Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise
This chapter contains the procedures on how to install and configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
This chapter contains the following procedures.
-
How to Install and Configure the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Software
-
How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise
-
How to Connect the Command Center to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Servers
Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end servers as a failover data service. Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Interaction Managers as a scalable data service. See the Sun Cluster Concepts Guide for Solaris OS document and “Planning for Sun Cluster Data Services” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for general information about data services, resource groups, resources, and other related topics.
Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Overview
Use the information in this section to understand how Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise makes BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise highly available.
For conceptual information on failover and scalable services, see the Sun Cluster Concepts Guide for Solaris OS.
Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise provides fault monitoring and automatic failover for the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers. This data service uses fault monitoring and automatic failover to eliminate single points of failure in a BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise site.
Table 1–1 Protection of BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Site Components|
BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise site component |
Protected by |
|---|---|
|
BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise database |
Sun Cluster HA for Oracle or Sun Cluster HA for Sybase ASE |
|
BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Interaction Managers |
Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise (scalable configuration) |
|
BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end servers |
Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise (failover configuration) |
|
HTTP servers |
Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Web Server or Sun Cluster HA for Apache |
Task Map: Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise
Table 1–2 lists the tasks for installing and configuring Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise. Perform these tasks in the order that they are listed.
Table 1–2 Task Map: Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise|
Task |
For Instructions, Go To … |
|---|---|
|
Plan the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation and configuration |
Chapter 1 of Sun Cluster Data Service for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Guide for Solaris OS Planning the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Configuration |
|
Prepare the nodes and disks | |
|
Install and configure the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software, the HTTP servers, and the database |
How to Install and Configure Sun Cluster HA for DBMS How to Install and Configure Your HTTP Server How to Install and Configure the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Software [ To configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end servers to use one failover resource group with n logical hostnames, proceed to Alternative Configuration. Follow the procedures that are listed in Alternative Configuration to complete the installation. Otherwise, continue to How to Configure and Verify the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Software, Database, and HTTP Server Installation.] |
|
Install the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages | |
|
Register and configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise |
How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise |
|
Connect the Command Center to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers |
How to Connect the Command Center to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Servers |
|
View Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise fault monitor information |
Operation of the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Fault Monitor |
|
View BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise functionality |
Planning the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Configuration
This section contains the information you need to plan your Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation and configuration.
Configuration Restrictions
Your data service configuration might not be supported if you do not observe these restrictions.
Use the restrictions in this section to plan the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise. This section provides a list of software and hardware configuration restrictions that apply to Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
For restrictions that apply to all data services, see the Sun Cluster Release Notes for Solaris OS.
-
Use a BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software version that is qualified with your release of Sun Cluster.
Configuration Requirements
Your data service configuration might not be supported if you do not adhere to these requirements.
Use the requirements in this section to plan the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise. These requirements apply to Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise only. You must meet these requirements before you proceed with your Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation and configuration.
For requirements that apply to all data services, see “Identifying Data Service Special Requirements” on page 3.
-
Install the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software on the cluster file system.
-
Create a BroadVision user that is identical on all of the cluster nodes.
-
Install all of the necessary patches that are supplied by BroadVision to enable the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software to run in the Sun Cluster environment.
-
Configure the Interaction Managers, back-end servers, and root hosts in the $BV1TO1_VAR/etc/bv1to1.conf configuration file, as shown in Standard Data Service Configurations.
-
Start your database before you start the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers.
Standard Data Service Configurations
Use the standard configurations in this section to plan the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise. Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise supports the standard configurations in this section. Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise might support additional configurations. However, you must contact your Enterprise Services representative for information on additional configurations.
For all of the supported configurations, set up your highly available database and HTTP server to match Sun Cluster HA for DBMS and HTTP Server Configuration.
Sun Cluster HA for DBMS and HTTP Server Configuration
Configure Sun Cluster HA for DBMS and HTTP server as follows.
-
Configure Sun Cluster HA for Oracle or Sun Cluster HA for Sybase ASE to use a logical hostname.
-
Configure Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Web Server or Sun Cluster HA for Apache to use a logical hostname (for failover configuration) or to use a shared address (for scalable configuration).
Cluster With Multiple Resource Groups for the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Software
Configure the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise root host, back-end, and Interaction Manager processes as follows.
-
Configure the root host resource to use one logical hostname in one resource group.
-
Configure back-end resources to use the remaining logical hostnames in multiple resource groups.
-
Configure the Interaction Manager resource on one of the following locations.
-
All of the cluster nodes.
-
All of the cluster private hostnames. See the Sun Cluster Software Installation Guide for Solaris OS for details on cluster interconnect and private hostnames.
Figure 1–1 illustrates a sample configuration that meets these guidelines.
Figure 1–1 Sample Configuration: Cluster With Three Logical Hostnames Configured Into Separate Resource Groups
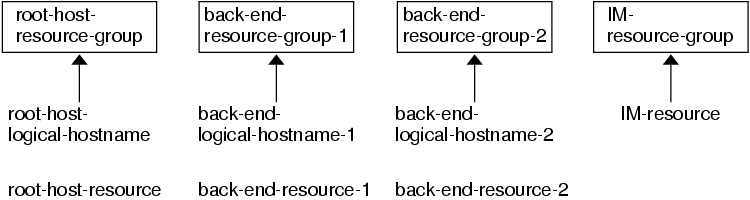
Note –Configure Interaction Manager resources on all of the cluster nodes or on all of the cluster private hostnames. If you configure the Interaction Managers on all of the cluster private hostnames, set up the HTTP servers on the same cluster. Alternatively, if you configure the Interaction Managers on all of the cluster nodes, the HTTP servers can be set up outside of the cluster.
