Using the FTP Binding Component
The topics in this document provides information about using the FTP Binding Component in a Project.
What You Need to Know
These topics provide information about the functional behavior of the FTP Binding Component.
Configuring the FTP Binding Component for Clustering
For information on GlassFish ESB Clustering and the FTP Binding Component see the following.
-
How To Create a Cluster-Ready Composite Application with FTP BC (http://wiki.open-esb.java.net/Wiki.jsp?page=FTPBCClusteringHowTo)
More Information
Much more information about the FTP Binding Component can be found in the tutorial, Working with the FTP Binding Component. Please refer to this document for further information about the FTP Binding Component.
FTP Binding Component — Overview
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Binding Component (BC) (referred as FTP BC) is a binding component implementation that complies with JBI Specification 1.0.
The FTP Binding Component is a JSR-208 compliant JBI runtime component that provides inbound and outbound JBI messaging using the FTP protocol as specified in RFC 959.
The Binding Components are used to send and receive messages using specific protocols and transports. The components provide normalization and de-normalization to isolate the JBI environment from the particular protocol-specific formats. These allow the JBI environment to deal only with normalized messages.
Note –
Protocol-specific metadata can be attached to a normalized message, or the message exchange, in their metadata, allowing protocol-specific information to be conveyed to a Service Engine (SE) or Binding Component (BC) in a manner that is opaque to other JBI environment components.
The Binding Components provide a message transportation using the FTP protocol and also helps to define services (which comprise operations) using WSDL. Later the components bind them to FTP as the underlying message transportation protocol. These also assists binding other components in a JBI environment (for example, an SE can orchestrate the services consumption and provision).
The FTP Binding Component implements all required Binding Component interfaces using JBI specification to facilitate deployment and execution in any JBI compliant target environment.
The implementation has a design-time component to facilitate the process of service definition and binding.
A NetBeans module also makes WSDL authoring and FTP binding a convenient process in the NetBeans IDE.

Supporting Features in the FTP Binding Component
This following are the supported features implemented in the FTP Binding Component.
-
FTP Binding Component Extensibility Elements
-
ftp:transfer- Specify message transportation involving a sending party and a receiving party through FTP
-
ftp:message - Specify message transportation between a service consumer and a service provider through FTP
-
ftp:address - Specify an endpoint for message transport using FTP
-
ftp:binding - Specify a FTP binding indication
-
ftp:operation - Specify a FTP operation indication
-
-
External Protocols
-
FTP (RFC 959)
-
FTP/TLS (RFC 2228 + RFC 4217) - Explicit SSL
-
FTP/TLS - Implicit SSL
-
-
Directory Listing Styles
A built-in parsing logic has been introduced to parse the directory listing for the following directory listing style. This must address diversification on FTP servers running on different Operating Systems.
-
UNIX
-
AS400
-
AS400-UNIX
-
HCLFTPD 6.0.1.3
-
HCLFTPD 5.1
-
HP NonStop/Tandem
-
MPE
-
MSFTPD 2.0
-
MSP PDS (Fujitsu)
-
MSP PS (Fujitsu)
-
MVS GDG
-
MVS PDS
-
MVS Sequential
-
Netware 4.11
-
NT 3.5
-
NT 4.0
-
UNIX (EUC-JP)
-
UNIX (SJIS)
-
VM/ESA
-
VMS
-
VOS3 PDS (Hitachi)
-
VOS3 PS (Hitachi)
-
VOSK (Hitachi)
A configuration file containing directory listing parsing information is provided to handle user-defined FTP directory list parsing. Users can specify the parsing rules (heuristics) for directory listing.
-
-
Proxy Protocols
-
SOCKS4
-
SOCKS5
Note –The proxy configuration is not a per-service information, but is part of the FTP Binding Component deployed on a host. Its configuration is a FTP Binding Component Runtime configuration parameter.
-
-
Environment Variables
Name:value pairs can be defined as environment variables. The environment variables can be used to specify environment specifications in the WSDL configuration. These can be path names and host names. Environment variables are defined using a binding component runtime parameter.
