Routing through Proxy Arrays
For each request through a proxy array, a hash function assigns each proxy in the array a score that is based on the requested URL, the proxy’s name and the proxy’s load factor. The request is then routed to the proxy with the highest score.
Since requests for URLs can come from both clients and proxies, there are two types of routing through proxy arrays: client to proxy routing and proxy to proxy routing.
In client to proxy routing, the client uses the Proxy Auto Configuration (PAC) mechanism to determine which proxy to go through. However, instead of using the standard PAC file, the client uses a special PAC file which computes the hash algorithm to determine the appropriate route for the requested URL, Routing through Proxy Arrays shows client to proxy routing.
In Routing through Proxy Arrays, each member of the proxy array loads and polls the master proxy for updates to the PAT file. Once the client has a PAC file, it only needs to download this file again if the configuration changes. Generally, clients will download the PAC file at restart.
The proxy server can automatically generate the special PAC file from the Proxy Array Membership Table (PAT) specifications made through the administration interface.
In proxy to proxy routing, proxies use a PAT (Proxy Array Table) file to compute the hash algorithm instead of the PAC file used by clients. The PAT file is an ASCII file that contains information about a proxy array, including the proxies’ machine names, IP addresses, ports, load factors, cache sizes, etc. For computing the hash algorithm at the server, it is much more efficient to use a PAT file than a PAC file (which is a JavaScript file that has to be interpreted at run-time). However, most clients do not recognize the PAT file format, and therefore, must use a PAC file. Routing through Proxy Arrays shows proxy to proxy routing.
The PAT file will be created on one proxy in the proxy array - the master proxy. The proxy administrator must determine which proxy will be the master proxy. The administrator can change the PAT file from this master proxy server and all other members of the proxy array can then manually or automatically poll the master proxy for these changes. You can configure each member to automatically generate a PAC file from these changes.
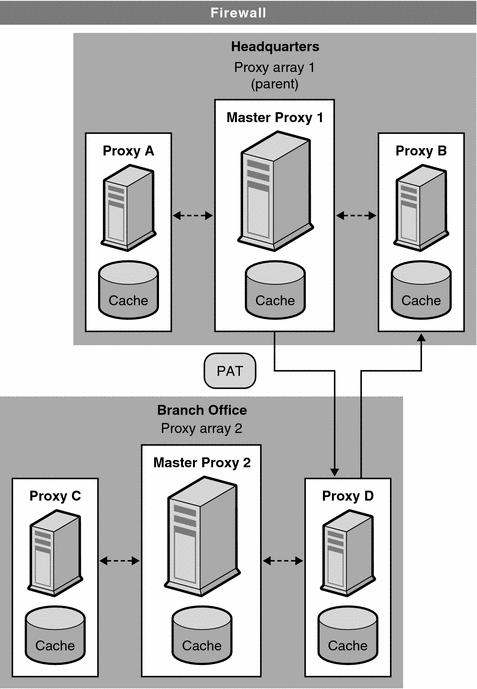
You can also chain proxy arrays together for hierarchical routing. If a proxy server routes an incoming request through an upstream proxy array, the upstream proxy array is then known as a parent array. A parent array is a proxy array that a proxy server goes through. In other words, if a client requests a document from Proxy X, and Proxy X does not have the document, it sends the request to Proxy Array Y instead of sending it directly to the remote server. So, Proxy Array Y is a parent array. In Routing through Proxy Arrays, Proxy Array 1 is a parent array to Proxy Array 2. A member of Proxy Array 2 loads and polls for updates to the parent array’s PAT file. Usually, it polls the master proxy in the parent array. The hash algorithm for the requested URL is computed using the downloaded PAT file and the member in the Proxy Array 2 then retrieves the requested URL from whichever proxy in Proxy Array1 that has the highest score. In Routing through Proxy Arrays, Proxy B has the highest score for the URL requested by the client.
Figure 12–4 Client to Proxy Routing
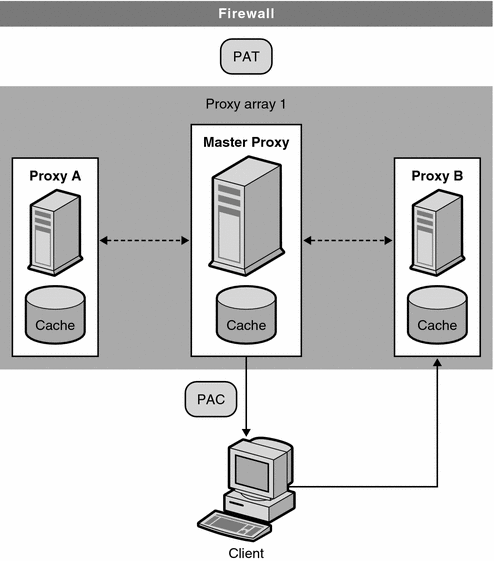
Figure 12–5 Proxy to Proxy Routing
 To set up a proxy array
To set up a proxy array
Steps
-
From the master proxy, do the following steps:
-
Create the proxy array. For more information on creating the member list, see Creating a Proxy Array Member List .
-
Generate a PAC file from your PAT file. You only need to generate a PAC file if you are using client to proxy routing. For more information on generating a PAC file from a PAT file, see Generating a PAC File from a PAT File .
-
Configure the master member of the array. For more information on configuring master members, see Configuring Proxy Array Members .
-
Enable routing through a proxy array. For more information on enabling routing through a proxy array, see Enabling Routing Through a Proxy Array .
-
Create a PAT mapping to map the URL “/pat” to the PAT file.
-
Enable your proxy array. For more information on enabling a proxy array, see Enabling a Proxy Array .
-
-
From each of the non-master proxies, do the following steps:
-
Configure the non-master member of the array. For more information on configuring non-master members, see Configuring Proxy Array Members
-
Enable routing through a proxy array. For more information on enabling routing through a proxy array, see Enabling Routing Through a Proxy Array.
-
Enable your proxy array. For more information on enabling a proxy array, see Enabling a Proxy Array .
Note –If your proxy array is going to route through a parent array, you also need to enable the parent array and configure each member to route through a parent array for desired URLs. For more information on parent arrays, see Routing through Parent Arrays.
-
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