-
Alternative Configuration: Cluster With One Resource Group for the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Back-End and Root Host Servers
Depending on the flexibility and granularity of administration that you require for each back-end resource, you can configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end servers to use only one resource group. To set up this alternative configuration, configure the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise root host, back-end, and Interaction Manager processes as follows.
-
Configure root host and all of the back-end resources to use n logical hostnames inside of the same failover resource group.
-
Configure the Interaction Manager resource on one of the following locations.
-
All of the cluster nodes.
-
All of the cluster private hostnames. See the Sun Cluster Software Installation Guide for Solaris OS for details on cluster interconnect and private hostnames.
This configuration, which Figure 1–2 illustrates, requires alternative steps. See Alternative Configuration for more information.
Figure 1–2 Sample Configuration: Cluster With Three Logical Hostnames Configured Into One Resource Group
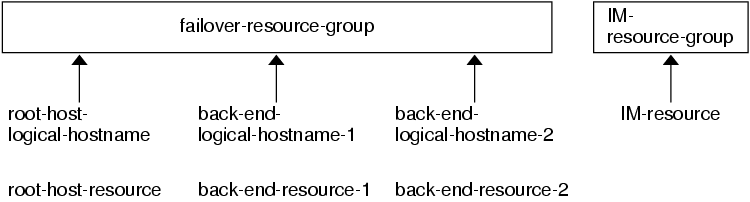
Note –Configure Interaction Manager resources on all of the cluster nodes or on all of the cluster private hostnames. If you configure the Interaction Managers on all of the cluster private hostnames, set up the HTTP servers on the same cluster. Alternatively, if you configure the Interaction Managers on all of the cluster nodes, the HTTP servers can be set up outside of the cluster.
-
Configuration Considerations
Use the information in this section to plan the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise. The information in this section encourages you to think about the impact your decisions have on the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
-
BroadVision user home directory – Create an identical BroadVision user (bvuser) on all of the cluster nodes. Place the BroadVision user home directory on the cluster file system. Direct all of the BroadVision users on all of the cluster nodes to the same home directory.
-
BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software – Install the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software on the cluster file system so that all of the cluster nodes can access the same BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise binaries and configuration files.
Configuration Planning Questions
Use the questions in this section to plan the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise. Insert the answers to these questions into the data service worksheets in the “Configuration Worksheets” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS. See Configuration Considerations for information that might apply to these questions.
-
Will you run Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise as a failover or as a scalable data service?
-
If you run Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise as a scalable service, what nodes will host the scalable service?
-
What resource groups will you use for network addresses and application resources and the dependencies between them?
-
What is the logical hostname (for failover services) or shared address (for scalable services) for clients that will access the data service?
-
Where will the system configuration files reside?
See “Determining the Location of the Application Binaries” on page 3 of the Sun Cluster Data Service for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Guide for Solaris OS for the advantages and disadvantages of placing the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise binaries on the local file system as opposed to the cluster file system.
Preparing the Nodes and Disks
This section contains the procedures you need to prepare the nodes and disks.
How to Prevent a Server-Port Conflict
Use this procedure to prepare for the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
By default, the orbix daemon chooses an available port number that the IT_DAEMON_SERVER_BASE and IT_DAEMON_SERVER_RANGE properties specify for use by a server that the daemon launches. When a client attempts to connect to a server for the first time, the client asks the orbix daemon for the port number. Then the client connects to the port that the orbix daemon specifies. If failover occurs after the client asks the orbix daemon for the port number but before the client connects to that port, the client might connect to the wrong server.
This procedure provides you two options to prevent a server-port conflict.
-
Which option do you prefer?
-
Configure the IT_LOCAL_SERVER_BASE property for each host so that ports that the orbix daemon assigns on different nodes will never overlap. For example, if you configure BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers and the Interaction Manager to run on cluster nodes A, B, and C, the bv1to1.conf file will have the following entries.
export ... IT_DAEMON_SERVER_RANGE = “200”; ... site bv { ... node A { export IT_LOCAL_SERVER_BASE = “1300”; ... } node B { export IT_LOCAL_SERVER_BASE = “1500”; # 1300 + 200 ... } node C { export IT_LOCAL_SERVER_BASE = “1700”; # 1500 + 200 ... } ... } -
Add the iiop_port parameter to each process entry in the bv1to1.conf file, and ensure that no two server-port entries conflict. The iiop_port is an undocumented parameter of the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise server that specifies which port a server should use. For example, the following process entry defines the cntdb server on port 1305.
process cntdb { parameter iiop_port = “1305”; }C++ CORBA servers support the iiop_port parameter. For Java servers, you must upgrade to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise 6.0AB or later versions.
Installing and Configuring the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Software, the Database, and the HTTP Server
This section contains the procedures you need to install and configure the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software, the database software, the HTTP software.
How to Install and Configure Sun Cluster HA for DBMS
See Sun Cluster Data Service for Oracle Guide for Solaris OS to install Sun Cluster HA for Oracle or Sun Cluster Data Service for Sybase ASE Guide for Solaris OS to install Sun Cluster HA for Sybase ASE.
How to Install and Configure Your HTTP Server
If Sun Java System Web Server is your HTTP server, follow the instructions in Sun Cluster Data Service for Sun Java System Web Server for Solaris OS to configure Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Web Server. If Apache Web Server is your HTTP server, follow the instructions in Sun Cluster Data Service for Apache for Solaris OS to configure Sun Cluster HA for Apache.
How to Install and Configure the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Software
Use this procedure to install and configure the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software and how to enable the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software to run in the Sun Cluster environment.
-
Follow the guidelines that are listed in Planning the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Configuration and Configuration Considerations.
