Reinitializing a Topology
This section describes how to analyze your topology to determine which systems need to be reinitialized. It also describes the methods you can use to reinitialize your replication topology.
Note –
When a replica has been reinitialized, all of its consumer replicas must also be reinitialized.
Determining What to Reinitialize
When you reinitialize your topology, you take a good copy of the data from a supplier and overwrite the bad data on the consumers in the topology. Before you reinitialize your topology, determine which systems are unsynchronized and need to reinitialized. This critical step can prevent your from wasting time by overwriting data that is already synchronized.
For example, the following figure illustrates a topology where replication is broken on hub 1.
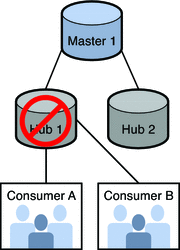
Because hub 1 provided data to consumers A and B, you need to reinitialize hub 1, consumer A, and consumer B.
In the following example, consumers A and B also receive updates from hub 2.
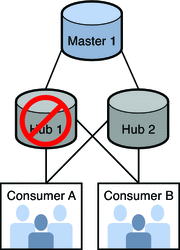
Consumers A and B may be synchronized with the supplier of the reinitialized replica because they receive updates from both hubs. Their status depends on which replica you select to reinitialize your topology. If you use RUVs to ensure that you have the latest changes, then these replicas may be up-to-date and you may not need to reinitialize consumers A and B.
Overview of Reinitialization Methods
You can use the following methods to reinitialize your topology:
-
Using the DSCC. This method is best if you are reinitializing only a single server or several small databases.
For more information about using the DSCC to reinitialize your topology, see To Reinitialize a Suffix Using the DSCC
Note –You can not use earlier versions of the console to reinitialize replication on Directory Server 5.x.
-
Using an import and export operation.
You can reinitialize a suffix by exporting the data and then importing it everywhere else in your topology. This method is appropriate for a big system and only applies to one suffix.
For information about reinitializing replication using an import and export, see Replica Initialization From LDIF in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.3 Administration Guide.
-
Using a binary copy.
A binary copy enables you to clone an entire server by using the binary backup files from one server to restore the identical directory contents onto another server. You can use a binary copy to reinitialize any server from the binary copy of a master or hub server, or a consumer from the binary copy of another consumer server. This method is available in Directory Server 5.2 and later. This method is the fastest, though poses some restriction on 5.x and earlier versions of Directory Server.
For information about reinitializing replication using a binary copy, see Initializing a Replicated Suffix by Using Binary Copy in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.3 Administration Guide.
Doing a Clean Reinitialization
All of the reinitialization methods copy unnecessary data, for example data that contains values that were deleted or that maintain state information or other historical data. This unnecessary data makes the entry larger in disk. Also, the entry state information may need to be purged. If the root cause of the replication problem is related to this state information, the data is still present in the database and can cause another replication error. To avoid importing this unnecessary and potentially problematic data, you can do a clean reinitialization of your topology.
When you do a clean reinitialization, you create a clean master copy of the data that contains smaller databases, indexes, and empty change logs. A clean reinitialization uses less disk space and takes less time because it does not make backup copies of the database files. It also reduces index fragmentation, which can reduce performance. However, it requires you to stop the server that is being cloned to ensure that the database files are in a coherent state.
 To Create Clean Master Data in a 6.3 Version of Directory Server
To Create Clean Master Data in a 6.3 Version of Directory Server
-
Stop the master server.
-
Export the database contents using the dsadm command.
Specify the -Q option so that replication information is not included in the export.
# dsadm export -Q instance-path suffix-DN /tmp/clean-export.ldif
-
Reimport the exported data to the same master server using the dsadm command.
# dsadm import instance-path /tmp/clean-export.ldif suffix-DN
-
Restart the master server.
The master server now contains clean data, meaning it contains smaller databases, indexes, and empty change logs.
-
Import the clean master data, to all of the other servers in your system.
Use one of the three methods described in Overview of Reinitialization Methods.
 To Create Clean Data in a 5.x Version of Directory Server
To Create Clean Data in a 5.x Version of Directory Server
-
Stop the master server.
-
Export the database contents using the db2ldif script without the -r option.
# db2ldif -n database1 -a /tmp/clean-export.ldif
-
Reimport the exported data to the same master server using the ldif2db script.
# ldif2db -n database1 -i /tmp/clean-export.ldif
-
Restart the master server.
The master server now contains clean data, meaning it contains smaller databases, indexes, and empty change logs.
-
Import the clean master data, to all of the other servers in your system.
Use one of the three methods described in Overview of Reinitialization Methods.
 To Reinitialize a Suffix Using the DSCC
To Reinitialize a Suffix Using the DSCC
This method requires a replication agreement between the supplier and the consumers suffixes. Use this method to reinitialize a single suffix or to reinitialize many small suffixes.
Note –
If you are using an earlier version of the Directory Server console, go to the Configuration panel and select the Replication node. Select the suffix you want to initialize in the consumer. Select the replication agreement to the consumer. Right click the agreements and select Initialize consumer now.
-
On the supplier server, log in to DSCC.
-
Click the Directory Servers tab, then click the Suffixes tab.
-
In the Suffixes tab, select the suffix or suffixes that you need to reinitialize.
Select Initialize Suffix from Data from the drop-down menu.
-
In Step 1, select Initialize Using Existing Replication Agreements.
-
In Step 2, specify the supplier suffix from which you want to copy the data.
-
Verify that the import is complete by checking the errors log of the consumers.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
