Periodic Access Reviews and Attestation
Waveset provides a process for conducting access reviews that enable managers or other responsible parties to review and verify user access privileges. This process helps to identify and manage user privilege accumulation over time, and helps to maintain compliance with Sarbanes-Oxley, GLBA, and other federally regulated mandates.
Access reviews can be performed as needed or scheduled to occur periodically. such as every calendar quarter, enabling you to conduct periodic access reviews to maintain the correct level of user privileges. An access review can optionally include audit policy scans.
About Periodic Access Reviews
Periodic access review is the periodic process of attesting that a set of employees has the appropriate privileges on the appropriate resources at a specific point in time.
A periodic access review involves the following activities:
-
Access review scans. Scans that perform rule-based evaluations of user entitlements to determine if attestation is needed.
-
Attestation. Process of responding to attestation requests by approving or rejecting user entitlements.
A user entitlement is a detailed record of a user’s accounts on a specific set of resources.
Access Review Scans
To initiate a periodic access review, you must first define at least one access scan.
The access scan defines who will be scanned, which resources will be included in the scan, any optional audit policies to be evaluated during the scan, and rules to determine which entitlement records will be manually attested, and by whom.
Access Review Workflow Process
In general, the Waveset access review workflow:
-
Constructs a list of users, gets account information for each user, and evaluates optional audit policies
-
Creates user entitlement records
-
Determines if attestation is required for each user entitlement record
-
Assigns work items to each attestor
-
Waits for all attestors to approve, or for the first rejection
-
Escalates to the next attestor, if no response to a request is received within a specified timeout period
-
Updates user entitlement records with resolutions
See Access Review Remediation for a description of the remediation capabilities.
Required Administrator Capabilities
To conduct a periodic access review and manage the review processes, a user must have the Auditor Periodic Access Review Administrator capability. A user with Auditor Access Scan Administrator capability can create and manage access scans.
To assign these capabilities, edit the user account and modify the security attributes. For more information about these and other capabilities, see Understanding and Managing Capabilities in Chapter 6, Administration.
Attestation Process
Attestation is the certification process performed by one or more designated attestors to confirm a user entitlement as it exists on a specific date. During an access review, the attestor (or attestors) receives notice of the access review attestation requests through email notification. An attestor must be an Waveset user, but is not required to be an Waveset administrator.
Attestation Workflow
Waveset uses an attestation workflow that is launched when an access scan identifies entitlement records requiring review. The access scan makes this determination based on the rules defined in the access scan.
A rule evaluated by the access scan determines if the user entitlement record needs to be manually attested, or if it can be automatically approved or rejected. If the user entitlement record needs to be manually attested, then the access scan uses a second rule to determine who the appropriate attestors are.
Each user entitlement record to be manually attested is assigned to a workflow, with one work item per attestor. Notification to the attestor of these work items can be sent using a ScanNotification workflow that bundles the items into one notification, per attestor, per scan. Unless the ScanNotification workflow is selected, notification will be per user entitlement. This means an attestor could receive multiple notifications per scan, and possibly a large number depending on the number of users scanned.
Attestation Security Access
These authorization options are for work items of authType AttestationWorkItem:
-
The Work Item owner
-
A direct or indirect manager of the Work Item owner
-
An administrator who controls an organization in which the Work Item owner belongs
-
Users who have been validated through authentication checks
By default, the behavior for authorization checks is one of the following:
-
Owner is User attempting the action
-
Owner is in Organization controlled by user attempting the action
-
Owner is a subordinate of user attempting the action
The second and third checks are independently configurable by modifying these form properties:
-
controlOrg — Valid values are true or false
-
subordinate — Valid values are true or false
-
lastLevel — Last subordinate level to include in the result; -1 means all levels
The integer value for lastLevel defaults to -1, meaning direct and indirect subordinates.
You can add or modify these options in the following:
UserForm: AccessApprovalList.
Note –
If you set security on attestations to organization-controlled, then the Auditor Attestor capability is also required to modify another user’s attestations.
Delegated Attestation
By default, the access scan workflow respects delegations, for work items of type Access Review Attestation and Access Review Remediation, created by users for attestation work items and notifications. The access scan administrator may deselect the Follow Delegation option to ignore delegation settings. If an attestor has delegated all work items to another user but the Follow Delegation option is not set for an access review scan, then the attestor, not the user to which delegations have been assigned, will receive attestation request notifications and work items.