-
Follow the instructions in the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide to install the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software on the cluster file system.
Note –Install the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software only once, on the cluster file system, from any cluster node.
-
Configure the $BV1TO1_VAR/etc/bv1to1.conf file.
Table 1–3 summarizes possible configurations in the $BV1TO1_VAR/etc/bv1to1.conf file for the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise components. See Standard Data Service Configurations and the instructions in the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide for details.
Table 1–3 Configuring the $BV1TO1_VAR/etc/bv1to1.conf File
Note –If you configure the Interaction Managers on all of the cluster private hostnames, set up the HTTP servers on the same cluster. Alternatively, if you configure the Interaction Managers on all of the cluster nodes, the HTTP servers can be set up outside of the cluster.
Note –Configure your cluster so that BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end servers can access the database from any cluster node.
Where to Go From Here
Depending on the flexibility and granularity of administration that you require for each back-end resource, you can set up your failover resource groups in one of the following ways.
-
Set up multiple failover resource groups to use multiple logical hostnames. If you plan to use this option, go to How to Verify the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Configuration.
-
Set up one failover resource group to use n logical hostnames and to contain all of the back-end and root host resources. If you plan to use this option, proceed to Alternative Configuration and follow the procedures in that section to complete the installation.
Note –
See Standard Data Service Configurations for more information.
How to Configure and Verify the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Software, Database, and HTTP Server Installation
Use this procedure to test starting and stopping the back-end processes on all of the nodes on which the back-end host and root host can run in a failover configuration. Additionally, perform this procedure to test the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Interaction Managers that you configured in the cluster.
Depending on the flexibility and granularity of administration that you require for each back-end resource, you can set up your failover resource groups in one of the following ways.
-
Set up multiple failover resource groups to use multiple logical hostnames. If you plan to use this option, proceed to Step 1.
-
Set up one failover resource group to use n logical hostnames and to contain all of the back-end and root host resources. If you plan to use this option, go to Alternative Configuration and follow the procedures in that section to complete the installation.
Note –
See Standard Data Service Configurations for more information.
-
To contain the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise root host resource, create a failover resource group that uses the root host logical hostname.
# scrgadm -a -g root-host-resource-group [-h nodelist]
- -g root-host-resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the resource group that uses the root host logical hostname and contains the BroadVision root host resource. The name of the root host resource group can be your choice but must be unique for resource groups within the cluster.
- [-h nodelist]
-
Specifies an optional, comma-separated list of physical node names or IDs that identify potential masters. The order here determines the order in which the Resource Group Manager (RGM) considers primary nodes during failover.
-
Create failover resource groups for the root host and back-end processes.
Run the scrgadm(1M) command to configure n failover resource groups for back-end processes that are configured on n logical hostnames.
# scrgadm -a -g back-end-resource-group-1 [-h nodelist] # scrgadm -a -g back-end-resource-group-2 [-h nodelist] # scrgadm -a -g back-end-resource-group-3 [-h nodelist] ... # scrgadm -a -g back-end-resource-group-n [-h nodelist]
- -g back-end-resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the resource group that contains the back-end logical hostname and resource. The name of the back-end resource group can be your choice but must be unique for resource groups within the cluster.
-
Verify that you have added all of the logical hostnames that you use to your name service database.
Additionally, add all of the logical hostnames that you use to the /etc/inet/hosts file on each cluster node. Therefore, if the name service goes down, the nodes can still find the name-to-address mapping on their local hosts file.
-
Run the scrgadm command to add the logical hostname that each of the resource groups that you have created can use.
# scrgadm -a -L -g root-host-resource-group -l root-host-logical-hostname-1 [-n netiflist] # scrgadm -a -L -g back-end-resource-group-1 -l back-end-logical-hostname-1 [-n netiflist] # scrgadm -a -L -g back-end-resource-group-2 -l back-end-logical-hostname-2 [-n netiflist] ... # scrgadm -a -L -g back-end-resource-group-n -l back-end-logical-hostname-n [-n netiflist]
- -l root-host-logical-hostname
-
Specifies the logical hostname (failover IP address) that the root host resource group uses.
- -l back-end-logical-hostname
-
Specifies the logical hostname that each back-end resource group uses.
- [-n netiflist]
-
Specifies an optional, comma-separated list that identifies the IP Networking Multipathing groups that are on each node. Each element in netiflist must be in the form of netif@node. netif can be given as an IP Networking Multipathing group name, such as sc_ipmp0. The node can be identified by the node name or node ID, such as sc_ipmp0@1 or sc_ipmp@phys-schost-1.
Note –Sun Cluster does not currently support using the adapter name for netif.
-
Create a scalable resource group for the Interaction Managers.
# scrgadm -a -g im-resource-group -y Maximum_primaries=m -y Desired_primaries=n
- -g im-resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the scalable resource group that contains the Interaction Managers. This name can be your choice but must be unique for resource groups within the cluster.
- -y Maximum_primaries=m
-
Specifies the maximum number of active primary nodes allowed for this resource group. If you do not assign a value to this property, the default is 1.
- -y Desired_primaries=n
-
Specifies the desired number of active primary nodes allowed for this resource group. If you do not assign a value to this property, the default is 1.
-
From one cluster node, run the scswitch(1M) command to move the failover resource groups into the managed state and bring them online.
# scswitch -Z -g root-host-resource-group # scswitch -Z -g back-end-resource-group-1 # scswitch -Z -g back-end-resource-group-2 ... # scswitch -Z -g back-end-resource-group-n
Note –You do not need to bring the scalable resource group online because the scalable resource group does not yet contain resources. You must bring failover resource groups online because the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end processes cannot start if the logical hostname resource is unavailable.