Using environment variables provides greater flexibility in modifying configurations for the FTP Binding Component.
-
Pre-Transfer and Post-Transfer Operations
Some pre and/or post operations are performed after a FTP PUT or GET. For example, archiving a file that is downloaded so it does not download again, or moving file away that is in the way of a PUT so that it does not get overwritten, and so forth. The following pre/post transfer operations are supported:
-
COPY - For post GET operation
Create a duplicate of the target file at a location using the pre-operation parameters before file transfer.
-
RENAME - For pre GET, post GET, and post PUT operation
-
Use the pre-operation parameters to move the target file to a location before file transfer.
-
Use the post-operation parameters to move the target file to a location after file transfer.
-
-
DELETE - For post GET operation
Delete the target file after the transfer.
-
-
Connection Pooling
Pool connections to the FTP Server.
Systemic Qualities Implemented in the FTP Binding Component
These are the systemic qualities implemented in FTP Binding Components.
-
Transport Security
-
Explicit SSL - FTP/TLS (RFC 2228 + RFC 4217)
-
Implicit SSL - FTP on SSLSocket
-
-
Connection Pooling
-
Numerous QoS
-
Password Handling
Security often interacts with various external systems, protocols, and implementations. Security can be authorization, authentication, or encryption. This initiative provides a common mechanism for components that handle authorization and authentication using user names and passwords.
-
Usability Enhancement of WSDL Extensibility Element Editor
-
Component Logging Systemic Quality
-
Application Variable and Application Configuration
-
Runtime Monitoring (MBean)
Users can monitor the component and the application during runtime. After deploying and starting the server, it provides datapoints like endpoint statistics, component statistics and also measures performance.
-
Re-Delivery
-
Throttling
Throttling settings can be used to limit the number of concurrent messages sent over the NMR.
-
Normalized Message Properties
Normalized Message properties (or NM properties) are commonly used to specify metadata associated with the message content. Some standard NM properties defined in JBI specifications are: javax.jbi.security.subject and javax.jbi.messaging.protocol.type.
-
Getting/Setting transport context properties (for example, http headers in the coming HTTP request, file names read by the File Binding Component)
-
Getting/Setting protocol specific headers or context properties (SOAP headers)
-
Getting/Setting additional message meta-data (for example, unique message identifier, endpoint name associated with a message)
-
Dynamic configurations (for example, dynamically overwrite the statically configured file name to write to at runtime)
-
-
FTP Binding Component Defined Normalized Message Properties
FTP Binding Component supports the unique message ID, that is, org.glassfish.openesb.messaging.messageid.
Unique Message ID can be used, for example, to correlate messages while responding to a request.
FTP Binding Component provides out-of-box request or response correlating using a UUID for every message.
-
Dynamic Addressing based on FTP Binding Component Normalized Message Properties
FTP Binding Component can derive binding information from Normalized Message properties from a message. It applies this information to the static binding obtained from WSDL. It derives the endpoint while the message is processed or routed. This is called Dynamic Addressing.
-
For Inbound: Normalized Message properties will be populated and attached to the message if and only if AllowDynamicEndpoint == true.
-
For Outbound: Normalized Message properties will be used to overwrite static binding if and only if: AllowDynamicEndpoint == true and org.glassfish.openesb.ftp.use.dynamic.endpoint == true
Dynamic Addressing can be of as a per message (outbound) endpoint binding (for example, to an external system).
Note –This is a different mechanism from the JBI Dynamic Endpoint Reference (EPR).
-
-
Invoking Messages in FTP Binding and Synchronous Request-Response Service
The FTP protocol is used for transporting messages between service consumer and service provider.
Service Engines can exchange messages through WSDL services that have FTP Binding Component extensibility elements. The extensibility elements of the FTP Binding Components can be defined based on nature of operation or binding mechanism.
