The Logical Architecture
A logical architecture identifies the Java Enterprise System components that provide the services described in a set of use cases. A logical architecture is typically represented graphically. The components needed for the evaluation use cases are illustrated in Figure 2–1.
Figure 2–1 Evaluation Deployment Logical Architecture
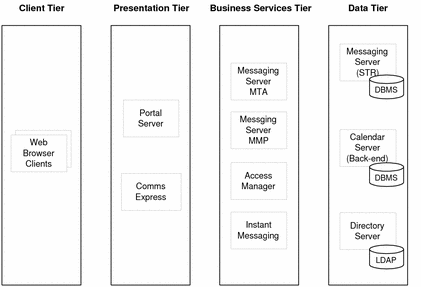
The components in Figure 2–1 are included in the logical architecture for the following reasons:
-
The portal services described in the use cases are provided by Portal Server. End users access the portal services through a web-based portal desktop. The web browser clients that appear at the far left, in the client tier, represent end users viewing the portal desktop in their web browsers. For the evaluation solution, you install a sample portal desktop.
-
Portal Server and several other web-based components must run in a web container. For the evaluation solution, you choose to install Web Server to provide the needed web container. AlthoughWeb Server does not directly provide any service, and is not shown in Figure 2–1, you do install it to provide web container support for Portal Server, Access Manager, Communications Express, and Instant Messaging.
-
End users access the mail and calender services described in the use cases through the web-based Communications Express interface. The web browser clients that appear at the far left, in the client tier, represent end users accessing Communications Express in their web browsers.
-
The mail services described in the use cases are provided by Messaging Server. Messaging Server has its own web container.
-
The calendar services described in the use cases are provided by Calendar Server. Calendar Server has its own web container.
-
The instant messaging services described in the use cases are provided by Instant Messaging.
-
The authentication and authorization services described in the use cases, including single sign-on and portal proxy authentication, are provided by Access Manager.
-
LDAP directory services are required to support the services described in the use cases. The LDAP services are provided by Directory Server. The LDAP directory stores configuration data about the other components, entries for administrative users, and entries for end users.
In Figure 2–1, the components are arranged in several tiers. The tiers represent the different roles that components play in the solution. In the evaluation solution, all of the tiers will be combined on a single computer system.
In a production solution, the roles that components play help you determine how to distribute your components and sub-components across your network, and how to configure them to interoperate with other software, such as stand-alone mail clients. For more information on the Java ES multi-tiered architecture, see Java Enterprise System Technical Overviewhttp://download.oracle.com/817-5764.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
