第 14 章 資源管理の構成例
この章では、資源管理のフレームワークについて考察し、仮想的なサーバー統合プロジェクトについて説明します。
この章の内容は次のとおりです。
統合前の構成
この例では、5 つのアプリケーションを 1 つのシステムに統合します。対象となるアプリケーションは、それぞれ資源要件、ユーザー数、およびアーキテクチャーが異なります。現在、各アプリケーションは、それぞれの要件を満たす専用サーバーに置かれています。次の表にアプリケーションとその特性を示します。
|
アプリケーション |
特性 |
|---|---|
|
アプリケーションサーバー |
2 CPU を超えるとスケーラビリティーが低くなります |
|
アプリケーションサーバー用のデータベースインスタンス |
負荷の高いトランザクション処理 |
|
テストおよび開発環境用のアプリケーションサーバー |
GUI に基づいたコードテスト |
|
トランザクション処理サーバー |
応答時間を保証します |
|
スタンドアロンのデータベースインスタンス |
大量のトランザクションを処理し、複数のタイムゾーンに対してサービスを提供します |
統合後の構成
次の構成を使用して、アプリケーションを 1 つのシステムに統合します。
-
アプリケーションサーバーは、2 つの CPU から構成されるプロセッサセットを持ちます。
-
アプリケーションサーバーのデータベースインスタンスとスタンドアロンのデータベースインスタンスは、4 つ以上の CPU から構成される 1 つのプロセッサセットに統合されます。スタンドアロンのデータベースインスタンスはその資源の 75% が保証されます。
-
テストおよび開発用のアプリケーションサーバーには IA スケジューリングクラスを適用して、UI の応答性を保証します。メモリーを制約して、不正なコードによる影響を低減します。
-
トランザクション処理サーバーには 2 つ以上の CPU から構成される専用のプロセッサセットを割り当てて、応答時間を短縮します。
この構成の対象には、各資源セットのプロセッササイクルを消費している実行中の既知のアプリケーションすべてが含まれます。したがって、プロセッサ資源を必要としているセットにプロセッサ資源をセット間で転送できるように、次のような制約を設定します。
-
wt-load 目標を設定して、使用率の高い資源セットに、より多くの資源を割り当てるようにします。
-
locality 目標を tight に設定して、プロセッサの近傍性が最大になるようにします。
また、どの資源セットについても使用率が 80% を超えないようにする制約も適用します。この制約により、アプリケーションは必要な資源に確実にアクセスできます。さらに、トランザクション処理のプロセッサセットについては、使用率を 80% 以下に保つという目標の重要性を、ほかの目標の 2 倍にします。この重要性は構成で定義します。
構成の作成
/etc/project データベースファイルを編集します。エントリを追加して必要な資源制御を実装し、ユーザーを資源プールにマップしたら、ファイルを表示します。
# cat /etc/project . . . user.app_server:2001:Production Application Server:::project.pool=appserver_pool user.app_db:2002:App Server DB:::project.pool=db_pool;project.cpu-shares=(privileged,1,deny) development:2003:Test and development::staff:project.pool=dev_pool; process.max-address-space=(privileged,536870912,deny)keep with previous line user.tp_engine:2004:Transaction Engine:::project.pool=tp_pool user.geo_db:2005:EDI DB:::project.pool=db_pool;project.cpu-shares=(privileged,3,deny) . . . |
注 –
開発チームはタスクを開発プロジェクトで実行する必要があります。これは、このプロジェクトへのアクセスをユーザーのグループ ID (GID) で制限しているためです。
pool.host という名前で入力ファイルを作成し、必要な資源プールの構成に使用します。次に、ファイルを表示します。
# cat pool.host create system host create pset dev_pset (uint pset.min = 0; uint pset.max = 2) create pset tp_pset (uint pset.min = 2; uint pset.max=8) create pset db_pset (uint pset.min = 4; uint pset.max = 6) create pset app_pset (uint pset.min = 1; uint pset.max = 2) create pool dev_pool (string pool.scheduler="IA") create pool appserver_pool (string pool.scheduler="TS") create pool db_pool (string pool.scheduler="FSS") create pool tp_pool (string pool.scheduler="TS") associate pool dev_pool (pset dev_pset) associate pool appserver_pool (pset app_pset) associate pool db_pool (pset db_pset) associate pool tp_pool (pset tp_pset) modify system tester (string system.poold.objectives="wt-load") modify pset dev_pset (string pset.poold.objectives="locality tight; utilization < 80") modify pset tp_pset (string pset.poold.objectives="locality tight; 2: utilization < 80") modify pset db_pset (string pset.poold.objectives="locality tight;utilization < 80") modify pset app_pset (string pset.poold.objectives="locality tight; utilization < 80") |
pool.host 入力ファイルを使って構成を更新します。
# poolcfg -f pool.host |
構成をアクティブにします。
