Inodes
An inode contains all the information about a file except its name, which is kept in a directory. An inode is 128 bytes. The inode information is kept in the cylinder information block, and contains:
-
The type of the file:
-
Regular
-
Directory
-
Block special
-
Character special
-
Symbolic link
-
FIFO, also known as named pipe
-
Socket
-
-
The mode of the file (the set of read-write-execute permissions)
-
The number of hard links to the file
-
The user ID of the owner of the file
-
The group ID to which the file belongs
-
The number of bytes in the file
-
An array of 15 disk-block addresses
-
The date and time the file was last accessed
-
The date and time the file was last modified
-
The date and time the file was created
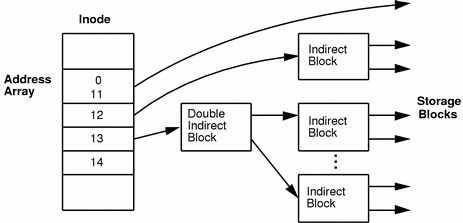
The array of 15 disk addresses (0 to 14) point to the data blocks that store the contents of the file. The first 12 are direct addresses; that is, they point directly to the first 12 logical storage blocks of the contents of the file. If the file is larger than 12 logical blocks, the 13th address points to an indirect block, which contains direct block addresses instead of file contents. The 14th address points to a double indirect block, which contains addresses of indirect blocks. The 15th address is for triple indirect addresses, if they are ever needed. The figure below shows this chaining of address blocks starting from the inode.
Figure 40-1 The File System Address Chain in a UFS System
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
