Chapter 1 N1 Provisioning Server Introduction
This chapter provides an introduction of the Infrastructure Fabric (I-Fabric) components and the N1 Provisioning Server. Later chapters of this guide describe in detail how to operate and perform day-to-day administrative tasks on the software and the I-Fabric.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
I-Fabric Overview
N1 Provisioning Server software provides a comprehensive infrastructure automation solution that enhances the visibility, and control of complex computing environments. An I-Fabric consists of various hardware components, such as blade system chassis, server blades, and load balancer blades, and the N1 Provisioning Server software. N1 Provisioning Server software controls how I-Fabric components interoperate. An I-Fabric, controlled and managed by N1 Provisioning Server software, combines computing and networking resources into a contiguous automated fabric of infrastructure that you deploy and reallocate to meet changing requirements. Resources are dedicated to a farm until returned to the common resource pool. With root access to devices, you can deploy any software or application onto the servers. Secure partitions enforced by N1 Provisioning Server software and methodologies enable you to exercise independent administrative control over each logical server farm.
Resources within an I-Fabric are accessed through the Control Center, a web-browser-based graphical user interface (GUI). This drag-and-drop interface enables you to design and deploy logical server farms. Within a design, you can define numerous characteristics, including topology, monitors, and alerts.
When you create a logical server farm design and apply it within the Control Center, N1 Provisioning Server software creates a logical description of the server farm design. The logical description is captured in the Farm Markup Language (FML), an eXtensible Markup Language (XML) dialect developed for N1 Provisioning Server software. FML enables the abstraction of design and configuration data for the deployment of actual physical resources. Abstraction of monitoring processes is captured using the Monitoring Markup Language (MML). Abstraction of the wiring configuration is captured using the Wiring Markup Language (WML).
I-Fabric Components
An I-Fabric integrates individually managed discontinuous networks, servers, and infrastructure devices into a coordinated, automated fabric. This fabric enables easy management, deployment, and redeployment of logical server farms. An I-Fabric is made up of three functional areas:
Control Plane
The control plane provides intelligence, management, and control of an I-Fabric. N1 Provisioning Server software, which provides the intelligence that enables an I-Fabric, resides within the control plane. The control plane consists of N1 Provisioning Server software, the Control Center server software, and the associated server hardware on which the software is deployed.
Fabric Layer
The fabric layer is a highly integrated Ethernet environment based on industry-standard networking technologies. The fabric layer contains the networking infrastructure and switching fabric that ties the control plane and resource pool together.
Resource Pool
The resource pool consists of infrastructure resources, such as Sun FireTM B1600 Blade System Chassis, load balancer blades, and server blades that function as resource pool servers for deployment to server farms. The resource pool of an I-Fabric contains all resource pool servers capable of being provisioned to a farm.
N1 Provisioning Server Configuration
The N1 Provisioning Server is set up in the following configuration:
-
All N1 Provisioning Server software runs on a single server in the control plane. The image library can either reside on a separate server or on the control plane server. Optionally, you can connect a terminal server. The Control Center GUI is accessed through a separate PC.
-
The resource pool configuration consists of one-blade to twelve-blade system chassis with 16 server blades on which you can deploy farms. For details on how to configure I-Fabric components see the N1 Provisioning Server 3.1, Blades Edition, Installation Guide.
Logical Server Farms
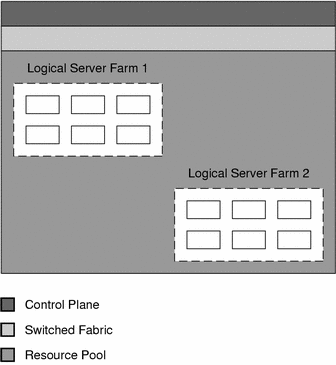
The control plane, fabric layer, and resource pool work together to dynamically create logical server farms within. Logical server farms are securely allocated from the resource pool and managed by N1 Provisioning Server software. N1 Provisioning Server software creates logical server farms from the resources available within the resource pool. Logical server farms are analogous to traditional, manually built, dedicated server farms except that you can create, grow, shrink, and delete them as data structures that reside within N1 Provisioning Server software.
Secure partitions enforced by N1 Provisioning Server software and methodologies enable you to exercise independent administrative control over each logical server farm. Although you can have administrative access on all devices within a logical server farm, you cannot view, access, or modify the devices or data associated with a different logical server farm unless you have the appropriate permission.
Figure 1–1 Logical Server Farms Provisioned Within the Resource Pool of an I-Fabric
N1 Provisioning Server Components
The N1 Provisioning Server provides a comprehensive set of infrastructure automation and management capabilities. The N1 Provisioning Server comprises two primary components: the Control Center and the control plane.
-
The Control Center is the web browser-based GUI that enables design, configuration, deployment, and ongoing management of logical server farms. For more details about the Control Center, see the N1 Provisioning Server 3.1, Blades Edition, Control Center Management Guide.
-
The control plane comprises the N1 Provisioning Server software, which provides the interface between the Control Center and the physical infrastructure resources, and any third-party components required to run the N1 Provisioning Server software.
Operating Environments
N1 Provisioning Server software runs on the SolarisTM 8 operating environment.
