第 5 章 软件包创建案例研究
本章提供了案例研究以展示打包方案,例如有条件地安装对象、在运行时确定要创建的文件数,以及在软件包安装和删除期间修改现有数据文件。
每个案例研究都以一段描述开始,然后介绍采用的打包技术的列表、使用这些技术时采取的方法,以及与案例研究相关的样例文件和脚本。
以下是本章中案例研究的列表:
请求来自管理员的输入
在此案例研究中,软件包有三种类型的对象。管理员可以选择安装哪一种对象类型,并选择对象在安装计算机上的位置。
技术
此案例研究展示以下技术:
-
有关参数化路径名的信息,请参见参数化路径名。
-
使用 request 脚本请求来自管理员的输入
有关 request 脚本的信息,请参见编写 request 脚本。
-
为安装参数设置条件值。
方法
要在此案例研究中设置选择性安装,您必须完成以下任务:
-
为每种可安装对象的类型定义一个类。
在此案例研究中,三种对象类型是:软件包可执行文件、手册页和 emacs 可执行文件。每种类型都有其自己的类: 分别是 bin、man 和 emacs。请注意在 prototype 文件中,所有对象文件均属于这三个类之一。
-
在 pkginfo 文件中将 CLASSES 参数初始化为 null。
通常在定义类时,应该在 pkginfo 文件的 CLASSES 参数中列出该类。否则,不会安装属于该类的任何对象。对于此案例研究,参数最初设置为 null,意味着不会安装任何对象。 CLASSES 参数将由 request 脚本根据管理员的选择进行更改。这样,CLASSES 参数会仅设置为管理员希望安装的那些对象类型。
注 –通常可取的方法是将参数设置为缺省值。如果此软件包有对所有三种对象类型通用的组件,可以将其指定给 none 类,然后将 CLASSES 参数设置为等于 none。
-
将参数化路径名插入到 prototype 文件。
request 脚本会将这些环境变量设置为管理员提供的值。然后,pkgadd 命令在安装时解析这些环境变量,从而知道软件包的安装位置。
此示例中使用的三个环境变量在 pkginfo 文件中设置为其缺省值,作用如下:
-
$NCMPBIN 定义对象可执行文件的位置
-
$NCMPMAN 定义手册页的位置
-
$EMACS 定义 emacs 可执行文件的位置
prototype 示例文件显示了如何定义含变量的对象路径名。
-
-
创建 request 脚本,用于询问管理员应该安装软件包的哪些部分及其放置位置。
此软件包的 request 脚本会询问管理员两个问题:
-
是否应该安装软件包的此部分?
当答复为是时,相应的类名被添加到 CLASSES 参数。例如,当管理员选择安装与此软件包关联的手册页时,类 man 将会添加到 CLASSES 参数。
-
如果是,应该将软件包的此部分放置在什么位置?
此时将设置相应的环境变量来响应此问题。在手册页示例中,变量 $NCMPMAN 设置为响应值。
对于三种对象类型的每种类型都会重复这两个问题。
在 request 脚本的末尾,参数将设置为对 pkgadd 命令和所有其他打包脚本的安装变量可用。request 脚本通过将这些定义写入调用实用程序提供的文件来实现这一点。对于此案例研究,没有提供其他脚本。
当查看此案例研究的 request 脚本时,请注意,上述问题由数据验证工具 ckyorn 和 ckpath 生成。有关这些工具的更多信息,请参见 ckyorn(1) 和 ckpath(1)。
-
案例研究文件
pkginfo 文件
PKG=ncmp NAME=NCMP Utilities CATEGORY=application, tools BASEDIR=/ ARCH=SPARC VERSION=RELEASE 1.0, Issue 1.0 CLASSES="" NCMPBIN=/bin NCMPMAN=/usr/man EMACS=/usr/emacs |
prototype 文件
i pkginfo i request x bin $NCMPBIN 0755 root other f bin $NCMPBIN/dired=/usr/ncmp/bin/dired 0755 root other f bin $NCMPBIN/less=/usr/ncmp/bin/less 0755 root other f bin $NCMPBIN/ttype=/usr/ncmp/bin/ttype 0755 root other f emacs $NCMPBIN/emacs=/usr/ncmp/bin/emacs 0755 root other x emacs $EMACS 0755 root other f emacs $EMACS/ansii=/usr/ncmp/lib/emacs/macros/ansii 0644 root other f emacs $EMACS/box=/usr/ncmp/lib/emacs/macros/box 0644 root other f emacs $EMACS/crypt=/usr/ncmp/lib/emacs/macros/crypt 0644 root other f emacs $EMACS/draw=/usr/ncmp/lib/emacs/macros/draw 0644 root other f emacs $EMACS/mail=/usr/ncmp/lib/emacs/macros/mail 0644 root other f emacs $NCMPMAN/man1/emacs.1=/usr/ncmp/man/man1/emacs.1 0644 root other d man $NCMPMAN 0755 root other d man $NCMPMAN/man1 0755 root other f man $NCMPMAN/man1/dired.1=/usr/ncmp/man/man1/dired.1 0644 root other f man $NCMPMAN/man1/ttype.1=/usr/ncmp/man/man1/ttype.1 0644 root other f man $NCMPMAN/man1/less.1=/usr/ncmp/man/man1/less.1 0644 inixmr other |
request 脚本
