Chapter 3 Connecting your Solstice PPP Client to a Server
This chapter tells you how to use ppptool(1m) to connect your Solstice PPP client to a remote server, and how to run common network applications such as mailtool(1) and the Netscape web browser over a PPP link.
About ppptool
The graphical user interface for Solstice PPP is called ppptool. Using ppptool you can connect your Solstice PPP client to any of the remote servers that you defined when you ran pppinit.
Note -
If you have not installed the software license system for Solstice PPP, you are limited to a single modem connection. You can still initiate calls to multiple remote servers; however, you can only communicate with one remote server at a time. If you have installed the software license system for Solstice PPP, you can make multiple modem connections; therefore, you can initiate several calls to remote servers simultaneously. See Solstice PPP 3.0.1 Installation Guide and Release Notes or the Solaris Server Intranet Extension 1.5 Installation Library for instructions on how to obtain and install a license for this product.
To Start ppptool
You can either start ppptool from the command line, or add the command to your workspace menu.
To start ppptool from the command line, type:
prompt% /usr/bin/ppptool |
When you start ppptool, the Hosts map is displayed, as shown in Figure 3-1. The Hosts map contains one icon for each of the servers you defined when you ran the initialization script pppinit.
Figure 3-1 The ppptool Hosts map
When you double-click SELECT on one of the server icons in the hosts map, the Connection window for that server appears, as shown in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 The Connection Window
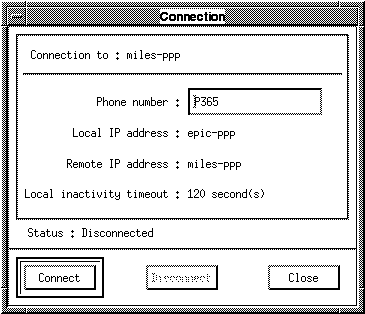
The Connection window displays the following information:
Connection to: The name used to identify the remote server for this connection.
Phone number The telephone number used to initiate calls to the server. This is the telephone number you assigned when you ran pppinit; however, it is an editable field so you can change the number if you want. Your changes are not saved when you exit ppptool.
Local IP address The IP address assigned to your Solstice PPP client, expressed either as a host name or in dot notation. This field will be set to <unassigned> if the remote server is going to supply the IP address. It will change to show the IP address or hostname received from the server when the connection is established.
Remote IP address The IP address assigned to the remote server, expressed either as a host name or in dot notation. This field will be set to <unassigned> if the remote server is going to supply the IP address. It will change to show the remote IP address or hostname received from the server when the connection is established.
Local inactivity timeout This is the time that the connection can remain unused before it is closed automatically.
Status: The current status of the connection.
Using ppptool
To Connect to a Server
When you initiate a connection to a server, you use the telephone number that you assigned using pppinit, preceded by the prefix associated with your current location. There is no prefix if the current location is <default>. To connect your Solstice PPP client to a server:
-
Double-click SELECT on the server's icon to display its Connection window.
-
Click SELECT on the Connect button to initiate the connection.
If your client uses an interactive CHAT script for this connection, a dialog box will appear. Type in the responses requested by the remote server. For example, user id and challenge passwords.
To Disconnect from a Server
The connection to the server is usually terminated automatically when the connection remains unused for the period of time defined by the local inactivity timeout. To disconnect your Solstice PPP client from a server manually:
-
Double-click SELECT on the server's icon to display its Connection window.
-
Click SELECT on the Disconnect button to terminate the connection.
To Change the Current Location
The Current Location is used to add a prefix to all the telephone numbers associated with the servers defined in the hosts map. This feature is used for mobile communications when you cross exchange and international boundaries. To change the Current Location:
Choose a new location from the Current Location pull-down menu.
To Add a new Location to the Current Location List
You can add a new location and prefix to the Current Location list at any time. To add a new location to the Current Location list:
-
Click SELECT on the Modify... button to display the Location window.
-
Click SELECT on the New Location button and enter the Location name and associated Prefix.
-
Click SELECT on the Add button to enter the new location in the list.
To Modify the Current Location List
You can modify the name and prefix of an existing location at any time. The change will take effect the next time you initiate a call from that location. To modify an existing location:
-
Click SELECT on the Modify... button to display the Location window.
-
Choose one of the locations from the list and modify its prefix.
-
Click SELECT on the Modify button to change the prefix.
To Delete a Location from Current Location List
You can delete an existing location at any time. To delete an existing location:
-
Click SELECT on the Modify... button to display the Location window.
-
Choose one of the locations from the list.
-
Click SELECT on the Delete button to remove it from the list.
