About Modules
A Java EE module is a collection of one or more Java EE components that execute in the same container type (for example, web or EJB) with annotations or deployment descriptors of that type. One descriptor is Java EE standard, the other is optional and Application Server specific. Annotations can be used instead of Java EE standard descriptors.
Types of Java EE modules are as follows:
-
Web Application Archive (WAR) — A web application is a collection of servlets, HTML pages, classes, and other resources that can be bundled and deployed to several Java EE application servers. A WAR file can consist of the following items: servlets, JavaServer PagesTM (JSPTM) files, JSP tag libraries, utility classes, static pages, client-side applets, beans, bean classes, and annotations or deployment descriptors (web.xml and sun-web.xml).
-
EJB JAR File — The EJB JAR file is the standard format for assembling enterprise beans. This file contains the bean classes (home, remote, local, and implementation), all of the utility classes, and annotations or deployment descriptors (ejb-jar.xml and sun-ejb-jar.xml). If the EJB component is a version 2.1 or earlier entity bean with container managed persistence, a .dbschema file and a CMP mapping descriptor, sun-cmp-mapping.xml, can be included as well.
-
Application Client JAR File — An application client is an Application Server specific type of Java EE client. An application client supports the standard Java EE Application Client specifications, and in addition, supports direct access to the Application Server. Its deployment descriptors are application-client.xml and sun-application-client.xml.
-
Resource RAR File — RAR files apply to J2EE CA connectors. A connector extends the EJB container to allow access to external systems much like a device driver provides access to a peripheral device from a process hosted by an operating system. It is a portable way of allowing EJB components to access a foreign enterprise system. Each Application Server connector has annotations or a Java EE XML file, ra.xml.
Package definitions must be used in the source code of all modules so the class loader can properly locate the classes after the modules have been deployed.
Because the information in a deployment descriptor is declarative, it can be changed without requiring modifications to source code. At run time, the Java EE server reads this information and acts accordingly.
The Application Server also supports lifecycle modules. See Chapter 13, Developing Lifecycle Listeners, in Sun Java System Application Server 9.1 Developer’s Guide for more information.
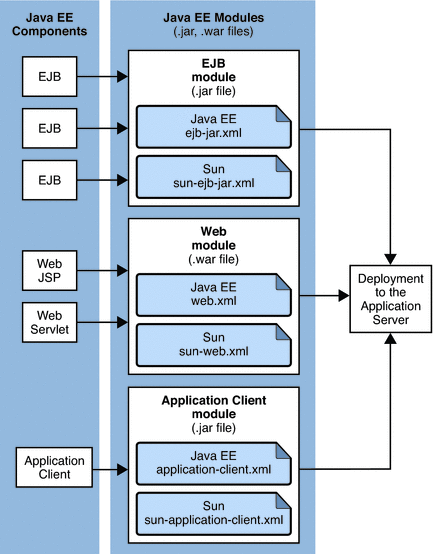
EJB JAR, Web, and application client modules can also be deployed separately, outside of any application, as in the following figure. EJB components are assembled in a JAR file with annotations or ejb-jar.xml and sun-ejb-jar.xml deployment descriptors. Web components are assembled in a WAR file with annotations or web.xml and sun-web.xml deployment descriptors. Application client components are assembled in a JAR file with application-client.xml and sun-application-client.xml deployment descriptors. These module types are deployed to the Application Server.
Figure 1–1 Module Assembly and Deployment
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
