Monitoring Alerts
Enterprise Manager enables you to monitor alerts at runtime. You can perform the following tasks:
-
View alerts
-
Filter alerts
-
Delete alerts
For basic information about Enterprise Manager, see Enterprise Manager Basics.
Java CAPS provides an Alert Management API. For detailed information about the Alert Management API, see Java CAPS Management and Monitoring APIs.
Alerts Overview
An alert is triggered when a specified condition occurs in a Project component. The condition might represent a problem that must be corrected, or the condition might be informational.
The following table lists the predefined alerts for Sun Enterprise Service Bus. Each predefined alert is identified by a code, such as COL-00001. The alert also includes a description, such as Collaboration running.
Table 1–1 Predefined Alerts for Sun Enterprise Service Bus|
Code |
Description |
Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
|
COL-00001 |
The Collaboration is running. |
This alert does not indicate any malfunction. No user actions are necessary. |
|
COL-00002 |
The Collaboration stopped. |
No recommended action. |
|
COL-00003 |
Collaboration user-defined alert |
The recommended action depends on the purpose of the user-defined alert. |
|
MS-00009 |
The Message Server has reached the throttling threshold of total number of messages. |
For topics, you must wait for the subscribers to consume more messages. In the meantime, stop attempting to deliver messages to the JMS IQ Manager. For queues, you must wait for the receivers to consume more messages. In addition, you can try adding receivers to improve the throughput. If you can stop the runtime application and restart the application server, then increase the server throttling threshold. |
|
MS-00010 |
The Message Server has moved below the throttling threshold of total number of messages. |
No recommended action. |
|
MS-00011 |
The Message Server has reached the throttling threshold for message destinations. |
No recommended action. |
|
MS-00012 |
The Message Server has moved below the throttling threshold for message destinations. |
No recommended action. |
To view information about the predefined alerts for Adapters, see Alert Codes for Java CAPS Adapters.
Project developers can add custom alerts.
The initial status of an alert is Unobserved. You can change the status to Observed or Resolved. Observed indicates that you looked at and acknowledged the alert. Resolved indicates that you fixed the problem that caused the alert.
By default, alerts are not persisted to an external database. For information about configuring persistence, see Configuring Alert Persistence.
Viewing Alerts
You can view alerts at runtime. In addition, you can change the status of an alert.
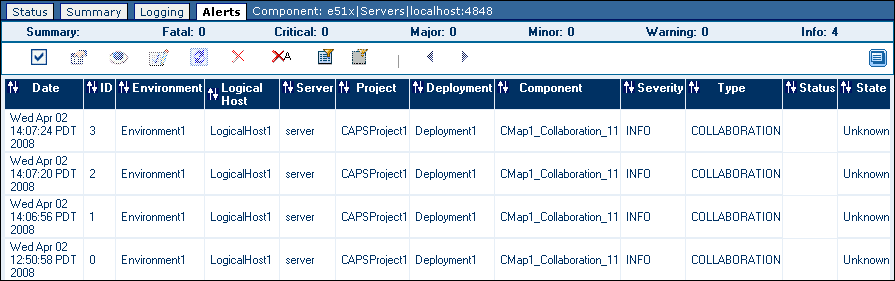
 To View Alerts
To View Alerts
-
In the Explorer panel of Enterprise Manager, select an application server, project component, or message server.
-
Click the Alerts tab or node.
The alerts for the selected component appear.
The summary row below the tabs displays the total number of alerts for each alert type (Fatal, Critical, Major, Minor, Warning, and Info).
The toolbar appears below the summary row.
-
By default, the alerts are sorted by date/time in reverse chronological order. To sort the alerts by different criteria, click the up/down arrows in the desired column.
-
To select all of the alerts, click the Select All icon.
-
To deselect the currently selected alerts, click the Select None icon.
 To View Alert Details
To View Alert Details
-
Either double-click the alert, or select the alert and click the View Details icon.
The Alert Details dialog box appears.
-
When you are done, click Close.
 To Change the Status of an Alert
To Change the Status of an Alert
-
Select the alert.
-
Click the Set Observed icon or Set Resolved icon.
You can also reset the status to Unobserved by clicking the Reset icon.
Filtering Alerts
You can control which alerts appear in Enterprise Manager.
 To Filter Alerts
To Filter Alerts
-
In the Explorer panel of Enterprise Manager, select an application server, project component, or message server.
-
Click the Alerts tab or node.
The alerts for the selected component appear.
-
Click the Filter icon.
The Alerts Filter dialog box appears. The fields that appear in the dialog box depend on the type of component that you selected in the Explorer panel.