-
Check that the database is accessible.
See your database documentation for details.
-
Ensure that you have configured the database to enable BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end servers to access the database from any cluster node.
See your database documentation for details.
-
As the BroadVision user, log in to the cluster node that hosts the root host resource group.
-
Follow the steps in the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide to run the following BroadVision commands.
-
Set the BV_LOCAL_HOST environment variable as root-host-logical-hostname.
-
Source the bv1to1.conf.sh file or the bv1to1.conf.csh file, depending on the shell that you use.
-
Run the bvconf bootstrap command on the root host to initialize the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation.
Note –Do not run the bvconf command as superuser.
% bvconf bootstrap -r root-host-logical-hostname
-
Set the BV_LOCAL_HOST environment variable as back-end-logical-hostname or im-hostname.
-
Source the bv1to1.conf.sh file or the bv1to1.conf.csh file, depending on the shell that you use.
-
Ensure that the /etc/opt/BVSNsmgr directory exists and has write and execute permissions.
-
For each back-end host and Interaction Manager host, run the bvconf execute command to configure and start the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise processes.
% bvconf execute -local -var shared -r root-host-logical-hostname
-
-
Run the BroadVision command bvconf gateway to generate gateway configuration files for the HTTP gateway applications.
This command generates the files and writes them to the $BV1TO1_VAR/etc/appName.cfg file.
% bvconf gateway -A appName
- -A appName
-
Specifies the gateway application name, which is defined in the $BV1TO1_VAR/etc/bv1to1.conf configuration file. See the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide for details.
-
Copy the gateway application configuration file to the /etc/opt/BVSNsmgr directory on each of the cluster nodes that runs HTTP instances.
Note –Ensure that you copy the gateway application configuration file with the extension .cfg.
See the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide for details.
-
Configure and start the HTTP servers.
See your HTTP server documentation for details. Additionally, see the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide for information on HTTP server configuration.
-
From a BroadVision client, connect to the BroadVision site, and check the installation.
-
If the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software is functioning correctly, perform the following steps to shut down the Interaction Managers, back-end processes, and root host processes.
-
Run the scswitch command to switch the resource groups to another cluster node, such as node2.
# scswitch -z -g root-host-resource-group -h node2 # scswitch -z -g back-end-resource-group-1 -h node2 # scswitch -z -g back-end-resource-group-2 -h node2 ... # scswitch -z -g back-end-resource-group-n -h node2
-
Restart the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software on node2.
-
Connect to the cluster from a BroadVision client, and check that the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software functions correctly.
-
Repeat Step 15 through Step 18 on all of the potential primaries of the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resource groups.
Where to Go From Here
After you verify the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software, database, and HTTP server installation, go to Installing the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Package.
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Package
If you did not install the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages during your initial Sun Cluster installation, perform this procedure to install the packages. Perform this procedure on each cluster node where you are installing the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages. To complete this procedure, you need the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3.
If you are installing more than one data service simultaneously, perform the procedure in “Installing the Software” in Sun Cluster Software Installation Guide for Solaris OS.
Install the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages by using one of the following installation tools:
-
The Web Start program
-
The scinstall utility
Note –
The Web Start program is not available in releases earlier than Sun Cluster 3.1 Data Services 10/03.
How to Install Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Packages Using the Web Start Program
You can run the Web Start program with a command-line interface (CLI) or with a graphical user interface (GUI). The content and sequence of instructions in the CLI and the GUI are similar. For more information about the Web Start program, see the installer(1M) man page.
-
On the cluster node where you are installing the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages, become superuser.
-
(Optional) If you intend to run the Web Start program with a GUI, ensure that your
DISPLAYenvironment variable is set. -
Load the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3 into the CD-ROM drive.
If the Volume Management daemon vold(1M) is running and configured to manage CD-ROM devices, it automatically mounts the CD-ROM on the /cdrom/cdrom0 directory.
-
Change to the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise component directory of the CD-ROM.
The Web Start program for the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise data service resides in this directory.
# cd /cdrom/cdrom0/\ components/SunCluster_HA_BV_3.1
-
Start the Web Start program.
# ./installer
-
When you are prompted, select the type of installation.
-
Follow instructions on the screen to install the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages on the node.
After the installation is finished, the Web Start program provides an installation summary. This summary enables you to view logs that the Web Start program created during the installation. These logs are located in the /var/sadm/install/logs directory.
-
Exit the Web Start program.
-
Unload the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3 from the CD-ROM drive.
Where to Go From Here
When you finish the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise package installation, go to How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
How to Install Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Packages by Using the scinstall Utility
-
Load the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3 into the CD-ROM drive.
-
Run the scinstall utility with no options.
This step starts the scinstall utility in interactive mode.
-
Choose the menu option, Add Support for New Data Service to This Cluster Node.
The scinstall utility prompts you for additional information.
-
Provide the path to the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3.
The utility refers to the CD as the “data services cd.”
-
Specify the data service to install.
The scinstall utility lists the data service that you selected and asks you to confirm your choice.
-
Exit the scinstall utility.
-
Unload the CD from the drive.
Where to Go From Here
When you finish the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise package installation, go to How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise
This section contains the procedures you need to configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Extension Properties
Use the extension properties in Table 1–4 to create your resources. Use the command line scrgadm -x parameter=value to configure extension properties when you create your resource. Use the procedure in “Administering Data Service Resources” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OSto configure the extension properties if you have already created your resources. You can update some extension properties dynamically. You can update others, however, only when you create or disable a resource. The Tunable entries indicate when you can update each property. See “Standard Properties” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for details on all Sun Cluster properties.