trap 'exit 3' 15 # determine if and where general executables should be placed ans=`ckyorn -d y \ -p "Should executables included in this package be installed" ` || exit $? if [ "$ans" = y ] then CLASSES="$CLASSES bin" NCMPBIN=`ckpath -d /usr/ncmp/bin -aoy \ -p "Where should executables be installed" ` || exit $? fi # determine if emacs editor should be installed, and if it should # where should the associated macros be placed ans=`ckyorn -d y \ -p "Should emacs editor included in this package be installed" ` || exit $? if [ "$ans" = y ] then CLASSES="$CLASSES emacs" EMACS=`ckpath -d /usr/ncmp/lib/emacs -aoy \ -p "Where should emacs macros be installed" ` || exit $? fi |
请注意,request 脚本可以在不在文件系统上留下任何文件的情况下退出。对于 2.5 和兼容版本之前的 Solaris 版本上的安装(其中没有 checkinstall 脚本可用),request 脚本是以确保安装成功所需的任何方式测试文件系统的正确位置。当 request 脚本以代码 1 退出时,安装将完全退出。
这些示例文件显示了使用参数化路径建立多个基目录。然而,首选的方法涉及使用由 pkgadd 命令管理并验证的 BASEDIR 参数。每当使用多个基目录时,在同一个平台上安装多个版本和体系结构时应格外小心。
在安装时创建文件并在删除期间保存文件
在此案例研究中,将在安装时创建一个数据库文件,并在删除软件包时保存数据库副本。
技术
此案例研究展示以下技术:
-
使用类和类操作脚本对不同的对象集执行特殊操作
有关更多信息,请参见编写类操作脚本。
-
使用 space 文件通知 pkgadd 命令要正确安装此软件包需要额外空间
有关 space 文件的更多信息,请参见在目标系统上保留额外空间。
方法
要为此案例研究在安装时创建一个数据库文件,并在删除时保存副本,您必须完成以下任务:
-
定义三个类。
在此案例研究中,软件包要求在 CLASSES 参数中定义以下三个类:
-
标准类 none,该类包含一组属于子目录 bin 的进程。
-
admin 类,该类包含可执行文件 config 和一个包含数据文件的目录。
-
cfgdata 类,该类包含一个目录。
-
-
使软件包可共同重定位。
请注意在 prototype 文件中,没有路径名以斜线或环境变量开头,这表明它们是可共同重定位的。
-
计算数据库文件需要的空间量,并创建一个要随软件包一起提供的 space 文件。此文件通知 pkgadd 命令软件包需要额外空间并指定空间量。
-
为 admin 类创建类操作脚本 (i.admin)。
该样例脚本使用属于 admin 类的数据文件初始化数据库。要执行此任务,该脚本执行以下操作:
-
将源数据文件复制到相应目标位置
-
创建一个名为 config.data 的空文件,并将其指定给 cfgdata 类
-
执行 bin/config 命令(与软件包一起提供并已安装)以使用属于 admin 类的数据文件填充 config.data 数据库文件
-
执行 installf -f 命令完成 config.data 的安装
由于在删除时 admin 类不需要特殊操作,因此不会创建删除类操作脚本。这意味着 admin 类中的所有文件和目录都会从系统中删除。
-
-
为 cfgdata 类创建删除类操作脚本 (r.cfgdata)。
删除脚本会在删除数据库文件之前创建该文件的副本。由于在安装时此类不需要特殊操作,因此不需要安装类操作脚本。
切记删除脚本的输入是要删除的路径名的列表。路径名始终按反向字母顺序显示。此删除脚本将文件复制到名为 $PKGSAV 的目录。当所有路径名都被处理后,脚本会返回并删除与 cfgdata 类关联的所有目录和文件。
此删除脚本的结果是将 config.data 复制到 $PKGSAV,然后删除 config.data 文件和数据目录。
案例研究文件
pkginfo 文件
PKG=krazy NAME=KrAzY Applications CATEGORY=applications BASEDIR=/opt ARCH=SPARC VERSION=Version 1 CLASSES=none cfgdata admin |
prototype 文件
i pkginfo i request i i.admin i r.cfgdata d none bin 555 root sys f none bin/process1 555 root other f none bin/process2 555 root other f none bin/process3 555 root other f admin bin/config 500 root sys d admin cfg 555 root sys f admin cfg/datafile1 444 root sys f admin cfg/datafile2 444 root sys f admin cfg/datafile3 444 root sys f admin cfg/datafile4 444 root sys d cfgdata data 555 root sys |
space 文件
# extra space required by config data which is # dynamically loaded onto the system data 500 1 |
i.admin 类操作脚本