Planning for a Periodic Access Review
An access review can be a labor- and time-intensive process for any business enterprise. The Waveset periodic access review process helps minimize the cost and time involved by automating many parts of the process. However, some of the processes still are time-consuming. For example, the process of fetching user account data from a number of locations for thousands of users can take a considerable amount of time. The act of manually attesting records can be time-consuming as well. Proper planning improves the efficiency of the process and greatly reduces the effort involved.
Planning for a periodic access review involves the following considerations:
-
Scan times can vary greatly depending on the number of users and the resources involved.
A single periodic access review for a large organization can take one or more days for scanning, as well as one or more weeks for manual attestation to complete.
For example, for an organization with 50,000 users and ten resources, an access scan might take approximately one day to complete, based on the following calculation:
1 sec/resource * 50K users * 10 resources / 5 concurrent threads = 28 hours
If resources are spread across geographies, network latencies can add to the process time.
-
Using multiple Waveset servers for parallel processing can speed up the access review process.
Running parallel scans is most effective when the resources are not common across the scans. When defining an access review, create multiple scans and restrict resources to a specific set of resources, using different resources for each scan. Then when you launch the task, select multiple scans and schedule them to run immediately.
-
Customizing the Attestation workflow and rules gives you greater control and can provide greater efficiency:
For example, customize the Attestor rule to spread attestation duties across multiple attestors. The attestation process assigns work items and sends out notifications accordingly.
-
Using Attestor Escalation Rules helps improve response time for attestation requests.
Set the Default Escalation Attestor rule, or use a customized rule, to set up an escalation chain of attestors. Also specify escalation timeout values.
-
Understand how to use the Review Determination Rules to save time by automatically determining which entitlement records need to be manually reviewed.
-
Bundle notification of attestation requests for a scan by specifying a scan-level Notification Workflow.
Tuning Scan Tasks
During the scan process, multiple threads access the user’s view, potentially accessing resources on which the user has accounts. After the view is accessed, multiple audit policies and rules are evaluated, which may result in the creation of compliance violations.
To prevent two threads from updating the same user view at the same time, the process establishes an in-memory lock on the user name. If this lock cannot be established in (by default) 5 seconds, then an error is written to the scan task and the user is skipped, thus providing protection for concurrent scans that are processing the same set of users.
You can edit the values of several “tunable parameters” that are provided as task arguments to the scan task:
-
clearUserLocks (Boolean). If true, then all current user locks are freed before the scan starts.
-
userLock (integer). Time (in milliseconds) to wait when trying to lock a user. The default value is 5 seconds. A negative value disables locking for that scan.
-
scanDelay (integer). Time (in milliseconds) to sleep between dispatching scan threads. The default value is 0 (no delay). If you provide a value for this argument, then the scan is slower, but the system is more responsive to other operations.
-
maxThreads (integer). Number of concurrent threads used to process a scan. The default value is 5. If resources are very slow to respond, increasing this number may increase scan throughput.
To change the values of these parameters, edit the corresponding Task Definition form. For more information, see Chapter 2, Waveset Forms, in Oracle Waveset 8.1.1 Deployment Reference.
Creating an Access Scan
-
Select Compliance -> Manage Access Scans.
-
Click New to display the Create New Access Scan page.
-
Assign a name to the access scan and add a description that is meaningful in identifying the scan (optional).
Note –Access scan names must not contain these characters:
apostrophe (’), period (.), pipe (|), left bracket ([), right bracket (]), comma (,), colon (:), dollar sign ($), double quote (“), backslash (\), or equals sign (=)
Also, avoid using these characters: underscore (_), percent-sign (%), caret (^), and asterisk (*).
-
Enable the Dynamic entitlements option to give attestors additional options.
These options include:
-
A pending attestation can be immediately re-scanned to refresh the entitlement data and reevaluate the need for attestation.
-
A pending attestation can be routed to another user for remediation. Following remediation, the entitlement data is refreshed and reevaluated to determine the need for attestation.
-
-
Specify the User Scope Type (Required).