-
Specify one or more fields.
-
Click Submit.
 To Remove the Filter
To Remove the Filter
Deleting Alerts
You can delete a single alert, or multiple alerts at a time.
 To Delete an Alert
To Delete an Alert
-
In the Explorer panel of Enterprise Manager, select an application server, project component, or message server.
-
Click the Alerts tab or node.
The alerts for the selected component appear.
-
Select the alert.
-
Click the Delete icon or press the Delete key.
A confirmation dialog box appears.
-
Click OK.
 To Delete More Than One Alert at a Time
To Delete More Than One Alert at a Time
-
Select the alerts that you want to delete.
-
To select all of the alerts, click the Select All icon.
-
To select alerts that may or may not be contiguous, use the CTRL key.
-
To select a contiguous range of alerts, click an alert at one end of the range, press the SHIFT key, and click the alert at the other end of the range.
-
-
Click the Delete icon or press the Delete key.
A confirmation dialog box appears.
-
Click OK.
 To Delete All Alerts For the Selected Component
To Delete All Alerts For the Selected Component
-
Click the Delete All icon.
A confirmation dialog box appears.
-
Click OK.
Note –If an alert does not currently appear because of a filter, then the alert is not deleted. See Filtering Alerts.
Configuring Alert Persistence
The alert persistence architecture includes the following databases.
-
Enterprise Manager's embedded database.
-
An external database that you can use to persist alerts. The external database contains one alert table per domain.
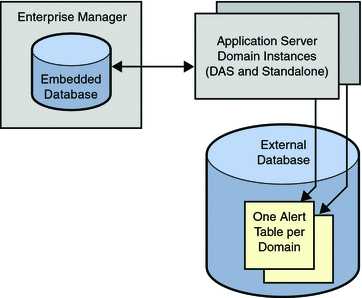
By default, alerts are not persisted to the external database. This topic describes how to enable persistence.
Be sure to understand the behavior of the various persistence configurations.
-
If persistence is disabled, then alerts are generated and sent to any monitoring instances that are currently running. The monitoring instances can include no more than one instance of Enterprise Manager, as well as any number of clients that use the Alert Management API. For detailed information about the Alert Management API, see Java CAPS Management and Monitoring APIs.
-
If persistence is enabled and journaling is disabled, then the alerts are stored temporarily in the external database. The system makes a best effort to send the alerts to all monitoring instances. When the reliable client indicates that it received an alert, the alert is deleted from the database.
There can be only one reliable client at a time. The most recent client to request reliable delivery becomes the reliable client. Enterprise Manager requests reliable delivery when you start the server. Clients that use the Alert Management API can request reliable delivery when they subscribe to the alert notification service.
Note –If the reliable client is shut down, then there is no reliable client until the next request for reliable delivery is made.
-
If persistence and journaling are both enabled, then alerts are stored permanently in the external database. When a client consumes an alert, the alert is not deleted from the database.
You can use any of the following database types for the external database. The Derby database is included with Sun Java System Application Server. The other database types are not included.
-
DB2
-
Derby
-
Oracle
-
PointBase
-
Sybase
If you want to use a database type other Derby, then you must perform additional configuration tasks. For example, you must use JavaTM DataBase Connectivity ("JDBCTM") software and the Java Naming and Directory InterfaceTM ("J.N.D.I.") API to set up access to the database.
For all database types, you must log in to the Configuration Agent and modify the alert notification fields.
 To Configure the Alert Table Name (Databases Other
Than Derby)
To Configure the Alert Table Name (Databases Other
Than Derby)
-
Open the eventmanagement.properties file in the JavaCAPS-install-dir/appserver/domains/domain-name/jbi/config directory.
-
If necessary, change the default value of the AlertTableName property and save the file.
You might need to change the default value to match your organization's naming conventions, or to comply with the database server's character limit for table names.
 To Set Up Database Access (Databases Other Than Derby)
To Set Up Database Access (Databases Other Than Derby)
-
Log in to the Sun Java System Application Server Admin Console.
-
Integrate the JDBC driver.
You can make the driver accessible to the common class loader or the system class loader.
For detailed information about how to integrate a JDBC driver, click Help in the Admin Console.
-
In the left pane, expand the Resources node and the JDBC node, and select the Connection Pools node.
-
Click New.
-
Create the JDBC connection pool.
For detailed information about how to create a JDBC connection pool, click Help in the Admin Console.
-
In the left pane, select the JDBC Resources node.
-
Click New.
-
Create the JDBC resource.
