How Access Manager Works
When Access Manager starts up, it initializes the Access Manager information tree with configuration data. The configuration data comes from Access Manager service plug-ins including Authorization, Policy, Identity Repository Management, and Service Configuration plug-ins. By default, the Access Manager information tree resides in Sun Java System Directory Server, the same data store as the identity repository.
Figure 1–2 Basic Access Manager Installation
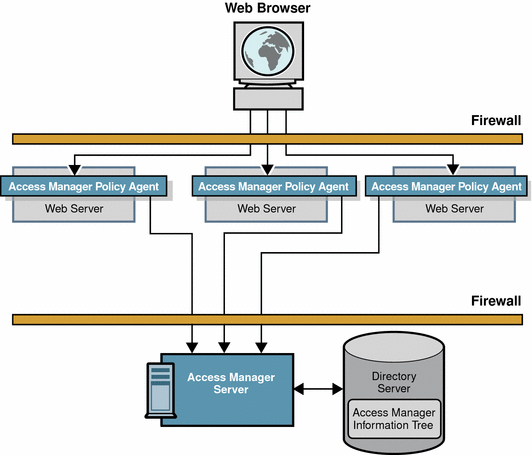
When a browser sends a request to access content or an application on a protected resource, Access Manager immediately binds to the appropriate Identity Repository to obtain user information. The user information may include definitions for roles, realms, user ids, and so forth. At the same time, a Policy Agent installed on the protected resource intercepts the initial HTTP request and examines the request. If no session token is found, the Policy Agent contacts the Access Manager server. Then Access Manager invokes authentication and authorization processes.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