Choose from the following options:
-
According to attribute condition rule. Scan users according to a selected User Scope Rule.
Waveset provides these default rules:
-
All Administrators
Note –You can add user scoping rules by using the Identity Manager IDE. For information about the Identity Manager IDE, go to https://identitymanageride.dev.java.net/.
-
All My Reports
-
All Non-Administrators
-
My Direct Reports
-
Users without a Manager
-
-
Assigned to resources. Scan all users that have an account on one or more selected resources. When you choose this option, the page displays the User Scope Resources, which lets you specify resources.
-
According to a specific role. Scan all members who have at least one role, or who have all the roles, that you specify.
-
Members of Organizations. Choose this option to scan all members of one or more selected organizations.
-
Reports to managers. Scan all users reporting to selected managers. Manager hierarchy is determined by the Waveset attribute of the user’s Lighthouse account.
If the user scope is organization or manager, then the Recursive Scope option is available. This option allows for user selection to occur recursively through the chain of controlled members.
-
-
If you also want to scan audit policies to detect violations during the access review scan, select the audit policies to apply to this scan by moving your selections from Available Audit Policies to the Current Audit Policies list.
Adding audit policies to an access scan results in the same behavior as performing an audit scan over the same set of users. However, in addition, any violations detected by the audit policies are stored in the user entitlement record. This information can make automatic approval or rejection easier, because the rule can use the presence or absence of violations in the user entitlement record as part of its logic.
-
If you scanned audit policies in the preceding step, you can use the Policy mode option to specify how the access scan determines which audit policies to execute for a given user. A user can have policies assigned both at the user level and/or at the organization level. The default access scan behavior is to apply the policies specified for the access scan only if the user does not already have any assigned policies.
-
Apply select policies and ignore other assignments
-
Apply selected policies only if user does not already have assignments
-
Apply selected policies in addition to user assignments
-
-
(Optional) Use the Specify the Review Process Owner option to specify an owner of the access review task being defined. If a Review Process Owner is specified, then an attestor who encounters a potential conflict in responding to an attestation request can abstain in lieu of approving or rejecting a user entitlement and the attestation request is forwarded to the Review Process Owner. Click the selection (ellipsis) box to search the user accounts and make your selection.
-
Select the Follow delegation option to enable delegation for the access scan. The access scan will only honor delegation settings if this option is checked. Follow Delegation is enabled by default.
-
Select the Restrict target resources option to restrict scanning to targeted resources.
This setting has a direct bearing on the efficiency of the access scan. If target resources are not restricted, each user entitlement record will include account information for every resource the user is linked to. This means that during the scan every assigned resource is queried for each user. By using this option to specify a subset of the resources, you can greatly reduce the processing time required for Waveset to create user entitlement records.
-
Generally, do not enable the Execute Violation Remediation option except for advanced cases.
When enabled and a violation is detected for any of the assigned audit policies, Waveset executes the respective audit policy’s remediation workflow.
-
Select the Access Approval Workflow and specify the default Standard Attestation workflow or select a customized workflow if available.
This workflow is used to present the user entitlement record for review to the appropriate attestors (as determined by the attestor rule). The default Standard Attestation Workflow creates one work item for each attestor. If the access scan specifies escalation, this workflow is responsible for escalating work items that have been dormant too long. If no workflow is specified, the user attestation will remain in the pending state indefinitely.
Note –For more information about the Identity Auditor rules mentioned in this step and the following steps, see Chapter 4, Working with Rules, in Oracle Waveset 8.1.1 Deployment Reference.
-
Use the Attestor Rule option to specify the Default Attestor rule or to select a customized attestor rule if available.
The attestor rule is given the user entitlement record as input, and returns a list of attestor names. If Follow Delegation is selected, the access scan transforms the list of names to the appropriate users following the delegation information configured by each user in the original list of names. If an Waveset user’s delegation results in a routing cycle, then the delegation information is discarded, and the work item is delivered to the initial attestor. The Default Attestor rule indicates that the attestor should be the manager (idmManager) of the user that the entitlement record represents, or the Configurator account if that user’s idmManager is null. If attestation needs to involve resource owners as well as managers, you must use a custom rule.
