Major Features
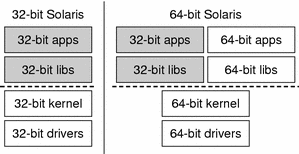
To explain the dual 32-bit and 64-bit support in the Solaris operating environment, the following figure shows the stacks side-by-side. The system on the left supports only 32–bit libraries and applications on top of a 32-bit kernel that uses 32-bit device drivers. The system on the right supports the same 32–bit applications and libraries as on the left. This system also supports 64-bit libraries and applications simultaneously on top of a 64-bit kernel that uses 64-bit device drivers.
Figure 2–1 The Solaris Operating Environment Architecture
The major features of the 64-bit environment include support for:
-
Large virtual address space
-
Large files
-
64-bit arithmetic
-
Removal of certain system limitations
Large Virtual Address Space
In the 64-bit environment, a process can have up to 64–bits of virtual address space, that is, 18 exabytes. This virtual address space is approximately 4 billion times the current maximum of a 32-bit process.
Note –
Because of hardware restrictions, some platforms might not support the full 64–bits of address space.
Large Files
If an application requires only support for large files, the application can remain 32-bit and use the Large Files interface. However, if portability is not a primary concern, consider converting the application to a 64-bit program. A 64-bit program takes full advantage of 64-bit capabilities with a coherent set of interfaces.
64–bit Arithmetic
64-bit arithmetic has long been available in previous 32-bit Solaris releases. However, the 64-bit implementation now uses the full 64-bit machine registers for integer operations and parameter passing. The 64-bit implementation allows an application to take full advantage of the capabilities of the 64-bit CPU hardware.
System Limitations Removed
The 64-bit system interfaces are inherently more capable than some of their 32-bit equivalents.
Application programmers concerned about year 2038 problems, when 32-bit time_t runs out of time, can use the 64–bit time_t. While 2038
seems a long way off, applications that do computations that concern future events,
such as mortgages, might require the expanded time capability.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
