Storing Configuration and Security Information in the /etc/netboot Hierarchy
The /etc/netboot directory contains the configuration information, private key, digital certificate, and certificate authority that are required for a WAN boot installation. This section describes the files and directories you can create in the /etc/netboot directory to customize your WAN boot installation.
Customizing the Scope of the WAN Boot Installation
During the installation, the wanboot-cgi program searches for the client information in the /etc/netboot directory on the WAN boot server. The wanboot-cgi program converts this information into the WAN boot file system, and then transmits the WAN boot file system to the client. You can create subdirectories within the /etc/netboot directory to customize the scope of the WAN installation. Use the following directory structures to define how configuration information is shared among the clients that you want to install.
-
Global configuration – If you want all the clients on your network to share configuration information, store the files that you want to share in the /etc/netboot directory.
-
Network-specific configuration – If you want only those machines on a specific subnet to share configuration information, store the configuration files that you want to share in a subdirectory of /etc/netboot. Have the subdirectory follow this naming convention.
/etc/netboot/net-ip
In this example, net-ip is the IP address of the client's subnet. For example, if you want all systems on the subnet with the IP address of 192.168.255.0 to share configuration files, create a /etc/netboot/192.168.255.0 directory. Then, store the configuration files in this directory.
-
Client-specific configuration – If you want only a specific client to use the boot file system, store the boot file system files in a subdirectory of /etc/netboot. Have the subdirectory follow this naming convention.
/etc/netboot/net-ip/client-ID
In this example, net-ip is the IP address of the subnet. client-ID is either the client ID that is assigned by the DHCP server, or a user-specified client ID. For example, if you want a system with the client ID 010003BA152A42 on the subnet 192.168.255.0 to use specific configuration files, create a /etc/netboot/192.168.255.0/010003BA152A42 directory. Then, store the appropriate files in this directory.
Specifying Security and Configuration Information in the /etc/netboot Directory
You specify the security and configuration information by creating the following files and storing the files in the /etc/netboot directory.
-
wanboot.conf – This file specifies the client configuration information for a WAN boot installation.
-
System configuration file (system.conf) – This system configuration file specifies the location of the client's sysidcfg file and custom JumpStart files.
-
keystore – This file contains the client's HMAC SHA1 hashing key, 3DES or AES encryption key, and SSL private key.
-
truststore – This file contains the digital certificates of certificate signing authorities that the client should trust. These trusted certificates instruct the client to trust the server during the installation.
-
certstore – This file contains the client's digital certificate.
Note –The certstore file must be located in the client ID directory. See Customizing the Scope of the WAN Boot Installation for more information about subdirectories of the /etc/netboot directory.
For detailed instructions on how to create and store these files, see the following procedures.
Sharing Security and Configuration Information in the /etc/netboot Directory
To install clients on your network, you might want to share security and configuration files among several different clients, or across entire subnets. You can share these files by distributing your configuration information throughout the /etc/netboot/net-ip/client-ID, /etc/netboot/net-ip, and /etc/netboot directories. The wanboot-cgi program searches these directories for the configuration information that best fits the client, and uses that information during the installation.
The wanboot-cgi program searches for client information in the following order.
-
/etc/netboot/net-ip/client-ID – The wanboot-cgi program first checks for configuration information that is specific to the client machine. If the /etc/netboot/net-ip/client-ID directory contains all the client configuration information, the wanboot-cgi program does not check for configuration information elsewhere in the /etc/netboot directory.
-
/etc/netboot/net-ip – If all the required information is not located in the /etc/netboot/net-ip/client-ID directory, the wanboot-cgi program then checks for subnet configuration information in the /etc/netboot/net-ip directory.
-
/etc/netboot – If the remaining information is not located in the /etc/netboot/net-ip directory, the wanboot-cgi program then checks for global configuration information in the /etc/netboot directory.
Figure 10–2 demonstrates how you can set up the /etc/netboot directory to customize your WAN boot installations.
Figure 10–2 Sample /etc/netboot Directory
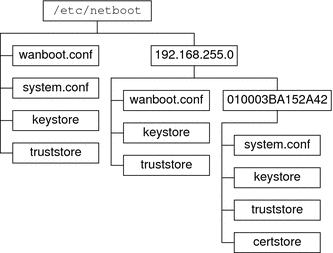
The /etc/netboot directory layout in Figure 10–2 enables you to perform the following WAN boot installations.
-
When you install the client 010003BA152A42, the wanboot-cgi program uses the following files in the /etc/netboot/192.168.255.0/010003BA152A42 directory.
-
system.conf
-
keystore
-
truststore
-
certstore
The wanboot-cgi program then uses the wanboot.conf file in the /etc/netboot/192.168.255.0 directory.
-
-
When you install a client that is located on the 192.168.255.0 subnet, the wanboot-cgi program uses the wanboot.conf, keystore, and truststore files in the /etc/netboot/192.168.255.0 directory. The wanboot-cgi program then uses the system.conf file in the /etc/netboot directory.
-
When you install a client machine that is not located on the 192.168.255.0 subnet, the wanboot-cgi program uses the following files in the /etc/netboot directory.
-
wanboot.conf
-
system.conf
-
keystore
-
truststore
-
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