# pooladm -c |
システム上でフレームワークが有効になっています。
構成の表示
フレームワークの構成には、システムによって作成されたデフォルトの要素も含まれています。この構成を表示するには、次のように入力します。
# pooladm
system host
string system.comment
int system.version 1
boolean system.bind-default true
int system.poold.pid 177916
string system.poold.objectives wt-load
pool dev_pool
int pool.sys_id 125
boolean pool.default false
boolean pool.active true
int pool.importance 1
string pool.comment
string pool.scheduler IA
pset dev_pset
pool appserver_pool
int pool.sys_id 124
boolean pool.default false
boolean pool.active true
int pool.importance 1
string pool.comment
string pool.scheduler TS
pset app_pset
pool db_pool
int pool.sys_id 123
boolean pool.default false
boolean pool.active true
int pool.importance 1
string pool.comment
string pool.scheduler FSS
pset db_pset
pool tp_pool
int pool.sys_id 122
boolean pool.default false
boolean pool.active true
int pool.importance 1
string pool.comment
string pool.scheduler TS
pset tp_pset
pool pool_default
int pool.sys_id 0
boolean pool.default true
boolean pool.active true
int pool.importance 1
string pool.comment
string pool.scheduler TS
pset pset_default
pset dev_pset
int pset.sys_id 4
string pset.units population
boolean pset.default false
uint pset.min 0
uint pset.max 2
string pset.comment
boolean pset.escapable false
uint pset.load 0
uint pset.size 0
string pset.poold.objectives locality tight; utilization < 80
pset tp_pset
int pset.sys_id 3
string pset.units population
boolean pset.default false
uint pset.min 2
uint pset.max 8
string pset.comment
boolean pset.escapable false
uint pset.load 0
uint pset.size 0
string pset.poold.objectives locality tight; 2: utilization < 80
cpu
int cpu.sys_id 1
string cpu.comment
string cpu.status on-line
cpu
int cpu.sys_id 2
string cpu.comment
string cpu.status on-line
pset db_pset
int pset.sys_id 2
string pset.units population
boolean pset.default false
uint pset.min 4
uint pset.max 6
string pset.comment
boolean pset.escapable false
uint pset.load 0
uint pset.size 0
string pset.poold.objectives locality tight; utilization < 80
cpu
int cpu.sys_id 3
string cpu.comment
string cpu.status on-line
cpu
int cpu.sys_id 4
string cpu.comment
string cpu.status on-line
cpu
int cpu.sys_id 5
string cpu.comment
string cpu.status on-line
cpu
int cpu.sys_id 6
string cpu.comment
string cpu.status on-line
pset app_pset
int pset.sys_id 1
string pset.units population
boolean pset.default false
uint pset.min 1
uint pset.max 2
string pset.comment
boolean pset.escapable false
uint pset.load 0
uint pset.size 0
string pset.poold.objectives locality tight; utilization < 80
cpu
int cpu.sys_id 7
string cpu.comment
string cpu.status on-line
pset pset_default
int pset.sys_id -1
string pset.units population
boolean pset.default true
uint pset.min 1
uint pset.max 4294967295
string pset.comment
boolean pset.escapable false
uint pset.load 0
uint pset.size 0
cpu
int cpu.sys_id 0
string cpu.comment
string cpu.status on-line
|
フレームワークのグラフィック表示が続きます。
図 14–1 サーバー統合の構成
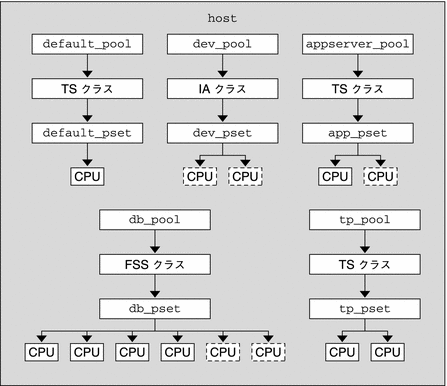
注 –
上記の図のプール db_pool では、スタンドアロンのデータベースインスタンスに CPU 資源の 75% が保証されています。
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
