Chapter 4 Entering Korean Input
This section describes Korean Solaris mechanisms for typing Korean characters. All of the following character types can be entered:
-
ASCII/English
-
Hangul
-
Hanja
-
Special symbols
All of these character types can be entered in input regions of various application subwindows as follows:
-
Terminal emulation (TTY) windows, such as a Terminal
-
Text entry subwindows, such as those used by Text Editor or Mailer
-
Control panel subwindows, such as those used by File Manager for typing a file name
-
Other special use subwindows, such as pop-ups
Character Sets
Four types of coding conventions are currently supported in the Korean Solaris software:
-
N-byte code - This single-byte code has each byte represent a consonant or vowel. These are combined together to build Hangul characters.
-
Johap or Packed code - This two-byte code consists of a leading bit followed by three 5-bit fields. These three fields contain the codes or a leading consonant, followed by a vowel, followed by a final consonant (if any) for a Hangul character. This two-byte code is specified in Korean Industry Standard KS C 5601-1992-3.
-
Wansung code - This two-byte code is specified in Korean Industry Standard KS C 5601-1987 for Hangul, Hanja, and other characters. In the Korean Solaris software these KS C 5601-1987 characters are in EUC codeset 1.
-
ko.UTF-8 - Korean Universal Multiple Octet Coded Character Set (UCS) Transmission Format. ko.UTF-8 supports all the characters of KS C 5601 and 11,172 characters from Johap, as well as all Korean-related Unicode 2.0 characters and fonts. ko.UTF-8 supports the following subset of Unicode:
-
Basic Latin and Latin-i (190 characters) - Row 00 of BMP (Basic Multilingual Plan)
-
Symbolic characters - Row 20 to Row 27, and Row 32 of BMP including box (line) drawing characters that are defined in KS C 5601
-
Numerals that are defined in KS C 5601 (20 characters) - Row 21 and Row FF of BMP
-
Roman, Greek, Japanese, and Cyrillic alphabet characters that are defined in KS C 5601 (362 characters) - Row 02, Row 04, Row 30 and Row FF of BMP
-
Jamo (Hangul alphabet) characters (94 characters) - Row 31 of BMP
-
Pre-composed Hangul syllables (11,172 characters) - From Row AC to Row D7 of BMP
-
Hanja characters defined in KS C 5601 (4,888 characters) - From Row 4E to Row 9F and from Row F9 to Row FA of BMP
-
These four Korean code conventions Chinese code conventions at three levels of support:
-
User commands support file transfers for existing files in different codes.
-
Library functions support application development for existing codes.
-
STREAMS modules support existing TTY devices using different codes.
Input Window Areas
Three separate areas of an application subwindow are used in entering characters. These areas are typically displayed, named, and used as follows:
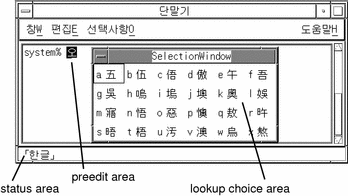
-
Preedit area--Highlighted (inverse video) entry display
-
Status area--Lower left corner input conversion mode display
-
Lookup choice area--Popup displaying multiple character or word choices
Preedit Area
The preedit area is a reverse video highlighted area that displays characters as they are entered or converted. It holds formations of characters before they are committed to the application, that is, before they are put in the text block being assembled for the application.
Status Area
The status area shows what the current input conversion mode is. Several modes are available, as discussed in following sections.
Lookup Choice Area
The lookup choice area is a popup that displays multiple Hanja or special character choices available for conversion of character(s) in the preedit area.
Entering and Converting Hangul/Hanja Characters
Each character type listed at the beginning of this chapter has its own input mode and input procedures, as described in following sections. The Control-key command combinations (initial default settings) for turning these modes and conversions on/off are listed in the table at the end of this chapter. The Back Space and Delete keys erase input (with peculiarities noted in the section "Backspacing and Deleting Characters" on page 31.)
ASCII/English Input Mode
The initial default setting is basic ASCII/English mode. Typing on the keyboard simply enters ASCII characters.
The status region in the lower left corner shows ASCII/English input mode:

Hangul Input Conversion Mode
The first step in entering any Korean character(s) is to turn on Hangul input conversion. Type Control-Space, or if you have a Hangul keyboard type the key labelled Hangul/English. (These keys toggle on/off Hangul input conversion.)
The status region then shows Hangul conversion on:

With Hangul input conversion on, typing appropriate sequences of keys composes Hangul characters in the preedit area on the screen.
Committing Hangul Input
The preceding preedit region contains five Hangul syllables that have not yet been committed. That is, they have not yet been added to the text block being assembled for the application.
These syllables could be committed to the application by typing Control-K. This nonprinting character is not committed in the input along with the syllables, for example:
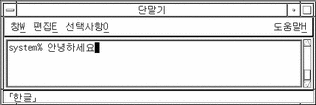

Otherwise these syllables could be committed by typing the Space bar or a number, punctuation mark, or other printable character that is not part of a valid Hangul character. Unlike Control-K, a printable character (like a question mark) is committed in the input along with the Hangul syllables, for example:

Converting to Hanja
Converting Hangul input to Hanja can be done in several ways, including character by character or word by word. The following examples and instructions go through the available ways step by step.
Hanja Character Step Mode
-
With Hangul input conversion on, type an appropriate sequence of keys to compose a Hangul character in the preedit area on the screen:
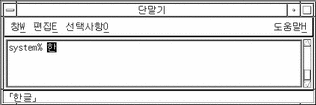
-
Type Control-N to convert it to a possible Hanja choice.
Typing Control-N again and again converts the Hangul character through the series of possible Hanja choices, one at a time (until the original Hangul reappears after all Hanjas have been displayed). Control-P converts back to the previous choice.

Committing a Hanja Choice
To choose and commit only the highlighted Hanja, type Control-K or any other nonprinting character except Control-N or Control-P. Then a new preedit area next to the just-committed Hanja is ready for the next Hangul input.
To commit the Hanja plus a space, number, punctuation mark, or other printable character, type the character's key. It and the highlighted Hanja are then both committed and a new preedit area next to the just-committed space, number, etc. is ready for the next Hangul input.
Hanja Character Lookup Choice Mode
-
With Hangul input conversion on, typing an appropriate sequence of keys composes a Hangul character in the preedit area on the screen:

-
Typing Control-W or the Hanja key on the keyboard displays a lookup choice area that contains possible Hanja choices:
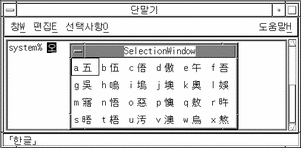
-
Typing Control-N displays the next lookup choice page if more choices are available. Control-P displays the previous page of choices.
Committing or Rejecting Hanja Choices
To choose and commit a Hanja choice, type the letter of the lookup area choice.
The chosen Hanja (for example, choice a) is then committed, and a new preedit area is ready for the next Hangul input:
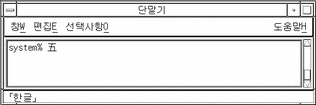
To abort the lookup choice mode without choosing a Hanja, type Control-A at any time. The preedit area then contains only unchanged Hangul input.
Hanja Word Conversion Modes
Hangul to Hanja conversion can be done also word by word just as it is done character by character (described in the preceding section). The steps for Hangul to Hanja word conversion are the same except conversion is not turned on until the preedit area contains a Hangul word.
Control-N (step mode) or Control-W (lookup choice mode) turns on Hanja conversion choices. The Hanja choices are a list of possible Hanja words plus a list of Hanja characters for only the last syllable of the Hangul word.
A display like the following appears after typing a Hangul word followed by Control-W:
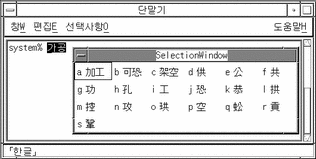
The above list contains three Hanja word choices and several choices for converting only the last syllable of the Hangul word.
The display for some Hangul words contains only single character Hanja choices for the last Hangul syllable. This happens when the Hangul-to-Hanja dictionary contains no corresponding Hanja word:
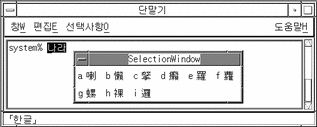
Entering Special Symbol Characters
Many non-Hangul/Hanja characters that cannot be typed directly on the keyboard can nevertheless be entered in the Korean Solaris operating environment. Two input modes very similar to the input modes described in preceding sections are available: hex code input and lookup choice.
Hex Code Input Mode
Any character with a hexadecimal code listed in KS C 5601 can be entered directly as follows. The KS C 5700 standard is supported by UTF-8 hexidecimal code. (The ko locale is used in the following example.)
The only keys that have any effect at this point are delete keys, letters a through f, numbers 0 through 9, and Control-X (which toggles hex mode off again).
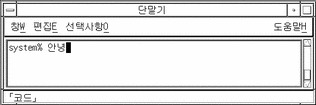
-
Type the first three keys of the hex code of the character, for example a2dd, in the preedit area.
The screen appears as follows after the first three numbers are typed:
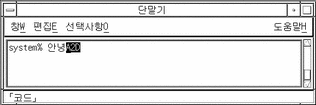
-
Type d.
The designated character is then displayed and automatically committed after the fourth number is typed:
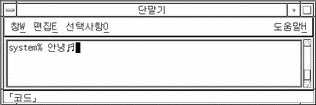
Hex mode remains on until toggled off by Control-X.
Special Lookup Choice Mode
This mode is another way to enter non-Hangul/Hanja characters that cannot be typed directly on the keyboard. It works the same as "Hanja Character Lookup Choice Mode" on page 23:
-
Typing Control-N or Control-P pages forward or back through the lookup choice area display
-
Typing the letter of the choice makes/commits the choice and returns to Hangul input mode
-
Typing Control-A at any time aborts the current lookup choice pages without choosing and returns to Hangul input conversion mode.
-
With Hangul input conversion on, type Control-J to display the page of category choices:
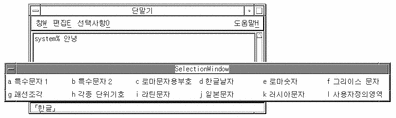
-
Type the letter of a category (a in the following example) to display the first page of choices:
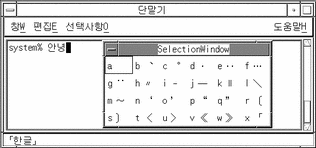
After Control-N has been typed nine times the following is displayed:
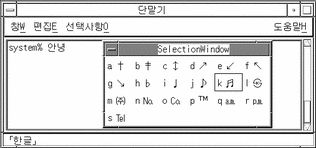
-
Type k to choose/commit the displayed character and return to Hangul input mode:
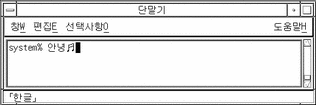
Backspacing and Deleting Characters
Backspace and Delete keys delete characters. But using one in the preedit area deletes only the last character (jamo) in the current syllable. This and following examples demonstrate Backspace/Delete operation.
-
Note the Hangul input mode preedit area appearance before backspacing:

-
Enter one backspace.
The input appears like this:

-
Type another backspace.
The input appears like this:
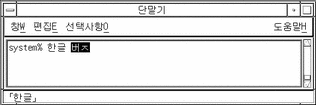
-
Type another backspace.
The input appears like this:

-
Type two backspaces.
At this point an entire syllable has been deleted.

- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates

