Mandatory Access Control
Mandatory access control (MAC) is a system-enforced access control mechanism that uses clearances and sensitivity labels to enforce security policy. Roughly speaking, MAC associates the programs a user runs with the security level (clearance or sensitivity label) at which the user chooses to work in the session and permits access to information, programs, and devices at the same or lower level only. MAC also prevents users from writing to files at lower levels. MAC is enforced according to your site's security policy and cannot be overridden without special authorization or privileges.
Clearances
As part of your site's security policy, your security administrator assigns a user clearance to everyone at your site. The user clearance represents the degree of security with which a user is entrusted. It has two components:
-
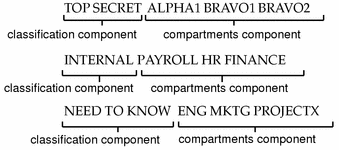
classification - indicates a (hierarchical) level of security. Applied to people, the classification represents a measure of trust; applied to data, it is the degree of protection required. In government, classifications are: TOP SECRET, SECRET, CONFIDENTIAL, and UNCLASSIFIED. Industry is not as standardized; a hypothetical classification hierarchy might be PUBLIC, INTERNAL, NEED TO KNOW, and REGISTERED.
-
compartment - represents a grouping, such as a work group, department, project, or topic. Access to compartments is granted on a need-to-know basis.
Some typical clearances are shown in the following figure.
Figure 1-2 Typical Clearances
Sensitivity Labels
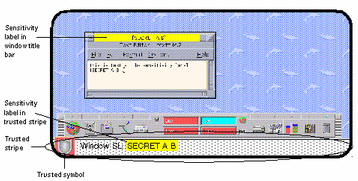
Trusted Solaris uses a string called a sensitivity label (SL) (containing a classification and compartments in similar fashion to clearances) to determine which information you can access. Sensitivity labels may be displayed inside square brackets ([]) in window title bars, in the trusted stripe (a special area at the bottom of the screen), or not at all, depending on how your system is configured. Figure 1-3 shows a configuration configured to display sensitivity labels; the sensitivity labels and trusted stripe are indicated.
Figure 1-3 Typical Environment with Sensitivity Labels Displayed
All subjects and objects in a system have sensitivity labels. A subject is an active entity, usually a process (running program), that causes information to flow among objects or changes the system state. An object is a passive entity that contains or receives data, such as a data file, directory, printer, or other device. In some cases, a process may be an object, such as when you use kill on a process.
The Part Sensitivity Labels Play in Transactions
Trusted Solaris mediates all attempted security-related transactions. It compares the subject's sensitivity label with the object's sensitivity label and permits or disallows the transaction depending on which label is dominant (as described below). An entity's sensitivity label is said to dominate another's if the following two conditions are met:
-
The classification component of the first entity's sensitivity label is equal to or outranks the object's classification.
-
All compartments in the second entity's labels are included in the first entity's label.
Two labels are said to be equal if they have the same classification and the same set of compartments. If they are equal, they dominate each other so that access is permitted. If one label has a higher classification or includes all of the second label's compartments or both, the first label is said to strictly dominate the second label. Two labels are said to be disjoint or noncomparable if neither label dominates the other.
In a read transaction, the subject's sensitivity label must dominate the object's sensitivity label. This rule ensures that the subject's level of trust meets the requirements for access to the object and that the subject's sensitivity label includes all compartment groupings that are allowed access to the object.
In a write transaction, that is, when a subject creates or modifies an object, the resulting object's sensitivity label must dominate the subject's sensitivity label. This rule prevents the subject from lowering the object's sensitivity label.
Users sometimes refer to the acronym WURD (write up / read down) to remind themselves of the permitted directions in mandatory access control. In practice, subjects and objects in read and write transactions usually have the same sensitivity label and strict dominance does not have to be considered.
Table 1-1 Examples of Label Relationships|
Label 1 |
Relationship |
Label 2 |
|---|---|---|
|
Top Secret A B |
(strictly) dominates |
Secret A |
|
Top Secret A B |
(strictly) dominates |
Secret A B |
|
Top Secret A B |
(strictly) dominates |
Top Secret A |
|
Top Secret A B |
dominates (equals) |
Top Secret A B |
|
Top Secret A B |
is disjoint with |
Top Secret C |
|
Top Secret A B |
is disjoint with |
Secret C |
|
Top Secret A B |
is disjoint with |
Secret A B C |
When you perform a drag-and-drop or copy-and-paste operation between files with different sensitivity labels, Trusted Solaris displays a confirmation dialog box if you are permitted to change the sensitivity label or, if you are not permitted, Trusted Solaris bars the transaction. You can accept the upgrade of the destination (if you have special authorization), downgrade the information so that the destination will maintain its existing sensitivity label, or cancel the transaction altogether.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