# PKGINST parameter provided by installation service # BASEDIR parameter provided by installation service while read src dest do cp $src $dest || exit 2 done # if this is the last time this script will be executed # during the installation, do additional processing here. if [ "$1" = ENDOFCLASS ] then # our config process will create a data file based on any changes # made by installing files in this class; make sure the data file # is in class `cfgdata' so special rules can apply to it during # package removal. installf -c cfgdata $PKGINST $BASEDIR/data/config.data f 444 root sys || exit 2 $BASEDIR/bin/config > $BASEDIR/data/config.data || exit 2 installf -f -c cfgdata $PKGINST || exit 2 fi exit 0 |
这里举例说明了一个很少见的实例,其中 installf 适用于类操作脚本。由于 space 文件用于在特定文件系统上保留空间,因此即使该新文件没有包括在 pkgmap 文件中也可以被安全地添加。
r.cfgdata 删除脚本
# the product manager for this package has suggested that # the configuration data is so valuable that it should be # backed up to $PKGSAV before it is removed! while read path do # path names appear in reverse lexical order. mv $path $PKGSAV || exit 2 rm -f $path || exit 2 done exit 0 |
定义软件包兼容性和相关性
在此案例研究中,软件包使用可选信息文件来定义软件包兼容性和相关性,以及在安装期间呈现版权新息。
技术
此案例研究展示以下技术:
-
使用 copyright 文件
-
使用 compver 文件
-
使用 depend 文件
有关这些文件的更多信息,请参见创建信息文件。
方法
要符合描述中的要求,您必须:
-
创建 copyright 文件。
copyright 文件包含版权信息的 ASCII 文本。样例文件中所示的信息将在软件包安装期间显示在屏幕上。
-
创建 compver 文件。
下图中显示的 pkginfo 文件将此软件包版本定义为 3.0 版。compver 文件将 3.0 版定义为与 2.3、2.2、2.1、2.1.1、2.1.3 和 1.7 版兼容。
-
创建 depend 文件。
安装软件包时 depend 文件中列出的文件必须已经安装在系统上。示例文件有 11 个软件包,安装时这些软件包必须已安装在系统上。
案例研究文件
pkginfo 文件
PKG=case3 NAME=Case Study #3 CATEGORY=application BASEDIR=/opt ARCH=SPARC VERSION=Version 3.0 CLASSES=none |
copyright 文件
Copyright (c) 1999 company_name All Rights Reserved. THIS PACKAGE CONTAINS UNPUBLISHED PROPRIETARY SOURCE CODE OF company_name. The copyright notice above does not evidence any actual or intended publication of such source code |
compver 文件
Version 3.0 Version 2.3 Version 2.2 Version 2.1 Version 2.1.1 Version 2.1.3 Version 1.7 |
depend 文件
P acu Advanced C Utilities Issue 4 Version 1 P cc C Programming Language Issue 4 Version 1 P dfm Directory and File Management Utilities P ed Editing Utilities P esg Extended Software Generation Utilities Issue 4 Version 1 P graph Graphics Utilities P rfs Remote File Sharing Utilities Issue 1 Version 1 P rx Remote Execution Utilities P sgs Software Generation Utilities Issue 4 Version 1 P shell Shell Programming Utilities P sys System Header Files Release 3.1 |
使用标准类和类操作脚本修改文件
在此案例研究中,使用标准类和类操作脚本在软件包安装期间修改现有文件。它使用三种修改方法之一。另外两种方法将在使用 sed 类和 postinstall 脚本修改文件和使用 build 类修改文件中进行介绍。修改的文件是 /etc/inittab。
技术
此案例研究展示如何使用安装类操作脚本和删除类操作脚本。有关更多信息,请参见编写类操作脚本。
方法
要使用类和类操作脚本在安装期间修改 /etc/inittab,您必须完成以下任务:
-
创建一个类。
创建名为 inittab 的类。必须为该类提供安装和删除类操作脚本。在 pkginfo 文件的 CLASSES 参数中定义 inittab 类。
-
创建一个 inittab 文件。