Table 1–4 Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Extension Properties|
Property Category |
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise configuration |
BVUSER |
The BroadVision user UNIX ID. Replace bvuser with your preferred username. Default: None Tunable: At creation |
|
BV1TO1_VAR |
The environment variable that is set as bvuser. Default: None Tunable: At creation |
|
|
Probe |
Monitor_retry_interval |
The time (in minutes) over which the Resource Group Manager (RGM) counts fault monitor failures. The number of times that the fault monitor fails can exceed the value that the extension property Monitor_retry_count specifies. If the number of failures exceeds the value of Monitor_retry_count within the time period that Monitor_retry_interval specifies, the Process Monitor Facility (PMF) does not restart the fault monitor. Default: 2 Tunable: Any time |
|
Monitor_retry_count |
The number of PMF restarts that the Sun Cluster software allows for the fault monitor. Default: 4 Tunable: Any time |
|
|
Probe_timeout |
The time-out value in seconds for the probes. Default: 180 Tunable: Any time |
|
|
Daemons |
START_ORB_SERVERS |
Type Boolean. By default, the data service starts the orbix daemon and all of the BroadVision daemons in the resource. The orbix daemon starts the orbix servers whenever needed. If you want the data service to start the orbix servers, set this property to TRUE. Default: FALSE Tunable: Any time |
How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise
Use this procedure to register and configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
Note –
Before you start Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise, check that your database is accessible.
-
Shut down all of the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers, including the root host, back-end, and Interaction Manager servers.
Note –Perform this step after you test the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation.
-
Run the ps(1) command to check that all of the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise processes and the orbix daemon (orbixd) are stopped on all of the cluster nodes.
-
Become superuser on one cluster node.
-
Run the scrgadm command to register the resource type for Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
# scrgadm -a -t SUNW.bv
- -a
-
Adds the resource type for the data service.
- -t SUNW.bv
-
Specifies the resource type name that is predefined for your data service.
-
Run the scrgadm command to create the root host, back-end, and Interaction Manager resources.
-
Create root host and back-end resources in the failover resource groups that you created in Step 2 of How to Configure and Verify the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Software, Database, and HTTP Server Installation.
Note –The bvuser and BV1TO1_VAR should be the same for all of the resources.
# scrgadm -a -j root-host-resource -g root-host-resource-group -t SUNW.bv -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory # scrgadm -a -j back-end-resource-1 -g back-end-resource-group-1 -t SUNW.bv -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory # scrgadm -a -j back-end-resource-2 -g back-end-resource-group-2 -t SUNW.bv -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory ... # scrgadm -a -j back-end-resource-n -g back-end-resource-group-n -t SUNW.bv -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory
- -j root-host-resource
-
Specifies the name of the root host resource.
- -x BVUSER=bvuser
-
Specifies your BroadVision username.
- -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory
-
Specifies the path to the $BV1TO1_VAR directory.
- -j back-end-resource-n
-
Specifies the name of the back-end resource.
-
Create the Interaction Manager resource in the scalable resource group.
Note –The bvuser and BV1TO1_VAR should be the same for all of the resources.
# scrgadm -a -j im-resource -g im-resource-group -t SUNW.bv -x BVUSER=bvuser / -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory
- -j im-resource
-
Specifies the name of the Interaction Manager resource.
-
-
Run the scswitch command to enable and bring online the resource groups that now include the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resources.
# scswitch -Z -g root-host-resource-group # scswitch -Z -g back-end-resource-group-1 # scswitch -Z -g back-end-resource-group-2 ... # scswitch -Z -g back-end-resource-group-n # scswitch -Z -g im-resource-group
How to Verify the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Configuration
Use this procedure to verify that you installed and configured Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise correctly.
-
From a web browser, log in to an application that you have configured with the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software.
-
Log in to the node that hosts the root host resource group.
-
Become the BroadVision user.
-
Shut down the root host processes.
-
Set the BV_LOCAL_HOST environment variable as root-host-logical-hostname.
-
Source the bv1to1.conf.sh file or the bv1to1.conf.csh file, depending on the shell that you use.
-
Run the following BroadVision command.
# bvconf shutdown -local
Note –The Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise fault monitors will restart the root host.
-
-
Ensure that your web browser connection to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise is still active.
-
Run the scswitch command to switch the root host resource group to another cluster node, such as node2.
# scswitch -z -g root-host-resource-group -h node2
-
Ensure that your web browser connection to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise is still active.
-
Repeat Step 2 through Step 7 for each back-end resource group.
Where to Go From Here
You have completed your Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation and configuration. See the following sections for supplemental information.
-
Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Extension Properties
-
Operation of the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Fault Monitor
How to Connect the Command Center to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Servers
Use this procedure to connect the Command Center to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers that are configured on a cluster. This procedure provides you two options to connect the Command Center to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers.
-
Which option do you prefer?
-
Force the Dynamic Control Center (DCC) to use POOP instead of IIOP. To do so, set the value of the My Computer/HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/BroadVision/Dynamic Control Center/4.2/Options/Use IIOP Windows registry entry to 0.
-
Set the IT_LOCAL_ADDR_LIST property to include the IP addresses of all of the cluster nodes and logical hostnames that will run the orbix daemon.
Example - Connecting Command Center to Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise
This example uses the following sample IP addresses to add to the bv1to1.conf file.
- root host
-
10.10.102.225
- back-end host
-
10.10.102.226
- Interaction Manager host
-
10.10.102.222
- Interaction Manager host
-
10.10.102.223
Based on these sample IP addresses, add the following line to the bv1to1.conf file, under the global export section, before the IT_DAEMON_PORT property.
IT_LOCAL_ADDR_LIST = “127.0.0.1” + “10.10.102.222” + “10.10.102.223” + “10.10.102.225” + “10.10.102.226” ; |
Note –
DCC cannot recover from a failover. Contact BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise support for more information.
Examples – Installing, Configuring, and Administering Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise
Example One – Installation and Configuration and Example Two – Administration Commands show how to install, configure, and administer Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise. The following tables list cluster information and BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise configuration information. This information applies to both of the examples.
Table 1–5 Examples – Cluster Information|
Node names |
phys-schost-1, phys-schost-2 |
|
Logical hostnames |
schost-1, schost-2 |
|
Resource groups |
root-host-resource-group (for root host resources), back-end-resource-group (for back-end resources), im-resource-group (for Interaction Manager resources) |
|
Resources |
root-host-resource (the BroadVision root host resource), back-end-resource (the BroadVision back-end resource), im-resource (BroadVision Interaction Manager resource) |
Table 1–6 Examples – BroadVision Configuration Information
|
BV User |
BVUSER (on all of the cluster nodes) |
|
BV1TO1_VAR directory |
/global/broadvision/bvuser/bv1to1_var |
|
Root host |
schost-1 |
|
Back-end host |
schost-2 |
|
Interaction Manager 1 |
phys-schost-1 |
|
Interaction Manager 2 |
phys-schost-2 |
Example One – Installation and Configuration
This example illustrates how to install and configure the data service.
(Register the BroadVision resource type.) phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -t SUNW.bv (Create failover resource groups for the back-end and root host processes.) phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -g root-host-resource-group phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -g back-end-resource-group (Create a scalable resource group for the Interaction Manager processes.) phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -g im-resource-group -y Maximum_primaries=2 / -y Desired_primaries=2 (Add logical hostnames to the failover resource groups.) phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -L -g root-host-resource-group -l schost-1 phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -L -g back-end-resource-group -l schost-2 (Create root host, back-end, and Interaction Manager resources.) phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -j root-host-resource -g root-host-resource-group / -t SUNW.bv -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=/global/broadvision/bvuser/bt1to1_var phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -j back-end-resource -g back-end-resource-group / -t SUNW.bv -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=/global/broadvision/bvuser/bt1to1_var phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -a -j im-resource -g im-resource-group -t SUNW.bv / -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=/global/broadvision/bvuser/bt1to1_var (Bring all of the resource groups online.) phys-schost-1:> scswitch -Z -g root-host-resource-group phys-schost-1:> scswitch -Z -g back-end-resource-group phys-schost-1:> scswitch -Z -g im-resource-group |
Example Two – Administration Commands
This example lists some common administration commands that you might wish to run.
(Check the status of the resource groups.) phys-schost-1:> scstat -g (Note: All of the BroadVision Interaction Manager 1, root host, and back-end processes should run on phys-schost-1. Interaction Manager 2 processes must run on phys-schost-2.) (Test failover. Switch the root-host-resource-group and the back-end-resource-group to another node.) phys-schost-1:> scswitch -z -g root-host-resource-group -h phys-schost-2 phys-schost-1:> scswitch -z -g back-end-resource-group -h phys-schost-2 (Note: All of the BroadVision root host and back-end processes should now run on phys-schost-2.) (Because the Maximum and Desired primaries are set to 2, the Interaction Manager runs on the two cluster nodes. Shut down Interaction Manager 2, which runs on phys-schost-2.) phys-schost-1:> scswitch -z -g im-resource-group -h phys-schost-1 (Shut down all of the resource groups.) phys-schost-1:> scswitch -F -g root-host-resource-group phys-schost-1:> scswitch -F -g back-end-resource-group phys-schost-1:> scswitch -F -g im-resource-group (Remove and disable all of the BroadVision resources and resource groups.) phys-schost-1:> scswitch -n -j root-host-resource phys-schost-1:> scswitch -n -j back-end-resource phys-schost-1:> scswitch -n -j im-resource phys-schost-1:> scswitch -n -j schost-1 phys-schost-1:> scswitch -n -j schost-2 phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -j root-host-resource phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -j back-end-resource phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -j im-resource phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -j schost-1 phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -j schost-2 phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -j root-host-resource-group phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -j back-end-resource-group phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -j im-resource-group (Remove the resource type.) phys-schost-1:> scrgadm -r -t SUNW.bv |
Alternative Configuration
Depending on the flexibility and granularity of administration that you require for each back-end resource, you can set up only one failover resource group to use n logical hostnames and to contain all of the back-end and root host resources.
Note –
See Alternative Configuration: Cluster With One Resource Group for the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Back-End and Root Host Servers for an illustration of this alternative configuration.
To set up this alternative configuration, perform the following procedures.
-
Note –With these procedures, you set up two resource groups. One failover resource group contains root host and back-end resources. One scalable resource group contains the Interaction Manager resource. Throughout the alternative configuration procedures, the failover resource group that contains root host and back-end resources is denoted as failover-resource-group.
Alternative Configuration: How to Configure and Verify the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise, Database, and HTTP Server Installation
Perform this procedure to test starting and stopping the back-end processes on all of the nodes on which the back-end host and root host can run in a failover configuration. Additionally, perform this procedure to test the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Interaction Managers that you configured in the cluster.
-
Create a failover resource group to contain the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end and root host resources.
# scrgadm -a -g failover-resource-group [-h nodelist]
- -g failover-resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the resource group that contains the back-end and root host logical hostnames and resources. The name of the failover resource group can be your choice but must be unique for resource groups within the cluster.
- [-h nodelist]
-
Specifies an optional, comma-separated list of physical node names or IDs that identify potential masters. The order here determines the order in which the Resource Group Manager (RGM) considers primary nodes during failover.
-
Verify that you have added all of the logical hostnames that you use to your name service database.
Additionally, add all of the logical hostnames that you use to the /etc/inet/hosts file on each cluster node. Therefore, if the name service goes down, the nodes can still find the name-to-address mapping on their local hosts file.
-
Run the scrgadm(1M) command to add the logical hostnames that the failover resource group will use.
# scrgadm -a -L -g failover-resource-group -l root-host-logical-hostname-1 [-n netiflist] # scrgadm -a -L -g failover-resource-group -l back-end-logical-hostname-1 [-n netiflist] # scrgadm -a -L -g failover-resource-group -l back-end-logical-hostname-2 [-n netiflist] ... # scrgadm -a -L -g failover-resource-group -l back-end-logical-hostname-n [-n netiflist]
- -l root-host-logical-hostname
-
Specifies the logical hostname that the root host resource uses.
- -l back-end-logical-hostname-n
-
Specifies the logical hostname that each back-end resource uses.
- [-n netiflist]
-
Specifies an optional, comma-separated list that identifies the IP Networking Multipathing groups that are on each node. The netiflist must represent all of the nodes in the resource group's nodelist. If you do not specify this option, the scrgadm command attempts to discover a network adapter on the subnet that the hostname list identifies for each nodelist node.
-
Create a scalable resource group for the Interaction Managers.
# scrgadm -a -g im-resource-group -y Maximum_primaries=n -y Desired_primaries=n
- -g im-resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the scalable resource group that contains the Interaction Managers. This name can be your choice but must be unique for resource groups within the cluster.
- -y Maximum_primaries=m
-
Specifies the maximum number of active primary nodes allowed for this resource group. If you do not assign a value to this property, the default is 1.
- -y Desired_primaries=n
-
Specifies the desired number of active primary nodes allowed for this resource group. If you do not assign a value to this property, the default is 1.
-
From one cluster node, run the scswitch(1M) command to move the failover resource group into the managed state and bring it online.
# scswitch -Z -g failover-resource-group
Note –You do not need to bring the scalable resource group online because the scalable resource group does not yet contain resources. You must bring the failover resource group online because the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end processes cannot start if the logical hostname resource is unavailable.
-
Check that the database is accessible.
See your database documentation for details.
-
Ensure that you have configured the database to enable BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end servers to access the database from any cluster node.
See your database documentation for details.
-
As the BroadVision user, log in to the cluster node that hosts the failover resource group.
-
Follow the steps in the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide to run the following BroadVision commands.
-
Set the BV_LOCAL_HOST environment variable as root-host-logical-hostname.
-
Source the bv1to1.conf.sh file or the bv1to1.conf.csh file, depending on the shell that you use.
-
Run the bvconf bootstrap command on the root host to initialize the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation.
Note –Do not run the bvconf command as superuser.
% bvconf bootstrap -r root-host-logical-hostname
-
Set the BV_LOCAL_HOST environment variable as back-end-logical-hostname or im-hostname.
-
Source the bv1to1.conf.sh file or the bv1to1.conf.csh file, depending on the shell that you use.
-
For each back-end host and Interaction Manager host, run the bvconf execute command to configure and start the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation.
% bvconf execute -local -var shared -r root-host-logical-hostname
-
-
Run the BroadVision command bvconf gateway to generate gateway configuration files for the HTTP gateway applications.
This command generates the files and writes them to the $BV1TO1_VAR/etc/appName.cfg file.
% bvconf gateway -A appName
- -A appName
-
Specifies the gateway application name, which is defined in the $BV1TO1_VAR/etc/bv1to1.conf configuration file. See the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide for details.
-
Copy the gateway application configuration file to the /etc/opt/BVSNsmgr directory on each of the cluster nodes that runs HTTP instances.
Note –Ensure that you copy the gateway application configuration file with the extension .cfg.
See the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide for details.
-
Configure and start the HTTP servers.
See your HTTP server documentation for details. Additionally, see the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation and Administration Guide for information on HTTP server configuration.
-
From a BroadVision client, connect to the BroadVision site, and check the installation.
-
If the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software is functioning correctly, perform the following steps to shut down the Interaction Managers, back-end processes, and root host processes.
-
Run the scswitch command to switch the failover resource group to another cluster node, such as node2.
# scswitch -z -g failover-resource-group -h node2
-
Restart the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software.
-
Connect to the cluster from a BroadVision client, and check that the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software functions correctly.
-
Repeat Step 15 through Step 18 on all of the potential primaries of the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resource groups.
Alternative Configuration: How to Install Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Packages
Use this procedure to install the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages. You need the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3 to perform this procedure. This procedure assumes that you did not install the data service packages during your initial Sun Cluster installation. If you installed the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages as part of your initial Sun Cluster installation, proceed to Alternative Configuration: How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise to install and configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise. Otherwise, use this procedure to install the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise packages. Perform this procedure on all nodes that can run Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
-
Load the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3 into the CD-ROM drive.
-
Run the scinstall utility with no options.
This step starts the scinstall utility in interactive mode.
-
Choose the menu option, Add Support for New Data Service to This Cluster Node.
The scinstall utility prompts you for additional information.
-
Provide the path to the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3.
The utility refers to the CD as the “data services cd.”
-
Specify the data service to install.
The scinstall utility lists the data service that you selected and asks you to confirm your choice.
-
Exit the scinstall utility.
-
Unload the CD from the drive.
Alternative Configuration: How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise
To register and configure Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise, perform the following steps.
Note –
Before you start Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise, check that your database is accessible.
-
Shut down all of the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers, including the root host, back-end, and Interaction Manager servers.
Note –Perform this step after you test the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation.
-
Run the ps(1) command to check that all of the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise processes and the orbix daemon (orbixd) are stopped on all of the cluster nodes.
-
Become superuser on one cluster node.
-
Run the scrgadm command to register the resource type for Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
# scrgadm -a -t SUNW.bv
- -a
-
Adds the resource type for the data service.
- -t SUNW.bv
-
Specifies the resource-type name that is predefined for your data service.
-
Run the scrgadm command to create the root host, back-end, and Interaction Manager resources.
-
Set the Network_resources_used property for each resource to point to the proper logical hostname.
If you created two or more back-end resources in one resource group, and you do not set the Network_resources_used property, the validate method will fail.
# scrgadm -a -j root-host-resource -g failover-resource-group -t SUNW.bv -y Network_resources_used=root-host-logical-hostname -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory # scrgadm -a -j back-end-resource-1 -g failover-resource-group -t SUNW.bv -y Network_resources_used=back-end-logical-hostname-1 -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory ... # scrgadm -a -j back-end-resource-n -g failover-resource-group -t SUNW.bv -y Network_resources_used=back-end-logical-hostname-n -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory
- -j root-host-resource
-
Specifies the name of the root host resource.
- -x BVUSER=bvuser
-
Specifies your BroadVision username.
- -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory
-
Specifies the path to the $BV1TO1_VAR directory.
- -j back-end-resource-n
-
Specifies the name of the back-end resource.
Note –You should have created all of the logical hostnames that were defined in the Network_resource_used property in the failover resource group (see Step 3 of the procedure, Alternative Configuration: How to Configure and Verify the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise, Database, and HTTP Server Installation).
-
Create the Interaction Manager resource in the scalable resource group that you created in Step 4 of the procedure, Alternative Configuration: How to Configure and Verify the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise, Database, and HTTP Server Installation.
# scrgadm -a -j im-resource -g im-resource-group -t SUNW.bv -x BVUSER=bvuser -x BV1TO1_VAR=path-to-bv1to1_var-directory
- -j im-resource
-
Specifies the name of the Interaction Manager resource.
-
-
Run the scswitch command to enable the resource group that now includes the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end and root host resources.
# scswitch -Z -g failover-resource-group # scswitch -Z -g im-resource-group
Alternative Configuration: How to Verify the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Installation
Perform the following steps to verify the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise installation.
-
From a web browser, log in to an application that you have configured with the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise software.
-
Log in to the node that hosts the failover resource group.
-
Become the BroadVision user.
-
Shut down the root host processes.
-
Set the BV_LOCAL_HOST environment variable as root-host-logical-hostname.
-
Source the bv1to1.conf.sh file or the bv1to1.conf.csh file, depending on the shell that you use.
-
Run the following BroadVision command.
# bvconf shutdown -local
Note –The Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise fault monitors will restart the root host.
-
-
Ensure that your web browser connection to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise is still active.
-
Run the scswitch command to switch the failover resource group to another cluster node, such as node2.
# scswitch -z -g failover-resource-group -h node2
-
Ensure that your web browser connection to BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise is still active.
Operation of the Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Fault Monitor
The Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise fault monitor checks BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise back-end and Interaction Manager process health. BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise process health impacts BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resources' failure history, which in turn drives the fault monitor's actions. For each BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resource, fault monitor actions include no action, restart, or failover.
Interaction Manager Fault Monitoring
For Interaction Manager resources, failover happens only when both of the following conditions are met.
-
The value of the desired primaries is less than the value of the maximum primaries.
-
One of the nodes is unavailable.
After failover, the fault monitor will not restart the resource on any cluster node if both of the following conditions occur.
-
The values of the maximum primaries and desired primaries of the Interaction Manager resource group are the same.
-
The fault monitor has completed restarting the Interaction Manager resource the number of times that the Retry_count property specifies.
Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Fault Probes
The fault monitors for each BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resource (root host, back-end host, and Interaction Manager host) monitor the following processes.
-
The orbix daemon (orbixd), which is common for all of the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resources – The probes use the ps(1) command to ensure that orbixd is functioning. If orbixd is not functioning, the probe considers the failure as complete, and the Resource Group Manager (RGM) restarts the orbix daemon.
The orbix daemon is started with the checkpoint feature. Therefore, the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise servers, which the previous instance of orbixd started, continue to run with the new instance of orbixd.
-
The BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise daemons that you have configured in the resource – If orbixd is healthy, the probe uses the BroadVision command bvconf ps to ensure that the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise daemons are functioning. If BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise daemons are not functioning, the RGM restarts the resource, which restarts all of the configured daemons.
BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise Functionality
This section contains information on expected behavior with Sun Cluster HA for BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise.
-
The One-To-One database fails and the back-end hosts fail over – If the database fails and the back-end hosts fail over before the database comes back online, the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resources cannot come online on any cluster node. When you successfully restart the database, start the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resources again.
-
The hosts in the startup order are offline – BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resources must be started in a particular order. The BroadVision command bvconf bootstrap lists this order. If both of the following conditions occur, the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise processes that are configured on the hostname in the resource group will not start.
-
Any of the resources in the startup order are offline.
-
You start a BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resource that is listed after the offline resources in the startup order.
If both of these conditions occur, the resource group will come online, but the processes will not start. The probe will wait for the resource group in the startup order to come online before the probe starts the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise processes for this resource.
-
-
The BroadVision and Oracle resource groups fail over at the same time – If you use Oracle, and the BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise backend resource groups and the Oracle resource group fail over at the same time, some BroadVision daemons might fail to restart. These daemons will fail to restart while the Oracle database is restarting. The BroadVision One-To-One Enterprise resource will attempt to restart the failed daemons until it succeeds.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