Running Applications over your PPP Link
Once you have connected your Solstice PPP client to a remote server, you can run network applications transparently over the PPP link in the same way as you would over your local area network connection.
Running Applications without using a Name Service
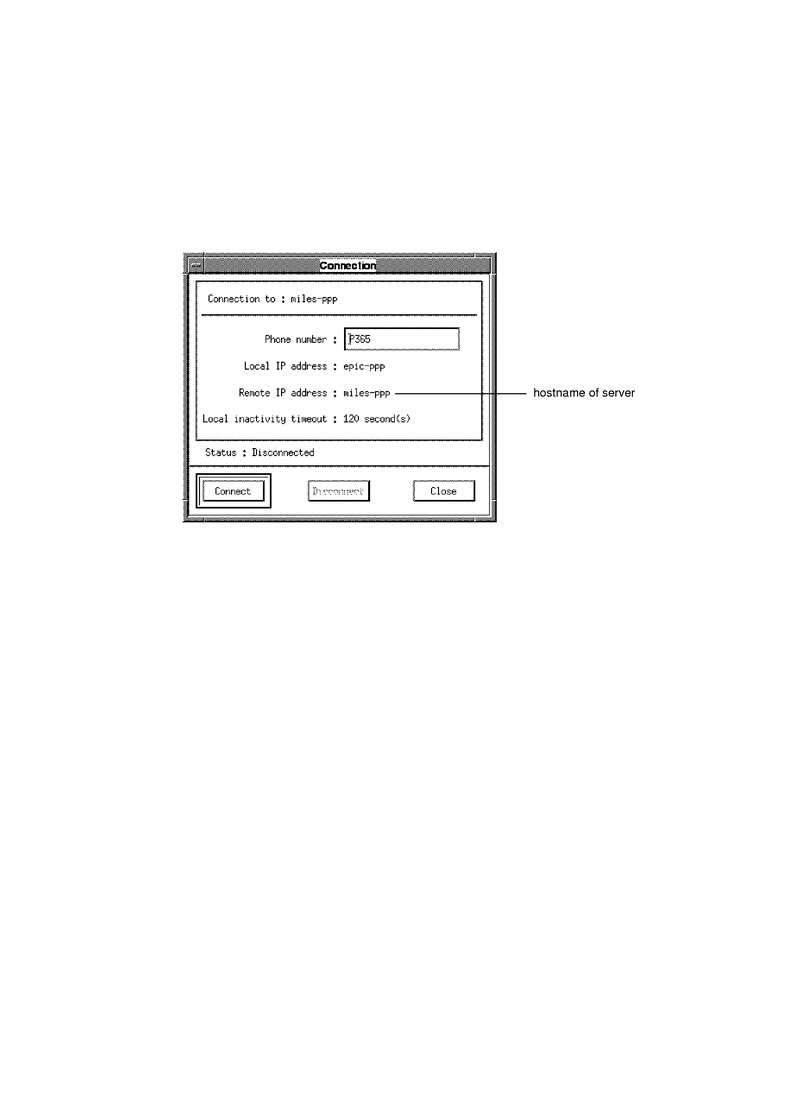
Name services, such as the Domain Name Service (DNS), are used to resolve hostnames into their corresponding IP addresses. You can run simple IP applications over your PPP link without enabling a name service on your client; however, you need to know the IP address or hostname of your server. This is the remote IP address displayed in the connection window by ppptool, as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Remote IP Address of Server
Once you are connected to the server, you can use Unix commands such as rlogin(1), rsh(1), telnet(1), and ftp(1) to access the resources of the remote network.
Running Applications with DNS Enabled
The Domain Name Service (DNS) is the most commonly used mechanism for resolving IP addresses and hostnames. You need to use a system such as DNS if you want to be able to browse a network or to reach further than your server. The server must be configured to route IP traffic, and your system administrator or Internet provider must give you the following information:
-
The domain name for the subnetwork
-
The IP address(es) of your name server(s)
The name server, and the server to which your client is connected, may be the same machine; but they do not have to be.
To enable DNS on your client:
hosts: files dns |
-
Create the file /etc/resolv.conf, and enter the domain name and the IP addresses of all the name servers as follows:
domain xyz.Company.COM nameserver 179.xxx.aaa.11 nameserver ... nameserver ...
-
Optionally, edit the file /etc/hosts to add the IP address and hostname of your server:
127.0.0.1 localhost 179.xxx.aaa.117 papyrus loghost 179.xxx.aaa.100 server
All of these changes take place automatically; there is no need to reboot your machine.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