此文件包含将添加到 /etc/inittab 的条目的信息。请注意在 prototype 文件图中,inittab 是 inittab 类的成员并且文件类型为 e(表示可编辑)。
-
创建安装类操作脚本 (i.inittab)。
切记类操作脚本每次执行时都必须产生相同结果。类操作脚本执行以下过程:
-
检查以前是否已添加该条目
-
如果是,删除该条目的所有以前版本
-
编辑 inittab 文件并添加注释行,以便您知道该条目的来源
-
将临时文件移回 /etc/inittab
-
当收到 ENDOFCLASS 指示符时,执行 init q 命令
请注意,此安装脚本可执行 init q 命令。此方法不需要使用只有一行的 postinstall 脚本。
-
-
创建删除类操作脚本 (r.inittab)。
删除脚本与安装脚本非常类似。安装脚本添加的信息会被删除,而且会执行 init q 命令。
此案例研究比下一个更为复杂;请参见使用 sed 类和 postinstall 脚本修改文件。在此案例研究中,不是提供两个文件而是需要三个文件,而且提供的 /etc/inittab 文件实际上只是包含要插入的条目片段的占位符。此占位符可能已被放置到 i.inittab 文件中,除非 pkgadd 命令必须将一个文件传递到 i.inittab 文件。此外,必须将删除过程放置到一个单独的文件 (r.inittab) 中。虽然此方法效果很好,但最好将其保留为在涉及多个文件的非常复杂的安装情况下使用。请参见在安装期间修改 crontab 文件。
由于 inittab 条目末尾的注释基于软件包实例,因此使用 sed 类和 postinstall 脚本修改文件中使用的 sed 程序支持多个软件包实例。使用 build 类修改文件中的案例研究给出了一种在安装期间编辑 /etc/inittab 的更简化的方法。
案例研究文件
pkginfo 文件
PKG=case5 NAME=Case Study #5 CATEGORY=applications BASEDIR=/opt ARCH=SPARC VERSION=Version 1d05 CLASSES=inittab |
prototype 文件
i pkginfo i i.inittab i r.inittab e inittab /etc/inittab ? ? ? |
i.inittab 安装类操作脚本
# PKGINST parameter provided by installation service while read src dest do # remove all entries from the table that # associated with this PKGINST sed -e "/^[^:]*:[^:]*:[^:]*:[^#]*#$PKGINST$/d" $dest > /tmp/$$itab || exit 2 sed -e "s/$/#$PKGINST" $src >> /tmp/$$itab || exit 2 mv /tmp/$$itab $dest || exit 2 done if [ "$1" = ENDOFCLASS ] then /sbin/init q || exit 2 fi exit 0 |
r.inittab 删除类操作脚本
# PKGINST parameter provided by installation service while read src dest do # remove all entries from the table that # are associated with this PKGINST sed -e "/^[^:]*:[^:]*:[^:]*:[^#]*#$PKGINST$/d" $dest > /tmp/$$itab || exit 2 mv /tmp/$$itab $dest || exit 2 done /sbin/init q || exit 2 exit 0 |
inittab 文件
rb:023456:wait:/usr/robot/bin/setup |
使用 sed 类和 postinstall 脚本修改文件
此案例研究在软件包安装期间修改安装计算机上存在的一个文件。它使用三种修改方法之一。另外两种方法将在使用标准类和类操作脚本修改文件和使用 build 类修改文件中进行介绍。修改的文件是 /etc/inittab。
技术
此案例研究展示以下技术:
方法
要使用 sed 类在安装时修改 /etc/inittab,您必须完成以下任务:
-
将 sed 类脚本添加到 prototype 文件。
脚本的名称必须是将编辑文件的名称。在本例中,将编辑的文件是 /etc/inittab,因此 sed 脚本被命名为 /etc/inittab。对于 sed 脚本的模式、所有者和组没有要求(在样例 prototype 中由问号表示)。sed 脚本的文件类型必须是 e(表示可编辑)。
-
设置 CLASSES 参数以包括 sed 类。
如示例文件所示,sed 是待安装的唯一类。不过,类的数目可以是任意的。
-
创建 sed 类操作脚本。
您的软件包不能提供您希望的形式的 /etc/inittab 副本,因为 /etc/inittab 是一个动态文件,您无法知道它在软件包安装时的外观形式。不过,可使用 sed 脚本在软件包安装期间修改 /etc/inittab 文件。
-
创建 postinstall 脚本。
您需要执行 init q 命令通知系统 /etc/inittab 已被修改。在此示例中,您可以执行该操作的唯一位置是在 postinstall 脚本中。查看 postinstall 示例脚本,您会发现它的唯一作用是执行 init q 命令。
这种在安装期间编辑 /etc/inittab 的方法有一个缺点:虽然只是为了执行 init q 命令也必须提供一个完整的脚本(postinstall 脚本)。
案例研究文件
pkginfo 文件
PKG=case4 NAME=Case Study #4 CATEGORY=applications BASEDIR=/opt ARCH=SPARC VERSION=Version 1d05 CLASSES=sed |
prototype 文件
i pkginfo i postinstall e sed /etc/inittab ? ? ? |
sed 类操作脚本 (/etc/inittab)
