Enabling and Disabling Monitoring
Monitored file system and OS health data for a provisionable server is not available unless an operating system is deployed on the provisionable server, and the OS monitoring feature has been installed.
Once the OS monitoring feature is installed on a server, monitoring is enabled by default. For information on installing the OS monitoring feature on a server, see Supporting Monitoring.
Use the set server monitored command to enable or disable monitoring. See Enabling and Disabling Monitoring. If the OS monitoring feature is not installed on a server or on every server in a group, using the set server monitored command enables only hardware monitoring for the server or group of servers.
The following graphic shows a section of the Server Details page. The server is powered on, an OS has been installed and the base management and OS monitoring features are supported. Monitoring is enabled for the server.
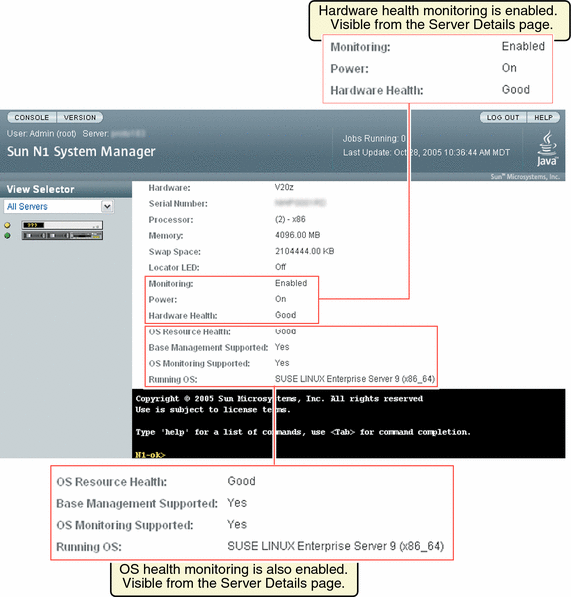
Disabling monitoring by use of the set server monitored command does not remove the monitoring support provided by the OS monitoring feature, which remains installed on the server. However, disabling monitoring by the set server monitored command disables both hardware health and OS health monitoring.
 To Monitor a Server or a Server Group
To Monitor a Server or a Server Group
The following procedure describes how to use the command line to enable the monitoring of hardware health and operating system health of a server or a server group. Hardware health and OS health monitoring are both enabled with this command, provided that the OS monitoring feature has been installed on the server or the server group. If the OS monitoring feature has not been installed on the server or server group, then only hardware health monitoring is enabled.
Before You Begin
To enable the management agent IP and security credentials on a server named server, add the management features on the server as explained in Supporting Monitoring.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Set the monitored attribute to true by using the set server command.
N1-ok> set server server monitored true
In this procedure, server is the name of the provisionable server that you want to monitor.
-
For a server group, set the monitored attribute to true by using the set group command.
N1-ok> set group group monitored true
This command is executed for the group of servers that you have already named. See set group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details. In this procedure, group is the name of the group of provisionable servers that you want to monitor.
-
-
View the server details.
N1-ok> show server server
-
For a server group, view the server group details to determine if monitoring is enabled for each server in the group.
N1-ok> show group group
Detailed monitoring information appears in the output. Information is displayed about hardware health, OS health and network reachability. OS health monitoring threshold values are also displayed.Monitoring threshold values are explained in Monitoring Threshold Values.
-
 To Disable Monitoring for a Server or a Server Group
To Disable Monitoring for a Server or a Server Group
The following procedure describes how to use the command line to disable the monitoring of hardware health and operating system health of a server or a server group. Hardware health and OS health monitoring are both disabled with this command, provided that the OS monitoring feature has been added.
You might want to disable monitoring of a hardware component to perform maintenance tasks without generating events.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Set the monitored attribute to false by using the set server command.
N1-ok> set server server monitored false
In this example, server is the name of the provisionable server that you want to stop monitoring. Executing this command disables monitoring of the server. With monitoring of a server disabled, the violation of threshold values by attributes related to that server does not generate events.
-
For a server group, set the monitored attribute to false by using the set group command.
N1-ok> set group group monitored false
This command is executed for the group of servers that you have already named. See set group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details. In this procedure, group is the name of the group of provisionable servers for which you want to disable monitoring.
-
-
View the server details.
N1-ok> show server server
The output shows that monitoring is disabled.
If you are not interested in the values of some OS health attributes, you can disable the threshold severity for the monitoring of those attributes, while continuing to monitor other OS health attributes. This action prevents annoyance alarms. Example 5–6 shows how to accomplish this task. For general information about threshold values, see Monitoring Threshold Values. You can also remove the OS health monitoring feature. See To Remove the OS Monitoring Feature.
Default States of Monitoring
The default status of monitoring in the Sun N1 System Manager for discovered servers and initialized operating systems is as follows:
- Default status of hardware monitoring
-
When a server or other hardware is discovered, monitoring of the server or other hardware is enabled by default. Before a server can be monitored, however, it must be discovered and correctly registered with the N1 System Manager. This process is described in Discovering Servers. The monitoring of hardware sensors is enabled by default for all managed servers. If a server is deleted and then rediscovered, all states related to that server for the purposes of monitoring are lost, regardless of whether monitoring was enabled or disabled for that server when the server was deleted. When the server is rediscovered, monitoring is set to true by default. For more information about discovering servers, see To Discover New Servers.
- Default status of OS health monitoring
-
Disabled by default. When an OS has been successfully provisioned on a provisionable server and the N1 System Manager management features are supported by using the add server feature command with the agentip specified, OS health monitoring is enabled. The OS provisioning can be performed either through the N1 System Manager or by an external OS installation.
If you are not interested in the values of some OS health attributes, you can disable the threshold severity for the monitoring of those attributes, while continuing to monitor other OS health attributes. This action prevents annoyance alarms. Example 5–6 shows how to accomplish this task. For general information about threshold values, see Monitoring Threshold Values.
- Default status of network reachability monitoring
-
When the management interface of the provisionable server is discovered, monitoring of the interface is enabled by default. When the management features are added, monitoring of other interfaces is enabled by default.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