-
Use the Attestor Escalation Rule option to specify the Default Escalation Attestor rule, or select a customized rule if available. You can also specify the Escalation Timeout value for the rule. The default escalation timeout value is 0 days.
This rule specifies the escalation chain for a work item that has passed the Escalation Timeout period. The Default Escalation Attestor rule escalates to the assigned attestor’s manager (idmManager), or to Configurator if the attestor’s idmManager value is null.
You can specify the Escalation Timeout value in minutes, hours, or days.
The book contains additional information about the Attestor Escalation Rule.
-
Specify a Review Determination Rule. (Required)
Select one of the following rules to specify how the scan process will determine the disposition of an entitlement record:
-
Reject Changed Users. Automatically rejects a user entitlement record if it is different than the last user entitlement from the same access scan definition and the last user entitlement was approved. Otherwise, forces manual attestation and approves all user entitlements that are unchanged from the previously approved user entitlement. By default, only the “accounts” portion of the user view is compared for this rule.
-
Review Changed Users. Forces manual attestation for any user entitlement record if it is different than the last user entitlement from the same access scan definition and the last user entitlement was approved. Approves all user entitlements that are unchanged from the previously approved user entitlement. By default, only the “accounts” portion of the user view is compared for this rule.
-
Review Everyone. Forces manual attestation for all user entitlement records.
The Reject Changed Users and Review Changed Users rules compare the user entitlement to the last instance of the same access scan in which the entitlement record was approved.
You can change this behavior by copying and modifying the rules to restrict comparison to any selected part of the user view.
This rule can return the following values:
-
-1. No attestation required
-
0. Automatically rejects the attestation
-
1. Manual attestation required
-
2. Automatically approves the attestation
-
3. Automatically remediates the attestation (auto-remediation)
The book contains additional information about the Review Determination Rule.
-
-
Select a Remediator Rule to determine who should remediate a specific user’s entitlement in the event of Auto-Remediation. The rule can examine the user’s current user entitlement and violations, and must return a list of users that should remediate. If no rule is specified, then no remediation will take place. A common use for this rule would be if the entitlement has compliance violations.
-
Select a Remediation User Form Rule that determines an appropriate form for attestation remediators when editing users. Remediators can set their own form, which overrides this one. This form rule would be set if the scan collects very specific data that matches a custom form.
-
Select one of the following Notification Workflow options to specify the notification behavior for each work item.
-
None (Default). This selection results in an attestor getting an email notification for each individual user entitlement that he must attest.
-
ScanNotification. This selection bundles attestation requests into a single notification. The notification indicates how many attestation requests were assigned to the recipient.
If there is a Review Process Owner specified in the access scan, the ScanNotification Workflow will also send a notification to the review process owner when the scan begins, and when it ends. See Creating an Access Scan.
The ScanNotification workflow uses the following email templates:
-
Access Scan Begin Notice
-
Access Scan End Notice
-
Bulk Attestation Notice
You can customize the ScanNotification Workflow.
-
-
-
Use the Violation limit option to specify the maximum number of compliance violations that can be emitted by this scan before the scan aborts. The default limit is 1000. An empty value field is equal to no limit.
Although typically during an audit scan or access scan the number of policy violations is small compared to the number of users, setting this value could provide protection from the impact of a defective policy that increases the number of violations significantly. For example, consider the following scenario:
If an access scan involves 50,000 users and generates two to three violations per user, the cost of remediation for each compliance violation can have a detrimental effect on the Waveset system.
-
Select the Organizations to which this access scan object is available. (Required).
-
Click Save to save the scan definition.
To define an access review scan, perform the following steps:
Deleting an Access Scan
You can delete one or more access scans. To delete an access scan, from the Compliance tab select Manage Access Scans, select the name of the scan, and then click Delete.
Managing Access Reviews
After defining an access scan, you can use or schedule it as part of an access review. After initiating an access review, several options are available to manage the review process.
Read the following sections for more information about:
Launching an Access Review
To launch an access review from the Administrator interface, use one of these methods:
-
Click Launch Review from the Compliance -> Access Reviews page.
-
Select the Access Review task in the Server Tasks -> Run Tasks page.
On the displayed Launch Task page, specify a name for the access review. Select the scans from the Available Access Scans list and move them to the Selected list.