!remove # remove all entries from the table that are associated # with this package, though not necessarily just # with this package instance /^[^:]*:[^:]*:[^:]*:[^#]*#ROBOT$/d !install # remove any previous entry added to the table # for this particular change /^[^:]*:[^:]*:[^:]*:[^#]*#ROBOT$/d # add the needed entry at the end of the table; # sed(1) does not properly interpret the '$a' # construct if you previously deleted the last # line, so the command # $a\ # rb:023456:wait:/usr/robot/bin/setup #ROBOT # will not work here if the file already contained # the modification. Instead, you will settle for # inserting the entry before the last line! $i\ rb:023456:wait:/usr/robot/bin/setup #ROBOT |
postinstall 脚本
# make init re-read inittab /sbin/init q || exit 2 exit 0 |
使用 build 类修改文件
此案例研究在软件包安装期间修改安装计算机上存在的一个文件。它使用三种修改方法之一。另外两种方法将在使用标准类和类操作脚本修改文件和使用 sed 类和 postinstall 脚本修改文件中进行介绍。修改的文件是 /etc/inittab。
技术
此案例研究展示如何使用 build 类。有关 build 类的更多信息,请参见build 类脚本。
方法
这种修改 /etc/inittab 的方法使用 build 类。build 类脚本作为 shell 脚本执行,其输出成为正在执行的文件的新版本。换句话说,与该软件包一起提供的 /etc/inittab 数据文件将会执行,执行后的输出将成为 /etc/inittab。
build 类脚本在软件包安装和删除期间执行。如果该文件在安装时执行,参数 install 会传递给该文件。请注意在 build 样例类脚本中,安装操作通过测试此参数来定义。
要使用 build 类编辑 /etc/inittab,您必须完成以下任务:
-
在 prototype 文件中定义生成文件。
prototype 文件中的生成文件条目应将该文件放置在 build 类中,并将其文件类型定义为 e。请确保将 pkginfo 文件中的 CLASSES 参数定义为 build。
-
创建 build 类脚本。
build 样例类脚本执行以下过程:
-
编辑 /etc/inittab 文件以删除对该软件包的任何现有更改。请注意,文件名 /etc/inittab 已被硬编码到 sed 命令中。
-
如果正在安装软件包,将新行添加到 /etc/inittab 的末尾。一个注释标记会包括在该新条目中,用于描述该条目的来源。
-
执行 init q 命令。
-
该解决方案解决了在使用标准类和类操作脚本修改文件和使用 sed 类和 postinstall 脚本修改文件的案例研究中描述的缺点。只需要一个很短的文件(除 pkginfo 和 prototype 文件之外)。因为使用了 PKGINST 参数,所以该文件适用于软件包的多个实例,而且由于 init q 命令可从 build 类脚本中执行,因此不需要 postinstall 脚本。
案例研究文件
pkginfo 文件
PKG=case6 NAME=Case Study #6 CATEGORY=applications BASEDIR=/opt ARCH=SPARC VERSION=Version 1d05 CLASSES=build |
prototype 文件
i pkginfo e build /etc/inittab ? ? ? |
生成文件
# PKGINST parameter provided by installation service # remove all entries from the existing table that # are associated with this PKGINST sed -e "/^[^:]*:[^:]*:[^:]*:[^#]*#$PKGINST$/d" /etc/inittab || exit 2 if [ "$1" = install ] then # add the following entry to the table echo "rb:023456:wait:/usr/robot/bin/setup #$PKGINST" || exit 2 fi /sbin/init q || exit 2 exit 0 |
在安装期间修改 crontab 文件
此案例研究在软件包安装期间修改 crontab 文件。
技术
此案例研究展示以下技术:
-
使用类和类操作脚本
有关更多信息,请参见编写类操作脚本。
-
在类操作脚本中使用 crontab 命令。
方法
在安装期间编辑多个文件的最高效方式是定义一个类,然后提供类操作脚本。如果您使用了 build 类方法,您将需要为每个编辑的 crontab 文件提供一个 build 类脚本。定义 cron 类是一种更通用的方法。要使用这种方法编辑 crontab 文件,您必须:
-
在 prototype 文件中定义将编辑的 crontab 文件。
在 prototype 文件中为每个将编辑的 crontab 文件创建一个条目。对于每个文件,将类定义为 cron 并将文件类型定义为 e。使用将编辑的文件的实际名称。
-
为软件包创建 crontab 文件。
这些文件包含您希望添加到同名的现有 crontab 文件的信息。
-
为 cron 类创建安装类操作脚本。
i.cron 样例脚本执行以下过程:
-
确定用户 ID (user ID, UID)。