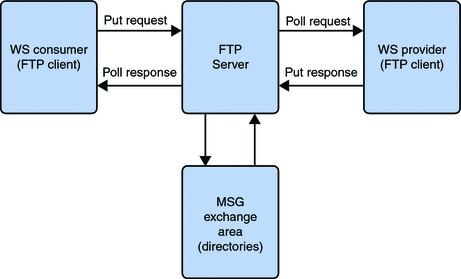
The figure illustrates a full message path including request (IN-ROUTE) and response (OUT-ROUTE). As illustrated, FTP Binding Component uses directories on FTP server as message persistence where service consumers and service providers exchange messages. During the implementation the following assumptions are made to facilitate message transportation in a FTP context.
When the FTP Binding Component acts as a JBI consumer, it puts a request (for certain service) and polls a response using the FTP protocol.
When the FTP Binding Component acts as a JBI provider, it uses the FTP protocol to route JBI normalized messages to a specified destination.
FTP Binding Component provides the following mode of operation. Each mode has two “flavors” corresponding to the Binding Schemes used. They are,
-
ftp:message
-
Inbound One Way — Poll Message
-
Inbound Request Response Messaging — Poll Request Message and Put Response Back (can be correlated and non-correlated)
Depends on the extensibility elements' attribute “messageCorrelate”
-
Outbound One Way — Put Message
-
Outbound Request Response Messaging — Put Request Message and Poll Response Back (can be correlated and non-correlated)
Depends on the extensibility elements' attribute “messageCorrelate”
-
On Demand Get Message — Get Message
For Binding Schema “Message”
-
-
ftp:transfer
-
Inbound One Way — Receive Request
-
Inbound Request Response Transferring — Receive Request and Send Response Back (can be correlated and non-correlated)
Depends on the extensibility elements' attribute “messageCorrelate”
-
Outbound One Way — Send Request
-
Outbound Request Response Transferring — Send Request and Receive Response Back (can be correlated and non-correlated)
Depends on the extensibility elements' attribute “messageCorrelate”
-
On Demand Receive Transferring — Receive Transfer
For Binding Schema “Transfer”
-
Note –
The service consumption can be synchronous, where the WS consumer posts the message to a location agreed between consumer and provider. It polls the response mutually from a location agreed between the consumer and the provider. The service consumption can be asynchronous where the WS consumer posts the message to a location agreed between the consumer and the provider. Later, it leaves a separate response to facilitate the poller to poll from a mutually agreed location.
Correlating a Request-Response
There are two methods used to correlate a request with a corresponding response message.
-
Using the BPEL correlate set method.
-
Synchronized Request/Response Processing: This is enabled using ftp:message —> messageCorrelate (if you are using the “Message” ftpbc binding scheme). If you are using the “Transfer” ftpbc binding scheme, ftp:transfer —> messageCorrelate.
Message Transportation Through FTP Binding Component
As illustrated in Figure, the FTP Binding Component uses directories on the FTP server as message persistence where service consumers and service providers exchange messages. In the current implementation, some assumptions are made so that there is a controlled transport of messages in the FTP context. This is true when multiple components access a directory.
The following are assumptions made under the current implementation.
-
Each service operation with FTP binding has an endpoint information like host name, port, account login, password and so forth. This information specifies a message exchange area on the remote FTP server where both the consumer and provider communicate.
For example, in the case of a requestresponse type operation, the following is performed in the message area during message transport from the consumer to the provider (request - IN-Route) and from the provider to the consumer (response - OUT-Route):
-
Consumer: Staging (Put) request
-
Consumer: Expose (Rename to target location) request to provider when staging completes
-
Provider: Poll (Get periodically) request
-
Provider: Archive/Remove request after received
-
Provider: Staging (Put) response
-
Provider: Expose (Rename to target location) response to consumer when staging completes
-
Consumer: Poll (Get periodically) response
-
Consumer: Archive/Remove response received
Figure: Message Transportation
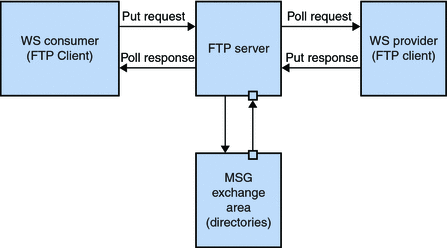
The message exchange area is a dedicated directory on the remote FTP server. The FTP Binding Component or the Administrator can create sub-directories (which serve as archiving area, staging area, exchange area, and so on) during runtime. This is similar to the queues and topics in the JMS paradigm.