If you select more than one scan, you can choose one of the following launch options:
-
immediately. This option starts running the scan immediately upon clicking the Launch button. If you select this option for multiple scans in the launch task, then the scans will run in parallel.
-
after waiting. This option allows you to specify a period of time to wait before launching the scan, relative to the launch of the access review task.
Note –
You can initiate more than one scan during an access review session. However, consider that each scan may involve a large number of users, and therefore the scan process can take many hours to complete. Best practice dictates that you manage your scans accordingly. For example, you might launch one scan to run immediately and schedule other scans at staggered intervals.
Click Launch to start the access review process.
Note –
The name you assign to an access review is important. Access reviews that run on a periodic basis with the same name can be compared by some reports.
When you launch an access review, the workflow process diagram is displayed, showing the steps in the process.
Scheduling Access Review Tasks
An access review task can be scheduled from the Server Tasks area. For example to set up access reviews on a periodic basis, select Manage Schedule and then define the schedule. You might schedule the task to occur every month or every quarter.
To define the schedule, select the Access Review task on the Schedule Tasks page and then complete the information on the Create task schedule page.
Click Save to save the scheduled task.
Note –
Waveset keeps the results from access review tasks for one week, by default. If you choose to schedule a review more often than once a week, set the Results Options to delete. If Results Options are not set to delete, the new review will not run because the previous task results still exist.
Managing Access Review Progress
Use the Access Reviews tab to monitor the progress of an access review. Access this feature through the Compliance tab.
From the Access Reviews tab you can review a summary of all active and previously processed access reviews. The following information is provided for each access review listed:
-
Status. Current status of the review process: initializing, terminating, terminated, number of scans in progress, number of scans scheduled, awaiting attestations, or completed.
-
Launch Date. The date (timestamp) the access review task started.
-
Total Users. Total number of users to be scanned.
-
Entitlements details. Additional columns in the table provide entitlement totals by status. These include details for pending, approved, rejected, terminated, and remediated entitlements, as well as total entitlements.
The Remediated column indicates the number of entitlements currently in the REMEDIATING state. After an entitlement is remediated, it goes to the PENDING state; therefore, at the conclusion of an access review, the value of this column is zero.
To view more detailed information about the review, select it to open a summary report.
Figure 15–4 shows a sample Access Review Summary report.
Figure 15–4 Access Review Summary Report Page
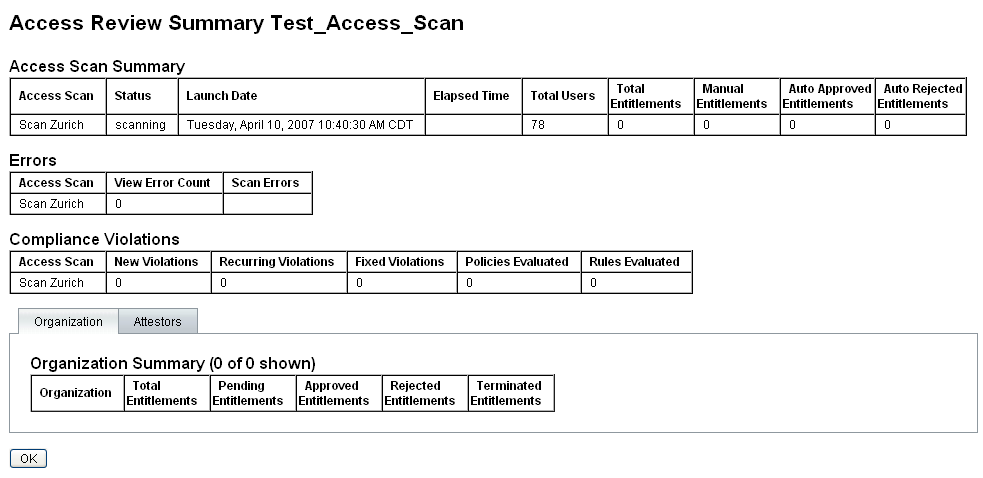
Click the Organization or Attestors form tab to view scan information categorized by those objects.
You can also review and download this information in a report by running the Access Review Summary Report.