i.cron 脚本将 user 变量设置为正在处理的 cron 类脚本的基名。该名称是 UID。例如,/var/spool/cron/crontabs/root 的基名是 root,该基名也是 UID。
-
使用 UID 和 -l 选项执行 crontab。
使用 -l 选项会告诉 crontab 为定义的用户将 crontab 文件内容发送到标准输出。
-
将 crontab 命令的输出通过管道输出到 sed 脚本,该脚本用于删除以前使用该安装技术添加的所有条目。
-
将编辑的输出放置到临时文件中。
-
将 root UID 对应的数据文件(随软件包提供)添加到临时文件,并添加一个标记,以便您知道这些条目的来源。
-
使用同一 UID 执行 crontab,并使用临时文件作为其输入。
-
-
为 cron 类创建删除类操作脚本。
r.cron 脚本与安装脚本基本相同,只不过前者没有用于向 crontab 文件添加信息的过程。
这些过程针对 cron 类中的每个文件执行。
案例研究文件
下述 i.cron 和 r.cron 脚本由超级用户执行。以超级用户身份编辑其他用户的 crontab 文件可能导致无法预测的结果。如果需要,请在每个脚本中将以下条目:
crontab $user < /tmp/$$crontab ||
更改为
su $user -c "crontab /tmp/$$crontab" ||
pkginfo 命令
PKG=case7 NAME=Case Study #7 CATEGORY=application BASEDIR=/opt ARCH=SPARC VERSION=Version 1.0 CLASSES=cron |
prototype 文件
i pkginfo i i.cron i r.cron e cron /var/spool/cron/crontabs/root ? ? ? e cron /var/spool/cron/crontabs/sys ? ? ? |
i.cron 安装类操作脚本
# PKGINST parameter provided by installation service while read src dest do user=`basename $dest` || exit 2 (crontab -l $user | sed -e "/#$PKGINST$/d" > /tmp/$$crontab) || exit 2 sed -e "s/$/#$PKGINST/" $src >> /tmp/$$crontab || exit 2 crontab $user < /tmp/$$crontab || exit 2 rm -f /tmp/$$crontab done exit 0 |
r.cron 删除类操作脚本
# PKGINST parameter provided by installation service while read path do user=`basename $path` || exit 2 (crontab -l $user | sed -e "/#$PKGINST$/d" > /tmp/$$crontab) || exit 2 crontab $user < /tmp/$$crontab || exit 2 rm -f /tmp/$$crontab done exit |
crontab 文件 #1
41,1,21 * * * * /usr/lib/uucp/uudemon.hour > /dev/null 45 23 * * * ulimit 5000; /usr/bin/su uucp -c "/usr/lib/uucp/uudemon.cleanup" > /dev/null 2>&1 11,31,51 * * * * /usr/lib/uucp/uudemon.poll > /dev/null |
crontab 文件 #2
0 * * * 0-6 /usr/lib/sa/sa1 20,40 8-17 * * 1-5 /usr/lib/sa/sa1 5 18 * * 1-5 /usr/lib/sa/sa2 -s 8:00 -e 18:01 -i 1200 -A |
注 –
如果对一组文件的编辑将导致文件总大小增加超过 10K,请提供一个 space 文件,以便 pkgadd 命令可以允许这种增加。有关 space 文件的更多信息,请参见在目标系统上保留额外空间。
使用过程脚本安装和删除驱动程序
此软件包可安装驱动程序。
技术
此案例研究展示以下技术:
-
使用 postinstall 脚本安装和装入驱动程序
-
使用 preremove 脚本卸载驱动程序
有关这些脚本的更多信息,请参见编写过程脚本。
方法
-
创建 request 脚本。
request 脚本通过询问管理员并将答复指定给 $KERNDIR 参数,确定管理员希望将驱动程序对象安装到的位置。
该脚本以一个例程结束,以使两个参数(即,CLASSES 和 KERNDIR)对于安装环境和 postinstall 脚本可用。
-
创建 postinstall 脚本。
postinstall 脚本实际上执行驱动程序安装。该脚本在 buffer 和 buffer.conf 两个文件安装后执行。在此示例中显示的 postinstall 文件执行以下操作:
-
使用 add_drv 命令将驱动程序装入到系统。
-
使用 installf 命令为设备创建链接。
-
使用 installf -f 命令完成安装。
-
创建 preremove 脚本。
preremove 脚本使用 rem_drv 命令从系统卸载驱动程序,然后删除链接 /dev/buffer0。
-
案例研究文件
pkginfo 文件
PKG=bufdev NAME=Buffer Device CATEGORY=system BASEDIR=/ ARCH=INTEL VERSION=Software Issue #19 CLASSES=none |
prototype 文件
要在安装时安装驱动程序,您必须在 prototype 文件中包括驱动程序的对象和配置文件。
在此示例中,驱动程序的可执行模块被命名为 buffer;add_drv 命令处理该文件。内核使用配置文件 buffer.conf 帮助配置驱动程序。