-
-
The service consumer and the service provider either login using the same FTP account (they share the same FTP context - For example, login home where all relative paths are referred), or use different accounts for a given service. If different accounts are used, an administrative configuration is needed to ensure that the login home is mapped to the same location on FTP server. Appropriate access rights have to be granted according to the chosen scenario.
-
Different service operations use dedicated message exchange areas on the remote FTP server. There is no overlapping between the base directories.
-
FTP file names are leveraged so that the consumers and providers can push and poll messages between them. For example, consumers post request messages into the FTP file with names that match the .msg pattern. The corresponding providers use the same pattern to retrieve these request messages from the agreed location. A similar process occurs for the response routing from providers to consumers. Numerous patterns are available for configuration of a particular message transfer (implemented as FTP Binding Component extensibility elements: ftp:message, ftp:messageActivePassive (deprecated), ftp:transfer). These ensure that the messages posted get polled according to their name pattern.
Note –Request-response messages cannot be correlated across FTP.
-
The FTP files serve as intermediary message persistence on FTP server. The names of the FTP files are leveraged to support Request-response correlation. The scenario works as follows:
On the Consumer Side:
The message routing starts with the consumer who invokes a service (INVOKE in BPEL script). On the other side of the NMR, FTP Binding Component OutboundProcessor accepts the request message, de-normalizes the message and labels the message body (which is the payload to a FTP file) with name as req (Refer to Figure: Message Transportation).
The consumer thread (FTP Binding Component OutboundProcessor) spawns off a ResponsePoller thread which starts polling a response with name resp.
Note –
The same UUID is used for request and response.
The request is fetched when resp. becomes available at the location agreed between the consumer and provider. This completes the request-response correlation sequence. The fetched message is wrapped up as a normalized message and sent into NMR using the same Message Exchange ID. This ensures that the response is available as the OUT variable of the INVOKE activity in the BPEL script.
Figure: UUID Tagged Response Message
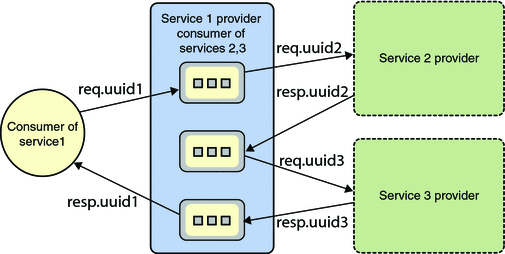
On the Provider Side:
The provider polls (RECEIVE activity in BPEL) the message receiving area (agreed between the consumer and provider) for a request. The provider polls for a request with the FTP file name pattern req.%u, where %u denotes any string that matches the pattern of a typical UUID in the string form (refer to JDK java.util.UUID - since 1.5) (Refer Figure 1: Message Transportation).
The UUID tag is extracted from the file name upon receipt of the request message (polled from remote FTP directory). The tag is attached as metadata for the message exchange. The payload is wrapped in a normalized message and sent into the NMR. The request message participates in any business logic in the service unit. A response is sent to the NMR with the same message exchange (ME - attached with meta information including the UUID tagged with the request). The OutboundProcessor fulfills the contract by associating the message to a FTP file named as resp. See Figure 3: UUID Tagged Response Message for examples of UUID tagged response messages. This completes the request-response correlation.
Note –
The message correlation scheme can be applied to multi-hop service invoking. For example, during the processing of the first service invoking, invoke service1.operation1, the provider can also invoke other services, such as service2.operation2.
Note –
UUID tagging is not the only means to achieve message correlation though the sample FTP Binding Component implementation seems to indicate. The service unit that transports the message can also use the information embedded inside the message payload to correlate at application level.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