You will enter the JNDI name of the JDBC resource in a later procedure.
Set the pool name to the JDBC connection pool that you just created.
For detailed information about how to create a JDBC resource, click Help in the Admin Console.
 To Run the Database Scripts (Databases Other Than
Derby)
To Run the Database Scripts (Databases Other Than
Derby)
-
Open the jbi_rt.jar file in the JavaCAPS-install-dir/appserver/jbi/lib directory.
-
Extract the SQL scripts for your database type.
-
If you are using Oracle, then create the tablespace and user that will be used to persist alerts.
-
Create the table that will be used to persist alerts.
 To Log In to the Configuration Agent
To Log In to the Configuration Agent
-
If the application server is not running, then start the application server.
-
In a browser, enter the following URL:
http://hostname:portnumber/configagent
Set the hostname to the TCP/IP host name of the computer where the application server is installed. Set the port number to the administration port number of the application server. For example:
http://myserver.company.com:4848/configagent
The Configuration Agent Security Gateway appears.
-
In the User ID field, enter an application server user name.
-
In the Password field, enter the corresponding password.
-
Click Login.
The Configuration Agent appears.
 To Modify the Alert Notification Fields
To Modify the Alert Notification Fields
-
Ensure that the database is running.
-
In the Configuration Agent, click the Alert Management Configuration tab.
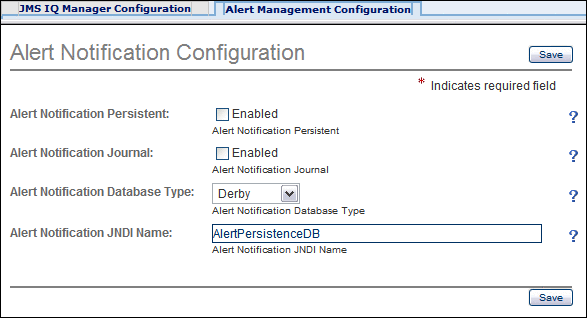
-
Select the Enabled check box to the right of the Alert Notification Persistence label.
-
If you want to enable journaling, then select the Enabled check box to the right of the Alert Notification Journal label.
-
Select the database type from the Alert Notification Database Type drop-down list.
-
If you are using a database other than Derby, then set the JNDI name to the JNDI name of the JDBC resource that you created.
-
Click Save.
-
Restart the application server domain.
Archiving Alerts
You can archive the alerts in Enterprise Manager's embedded database. The archive process writes the alerts to .csv files in the JavaCAPS-install-dir/emanager/EventRepositoryDb directory.
The eventdb_archive.properties file in the JavaCAPS-install-dir/emanager/server/shared/classes directory enables you to configure the archive process. The following table describes the properties.
Table 1–2 Alert Archive Properties|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
GROUP_MAX_COUNT |
A group is a set of alerts that have the same values for the following fields: Environment, Physical Host, Logical Host, Server, Deployment, Component, and Message Code. This property specifies the maximum number of alerts that can be in a group. When the number is exceeded, the oldest rows exceeding this number are archived. If the value is 0, then the archive process ignores this property. |
|
MAX_TIME_DELTA_FOR_ARCHIVE |
The maximum amount of time (in milliseconds) that can elapse between archive operations. If the value is 0, then the archive process ignores this property. |
|
MAX_EVENT_COUNT_FOR_ARCHIVE |
The archive process is run when this number of alerts is reached. If the value is 0, then the archive process ignores this property. |
|
MAX_AGE_OF_EVENTS |
When the archive process is run, alerts that exceed this age limit (in milliseconds) are archived. If the value is 0, then the archive process ignores this property. |
|
MAX_ROWCOUNTLIMIT_IN_ARCHIVE_FILE |
The maximum number of records that can be stored in a .csv file. When this number is reached, the archive process creates a new .csv file. |
If you change the value of one or more properties, then you must restart the Enterprise Manager server in order for the changes to take effect. See Enterprise Manager Basics.
Reducing Duplicate Alerts
In certain situations, a large number of alerts can be generated in a short period of time. For example, a system goes down and messages are repeatedly attempted to be processed.
You can use a property to reduce the number of alerts that appear. The property value is expressed in milliseconds. The default value is 5000, which equals 5 seconds. If multiple instances of an alert arrive during this period of time, then only one instance of the alert will appear.
A string is added to the beginning of the alert details field. The string indicates the number of duplicate alerts that were processed. For example:
[3x] Collaboration CMap1_jcdFileToJMS1 is RUNNING |
 To Reduce Duplicate Alerts
To Reduce Duplicate Alerts
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