i pkginfo i request i postinstall i preremove f none $KERNDIR/buffer 444 root root f none $KERNDIR/buffer.conf 444 root root |
查看此示例中的 prototype 文件,请注意以下事项:
-
因为不需要对软件包对象进行特殊处理,所以您可以将其放置在 none 标准类中。在 pkginfo 文件中 CLASSES 参数被设置为 none。
-
buffer 和 buffer.conf 的路径名以变量 $KERNDIR 开头。此变量在 request 脚本中设置,允许管理员决定驱动程序文件的安装位置。缺省目录是 /kernel/drv。
-
postinstall 脚本(将执行驱动程序安装的脚本)有一个对应条目。
request 脚本
trap 'exit 3' 15 # determine where driver object should be placed; location # must be an absolute path name that is an existing directory KERNDIR=`ckpath -aoy -d /kernel/drv -p \ “Where do you want the driver object installed”` || exit $? # make parameters available to installation service, and # so to any other packaging scripts cat >$1 <<! CLASSES='$CLASSES' KERNDIR='$KERNDIR' ! exit 0 |
postinstall 脚本
# KERNDIR parameter provided by `request' script err_code=1 # an error is considered fatal # Load the module into the system cd $KERNDIR add_drv -m '* 0666 root sys' buffer || exit $err_code # Create a /dev entry for the character node installf $PKGINST /dev/buffer0=/devices/eisa/buffer*:0 s installf -f $PKGINST |
preremove 脚本
err_code=1 # an error is considered fatal # Unload the driver rem_drv buffer || exit $err_code # remove /dev file removef $PKGINST /dev/buffer0 ; rm /dev/buffer0 removef -f $PKGINST |
使用 sed 类和过程脚本安装驱动程序
此案例研究描述如何使用 sed 类和过程脚本安装驱动程序。该案例研究还与前面的案例研究(请参见使用过程脚本安装和删除驱动程序)有所不同,因为此软件包由绝对和可重定位的对象组成。
技术
此案例研究展示以下技术:
-
使用绝对和可重定位的对象生成 prototype 文件。
有关生成 prototype 文件的更多信息,请参见创建 prototype 文件。
-
使用 postinstall 脚本
有关此脚本的更多信息,请参见编写过程脚本。
-
使用 preremove 脚本
有关此脚本的更多信息,请参见编写过程脚本。
-
使用 copyright 文件
有关此文件的更多信息,请参见编写版权信息。
方法
-
创建包含绝对和可重定位的软件包对象的 prototype 文件。
将会在prototype 文件中详细讨论此内容。
-
将 sed 类脚本添加到 prototype 文件。
脚本的名称必须是将编辑文件的名称。在本例中,将编辑的文件是 /etc/devlink.tab,因此 sed 脚本被命名为 /etc/devlink.tab。对于 sed 脚本的模式、所有者和组没有要求(在样例 prototype 中由问号表示)。sed 脚本的文件类型必须是 e(表示可编辑)。
-
设置 CLASSES 参数以包括 sed 类。
-
创建 sed 类操作脚本 (/etc/devlink.tab)。
-
创建 postinstall 脚本。
postinstall 脚本需要执行 add_drv 命令以向系统添加设备驱动程序。
-
创建 preremove 脚本。
preremove 脚本需要执行 rem_drv 命令以在删除软件包之前从系统删除设备驱动程序。
-
创建 copyright 文件。
copyright 文件包含版权信息的 ASCII 文本。样例文件中所示的信息将在软件包安装期间显示在屏幕上。
案例研究文件
pkginfo 文件
PKG=SUNWsst NAME=Simple SCSI Target Driver VERSION=1 CATEGORY=system ARCH=sparc VENDOR=Sun Microsystems BASEDIR=/opt CLASSES=sed |
prototype 文件
图 5–1 分层软件包目录结构
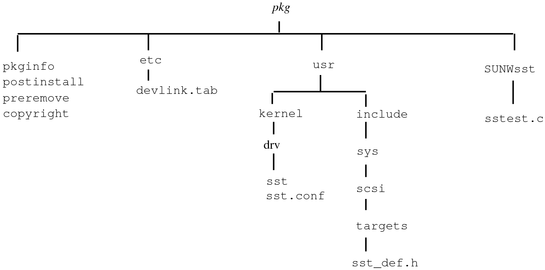
软件包对象的安装位置与上图 pkg 目录中的位置相同。驱动程序模块(sst 和 sst.conf)安装在 /usr/kernel/drv 中,而头文件安装在 /usr/include/sys/scsi/targets 中。sst、sst.conf 和 sst_def.h 文件是绝对对象。测试程序 sstest.c 及其目录 SUNWsst 是可重定位对象;它们的安装位置由 BASEDIR 参数设置。
软件包的其余组件(所有控制文件)安装在开发计算机上软件包的顶层目录中,但 sed 类脚本除外。它根据所修改的文件命名为 devlink.tab 并安装到 etc,该目录包含实际的 devlink.tab 文件。
find usr SUNWsst -print | pkgproto > prototype |
上述命令的输出如下所示:
d none usr 0775 pms mts d none usr/include 0775 pms mts d none usr/include/sys 0775 pms mts d none usr/include/sys/scsi 0775 pms mts d none usr/include/sys/scsi/targets 0775 pms mts f none usr/include/sys/scsi/targets/sst_def.h 0444 pms mts d none usr/kernel 0775 pms mts d none usr/kernel/drv 0775 pms mts f none usr/kernel/drv/sst 0664 pms mts f none usr/kernel/drv/sst.conf 0444 pms mts d none SUNWsst 0775 pms mts f none SUNWsst/sstest.c 0664 pms mts |
此 prototype 文件并不是完整文件。要完成此文件,您需要进行以下修改:
-
插入控制文件(文件类型 i)条目,因为它们与其他软件包对象的格式不同。
-
删除目标系统上已存在的目录的条目。
-
更改每个条目的访问权限和拥有权。
-
在绝对软件包对象之前添加一个斜线。
以下是最终的 prototype 文件:
i pkginfo i postinstall i preremove i copyright e sed /etc/devlink.tab ? ? ? f none /usr/include/sys/scsi/targets/sst_def.h 0644 bin bin f none /usr/kernel/drv/sst 0755 root sys f none /usr/kernel/drv/sst.conf 0644 root sys d none SUNWsst 0775 root sys f none SUNWsst/sstest.c 0664 root sys |
sed 脚本条目中的问号表明不应更改安装计算机上现有文件的访问权限和拥有权。
sed 类操作脚本 (/etc/devlink.tab)
在驱动程序示例中,sed 类脚本用于向 /etc/devlink.tab 文件中添加一个驱动程序条目。devlinks 命令使用此文件创建从 /dev 到 /devices 的符号链接。以下是 sed 脚本:
# sed class script to modify /etc/devlink.tab !install /name=sst;/d $i\ type=ddi_pseudo;name=sst;minor=character rsst\\A1 !remove /name=sst;/d |
pkgrm 命令不运行该脚本的删除部分。您可能需要向 preremove 脚本中添加一行,以便直接运行 sed 从 /etc/devlink.tab 文件删除条目。
postinstall 安装脚本
在此示例中,该脚本所需要做的只是运行 add_drv 命令。
# Postinstallation script for SUNWsst # This does not apply to a client. if [$PKG_INSTALL_ROOT = "/" -o -z $PKG_INSTALL_ROOT]; then SAVEBASE=$BASEDIR BASEDIR=””; export BASEDIR /usr/sbin/add_drv sst STATUS=$? BASEDIR=$SAVEBASE; export BASEDIR if [ $STATUS -eq 0 ] then exit 20 else exit 2 fi else echo "This cannot be installed onto a client." exit 2 fi |
add_drv 命令使用 BASEDIR 参数,因此该脚本必须在运行此命令之前取消设置 BASEDIR,并在以后恢复它。
add_drv 命令的操作之一是运行 devlinks,它使用由 sed 类脚本放置在 /etc/devlink.tab 中的条目为驱动程序创建 /dev 条目。
postinstall 脚本的退出代码作用很重要。退出代码 20 告诉 pkgadd 命令告知用户重新引导系统(安装驱动程序后必须这样做),而退出代码 2 则告诉 pkgadd 命令告知用户安装部分失败。
preremove 删除脚本
在此驱动程序示例中,该脚本删除 /dev 中的链接并对驱动程序运行 rem_drv 命令。
# Pre removal script for the sst driver echo “Removing /dev entries” /usr/bin/rm -f /dev/rsst* echo “Deinstalling driver from the kernel” SAVEBASE=$BASEDIR BASEDIR=””; export BASEDIR /usr/sbin/rem_drv sst BASEDIR=$SAVEBASE; export BASEDIR exit |
该脚本删除 /dev 条目本身; /devices 条目由 rem_drv 命令删除。
copyright 文件
以下是一个包含版权声明文本的简单 ASCII 文件。该声明在软件包安装开始时显示,显示时与此文件中的形式完全相同。
Copyright (c) 1999 Drivers-R-Us, Inc. 10 Device Drive, Thebus, IO 80586 All rights reserved. This product and related documentation is protected by copyright and distributed under licenses restricting its use, copying, distribution and decompilation. No part of this product or related documentation may be reproduced in any form by any means without prior written authorization of Drivers-R-Us and its licensors, if any. |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
