GSS-API Status Codes
Major status codes are encoded in the OM_uint32 as shown in the following figure.
Figure B–1 Major-Status Encoding
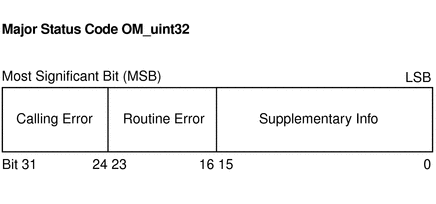
If a GSS-API routine returns a GSS status code whose upper 16 bits contain a nonzero value, the call has failed. If the calling error field is nonzero, the application's call of the routine was erroneous. The calling errors are listed in Table B–1. If the routine error field is nonzero, the routine failed because of a routine-specific error, as listed in Table B–2. The bits in the supplementary information field of the status code can be set whether the upper 16 bits indicate a failure or a success. The meaning of individual bits is listed in Table B–3.
GSS-API Major Status Code Values
The following tables list the calling errors that are returned by GSS-API. These errors are specific to a particular language-binding, which is C in this case.
Table B–1 GSS-API Calling Errors|
Error |
Value in Field |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_CALL_INACCESSIBLE_READ |
1 |
An input parameter that is required could not be read |
|
GSS_S_CALL_INACCESSIBLE_WRITE |
2 |
A required output parameter could not be written |
|
GSS_S_CALL_BAD_STRUCTURE |
3 |
A parameter was malformed |
The following table lists the GSS-API routine errors, generic errors that are returned by GSS-API functions.
Table B–2 GSS-API Routine Errors|
Error |
Value in Field |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_BAD_MECH |
1 |
An unsupported mechanism was requested. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_NAME |
2 |
An invalid name was supplied. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_NAMETYPE |
3 |
A supplied name was of an unsupported type. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_BINDINGS |
4 |
Incorrect channel bindings were supplied. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_STATUS |
5 |
An invalid status code was supplied. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_MIC, GSS_S_BAD_SIG |
6 |
A token had an invalid MIC. |
|
GSS_S_NO_CRED |
7 |
The credentials were unavailable, inaccessible, or not supplied. |
|
GSS_S_NO_CONTEXT |
8 |
No context has been established. |
|
GSS_S_DEFECTIVE_TOKEN |
9 |
A token was invalid. |
|
GSS_S_DEFECTIVE_CREDENTIAL |
10 |
A credential was invalid. |
|
GSS_S_CREDENTIALS_EXPIRED |
11 |
The referenced credentials have expired. |
|
GSS_S_CONTEXT_EXPIRED |
12 |
The context has expired. |
|
GSS_S_FAILURE |
13 |
Miscellaneous failure. The underlying mechanism detected an error for which no specific GSS–API status code is defined. The mechanism-specific status code, that is, the minor-status code, provides more details about the error. |
|
GSS_S_BAD_QOP |
14 |
The quality-of-protection that was requested could not be provided. |
|
GSS_S_UNAUTHORIZED |
15 |
The operation is forbidden by local security policy. |
|
GSS_S_UNAVAILABLE |
16 |
The operation or option is unavailable. |
|
GSS_S_DUPLICATE_ELEMENT |
17 |
The requested credential element already exists. |
|
GSS_S_NAME_NOT_MN |
18 |
The provided name was not a mechanism name (MN). |
The name GSS_S_COMPLETE, which is a zero value, indicates an absence of any API errors or supplementary information bits.
The following table lists the supplementary information values returned by GSS-API functions.
Table B–3 GSS-API Supplementary Information Codes|
Code |
Bit Number |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_CONTINUE_NEEDED |
0 (LSB) |
Returned only by gss_init_sec_context() or gss_accept_sec_context(). The routine must be called again to complete its function. |
|
GSS_S_DUPLICATE_TOKEN |
1 |
The token was a duplicate of an earlier token. |
|
GSS_S_OLD_TOKEN |
2 |
The token's validity period has expired. |
|
GSS_S_UNSEQ_TOKEN |
3 |
A later token has already been processed. |
|
GSS_S_GAP_TOKEN |
4 |
An expected per-message token was not received. |
For more on status codes, see GSS-API Status Codes.
Displaying Status Codes
The function gss_display_status() translates GSS-API status codes into text format. This format allows the codes to be displayed to a user or put in a text log. gss_display_status() only displays one status code at a time, and some functions can return multiple status conditions. Accordingly, gss_display_status() should be called as part of a loop. When gss_display_status() indicates a non-zero status code, another status code is available for the function to fetch.
Example B–1 Displaying Status Codes with gss_display_status()
OM_uint32 message_context;
OM_uint32 status_code;
OM_uint32 maj_status;
OM_uint32 min_status;
gss_buffer_desc status_string;
...
message_context = 0;
do {
maj_status = gss_display_status(
&min_status,
status_code,
GSS_C_GSS_CODE,
GSS_C_NO_OID,
&message_context,
&status_string);
fprintf(stderr, "%.*s\n", \
(int)status_string.length, \
(char *)status_string.value);
gss_release_buffer(&min_status, &status_string,);
} while (message_context != 0);
Status Code Macros
The macros, GSS_CALLING_ERROR(), GSS_ROUTINE_ERROR() and GSS_SUPPLEMENTARY_INFO(), take a GSS status code. These macros remove all information except for the relevant field. For example, the GSS_ROUTINE_ERROR() can be applied to a status code to remove the calling errors and supplementary information fields. This operation leaves the routine errors field only. The values delivered by these macros can be directly compared with a GSS_S_xxx symbol of the appropriate type. The macro GSS_ERROR() returns a non-zero value if a status code indicates a calling or routine error, and a zero value otherwise. All macros that are defined by GSS-API evaluate the arguments exactly once.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
