, contain the site prefix, representing the public topology. The next 16 bits, 0015, contain the subnet ID, representing the private topology for the site. The lower order, rightmost 64 bits, 0000:0000:1a2f:1a2b, contain the interface ID.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