Modifying Scan Attributes
After setting up an access scan, you can edit the scan to specify new options, such as specifying target resources to scan or specifying audit policies to scan for violations while the access scan is running.
To edit a scan definition, select it from the list of Access Scans, and then modify the attributes on the Edit Access Review Scan page.
You must click Save to save any changes to the scan definition.
Note –
Changing the scope of an access scan might change the information in newly-acquired user entitlement records, as it can affect the Review Determination Rule if that rule compares user entitlements to older user entitlement records.
Canceling an Access Review
From the Access Reviews page, click Terminate to stop a selected review in progress.
Terminating a review causes these actions to occur:
-
Any scheduled scans are unscheduled
-
Any active scans are halted
-
All pending workflows and work items are deleted
-
All pending attestations are marked canceled
-
Any attestations that users completed are left unchanged
Deleting an Access Review
From the Access Reviews page, click Delete to delete a selected review.
You can delete an access review if the status of the task is terminated or completed. An access review task in progress cannot be deleted unless it is first terminated.
Deleting an access review deletes all user entitlement records that were generated by the review. The delete action is recorded in the audit log.
To delete an access review, click Delete from the Access Reviews page.
Note –
Canceling and deleting an access review may result in updates to a large number of Waveset objects and tasks, and can take several minutes to complete. You can check the progress of the operation by viewing the task results in Sever Tasks -> All Tasks.
Managing Attestation Duties
You can manage attestation requests from the Waveset Administrator or User interface. This section provides information about responding to attestation requests and the duties involved in attestation.
Access Review Notification
During a scan, Waveset sends notification to Attestors when attestation requests require their approval. If attestor responsibilities have been delegated, the requests are sent to the delegate. If multiple attestors are defined, each attestor receives an email notification.
Requests appear as Attestation work items in the Waveset interface. Pending attestation work items are displayed when the assigned attestor logs in to Waveset.
Viewing Pending Attestation Requests
View attestation work items from the Work Items area of the interface. Selecting the Attestation tab in the Work Items area lists all the entitlement records requiring approval. From the Attestations page, you can also list entitlement records for all of your direct reports and for specified users for which you have direct or indirect control.
Acting on Entitlement Records
Attestation work items contain the user entitlement records requiring review. Entitlement records provide information about user access privileges, assigned resources, and policy violations.
The following are possible responses to an attestation request:
-
Approve. Attests that the entitlement is appropriate as of the date recorded in the entitlement record.
-
Reject. The entitlement record indicates possible discrepancies that cannot be currently validated or remediated.
-
Rescan. Requests a rescan to re-evaluate the user entitlement.
-
Forward. Enables you to specify another recipient for review.
-
Abstain. Attestation for this record is not appropriate, and a more appropriate attestor is not known. The attestation work item is forwarded to the Review Process Owner. This option is available only if a Review Process Owner has been defined in the Access Review task.
If an attestor does not respond to a request by taking one of these actions before the specified escalation timeout period, notice is sent to the next attestor in the escalation chain. The notification process continues until a response is logged.
Attestation status can be monitored from the Compliance -> Access Reviews tab.
Closed-Loop Remediation
You can avoid rejecting user entitlements by:
-
Marking an entitlement as needing to be fixed by requesting a fix from another user (Request Remediation). In this case, a new remediation work item is created and assigned to one or more specified remediators.
The new remediator can then choose to edit the user, either by using Waveset or independently, and then mark the work item as remediated when satisfied. At that point, the user entitlement is rescanned and evaluated again.
-
Requesting a reevaluation of the entitlement (Rescan). In this case, the user entitlement is rescanned and evaluated again. The original attestation work item is closed. A new attestation work item is created if the entitlement still requires attestation according to the rules defined in the access scan.
Requesting Remediation
If defined by the access scan, you can route a pending attestation to another user for remediation.
Note –
The Dynamic Entitlements option on the Create or Edit Access Scan pages enables this feature.
 To Request Remediation From Another User
To Request Remediation From Another User
-
Select one or more entitlements from the list of attestations, and then click Request Remediation.
The Select and Confirm to Request Remediation page appears.
-
Enter a user name, and then click Add to add the user to the Forward to field. Alternatively, click ... (More) to search for a user. Select the user in the search list, and then click Add to add the user to the Forward to list. Click Dismiss to close the Search area.