Control Center Software
The Control Center is the GUI to the N1 Provisioning Server software. You deploy and manage logical server farms through the Control Center. For more details about the Control Center, see the N1 Provisioning Server 3.1, Blades Edition, Control Center Management Guide.
N1 Provisioning Server Software
The N1 Provisioning Server software resides on the control plane server and provides the infrastructure automation services required to manage and deploy logical server farms within an I-Fabric. At a high level, the N1 Provisioning Server software manages the logical-to-physical mappings between a logical server farm and the physical resources assigned to it.
N1 Provisioning Server software comprises the following roles and software components:
-
Segment manager, which controls and coordinates activities for an I-Fabric
-
Farm manager, which monitors activities related to logical server farms
-
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name Server (DNS) services
-
Monitoring software, which monitors the health and state of an I-Fabric and the logical server farms within it
-
Storage manager client (STMC), an interface required by the farm manager to access storage functionality
-
Control plane database (CPDB), which is a persistent, central repository of data
-
The image server, which manages images. The image server can be any stand-alone server that supports network file server (NFS), or it can reside on the control plane server.
N1 Provisioning Server software provides six key areas of infrastructure automation services:
-
Provisioning and configuration services
-
Flexing services
-
Software image management services
-
Monitoring and messaging services
-
Failure and recovery services
-
Physical infrastructure management services
Provisioning and Configuration
The ability to automatically provision and configure resources within the resource pool of an I-Fabric is a core capability of the N1 Provisioning Server. The N1 Provisioning Server manages and automates the ongoing evolution of logical server farms and their initial activation. As resources are added or deleted on server farms, the N1 Provisioning Server continues to manage and automatically configure all virtual wiring as well as DHCP and DNS services.
Flexing
Flexing enables you to add or delete capacity on a farm. N1 Provisioning Server software automatically provisions and configures resources. N1 Provisioning Server software provides two types of flexing services:
-
Adding and deleting individual servers within a logical server farm
-
Adding and deleting server groups through a server group mechanism
Software Image Management
The N1 Provisioning Server manages software images and configurations of servers. The N1 Provisioning Server supports creation and management of two categories of images: global images and account images.
-
Global images consist of the operating system (including patches and service packs), integrated N1 Provisioning Server agents, and certain customizations. Global images may also contain applications. At the very least, the customizations are modifications that make images compatible with an I-Fabric. You also may choose to customize images with account-specific software and data.
-
Account images are for a particular account and consist of account-specific customizations of global images, blank disks, or application and data images.
I-Fabric Monitoring
The N1 Provisioning Server actively monitors the state and health of devices in an I-Fabric. Monitoring provides visibility of an I-Fabric and supports failover and recovery of devices or the restarting of failed processes.
Failure and Recovery of Devices in the Resource Pool
The N1 Provisioning Server automatically detects and then replaces failed devices in the resource pool, such as resource pool servers and load balancers. The failed device is replaced with a device of the same type from the available devices in the resource pool. The replacement device automatically takes on the network configuration of the failed device.
Load Balancer Failover Modes
Load balancers support the following failover modes:
-
Path failover
-
Device failover or high availability (HA)
-
Single device failover (non-HA)
A path failover occurs when one interface to the router fails. In that case, the path on the failed interface is automatically restored on the live interface. In a high availability setup, one load balancer device is on standby as the secondary load balancer, while the primary, active load balancer device handles processing. If the primary load balancer fails, the secondary load balancer automatically takes over processing. A single device failover situation is resolved manually through the replaceFailedDevice tool.
Physical Infrastructure Management
As a part of the N1 Provisioning Server initialization process, the N1 Provisioning Server performs resource and wiring validation. This validation enables the CPDB to have a complete physical topology map of all resources within the I-Fabric. The wiring validation provides an automated way of confirming the physical wiring map of all devices within an I-Fabric. The integrity of the physical wiring of the resources within an I-Fabric enables the N1 Provisioning Server to successfully manage the virtual wiring of a logical server farm.
Description Languages
N1 Provisioning Server software uses description languages based on eXtensible Markup Language (XML) to create a digital blueprint of a farm's logical structure. This logical blueprint facilitates the automation of many manual tasks involved in constructing logical server farms. N1 Provisioning Server software employs the following description languages:
-
Farm Markup Language (FML) - Represents the logical blueprint of a logical server farm and describes network and configuration data for physical resources associated with a logical server farm
-
Monitoring Markup Language (MML) - Describes monitor deployments and configurations as you defined them within the Control Center
-
Wiring Markup Language (WML) - Describes the physical wiring characteristics within an I-Fabric
I-Fabric Security
N1 Provisioning Server software and methodologies provide a multitenant infrastructure that can be securely partitioned and allocated. The benefits of multitenancy, such as resource optimization through reallocating and the ability to flex from a common resource pool, are achievable only if a rigorous security model and architecture are in place. An I-Fabric provides multiple types of security enforcement and ensures that security exists between logical server farms.
Within an I-Fabric, security is implemented at the following levels:
-
Fabric layer — Ethernet and Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) security
-
Resource pool — Power cycling and memory scrubbing of resources
-
Control plane — N1 Provisioning Server and Control Center security
-
Password encryption at all levels
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