-
Enter comments in the Comments field, and then click Proceed.
Waveset returns to the list of attestations.
Note –Details of the remediation request appear in the History area of the individual user entitlement.
Rescanning Attestations
If defined by the access scan, you can rescan and reevaluate a pending attestation.
Note –
The Dynamic Entitlements option on the Create or Edit Access Scan pages enables this feature.
 To Rescan A Pending Attestation
To Rescan A Pending Attestation
-
Select one or more entitlements from the list of attestations, and then click Rescan.
The Rescan User Entitlements page appears.
-
Enter comments about the rescan action in the Comments area, and then click Proceed.
Forwarding Attestation Work Items
You can forward one or more attestation work items to another user.
 To Forward Attestations
To Forward Attestations
-
Select one or more work items in the attestation list, and then click Forward.
The Select and Confirm Forwarding page appears.
-
Enter a user name in the Forward to field. Alternatively, click ... (More) to search for a user name.
-
Enter comments about the forwarding action in the Comments field.
-
Click Proceed.
Waveset returns to the list of attestations.
Note –Details of the forwarding action appear in the History area of the individual user entitlement.
Digitally Signing Access Review Actions
You can set up digital signing to handle access review actions. For information about configuring digital signatures, see Signing Approvals. The topics discussed there explain the server-side and client-side configuration required to add the certificate and CRL to Waveset for signed approvals.
Access Review Reports
Waveset provides the following reports that you can use to evaluate the results of an access review:
-
Access Review Coverage Report. Provides a list of users with user entitlement overlaps, differences, or both in table format, depending on how the report is defined. This report might also contain additional columns that show which access reviews contain overlaps and/or differences.
-
Access Review Detail Report. This report provides the following information, in table format:
-
Name. Name of user entitlement record
-
Status. Current status of the review process: initializing, terminating, terminated, number of scans in progress, number of scans scheduled, awaiting attestation, or completed
-
Attestor. Waveset users assigned as the attestor for the record
-
Scan Date. Timestamp recorded for when the scan occurred
-
Disposition Date. Date (timestamp) when entitlement record was attested
-
Organization. Organization of user in the entitlement records
-
Manager. Manager of a scanned user
-
Resources. Resources the user has accounts on that were captured in this user entitlement
-
Violations. Number of violations detected during the review
-
Click a name in the report to open the user entitlement record. Access Review Reports shows a sample of the information provided in the user entitlement record view.
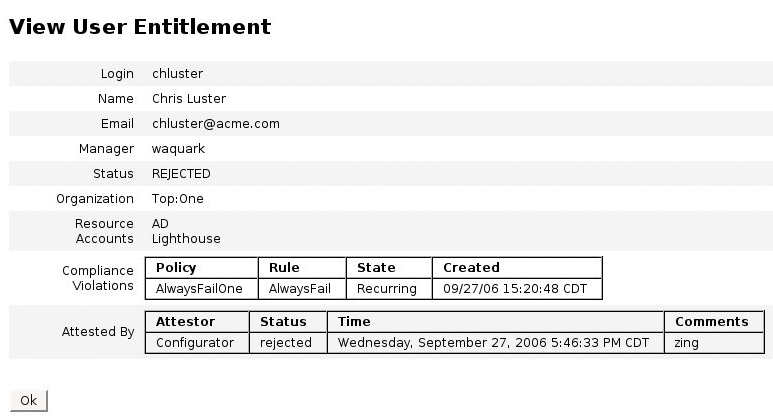
-
-
Access Review Summary Report.
This report, also discussed in Managing Access Review Progress and illustrated in Figure 15–4, shows the following summary information about the access scans you select for the report:
-
Review Name. Name of the access scan
-
Date. Timestamp for when the review was launched
-
User Count. Number of users scanned for the review
-
Entitlement Count. Number of entitlement records generated
-
Approved. Number of entitlement records approved
-
Rejected. Number of entitlement records rejected
-
Pending. Number of entitlement records still pending
-
Canceled. Number of entitlement records canceled
These reports are available for download, in Portable Document Format (PDF) or comma-separated value (CSV) format, from the Run Reports page.
-
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
