Understanding the HTTPS OTD
This section helps you understand the functionality of HTTPS OTD.
HTTPS Client OTD
The HTTPS OTD is specific to the HTTPS Adapter. It is used as an inbound or outbound OTD in a Collaboration.
OTDs have a tree-like hierarchical data structure composed of fields containing methods and properties.
The top root element of the OTD is the HTTPClientApplication interface, and the fields underneath contain Java methods. You can use these Java methods to create Business Rules that specify the HTTP message format and invoke messaging to and/or from an HTTP server.
To access other Java classes and methods, you can use the Collaboration Editor (Java) to utilize the entire contents available for HTTPClientApplication.
HTTP OTD Method Descriptions
The HTTP OTD includes the following methods used in HTTP data exchange:
- get
-
The method called in the Collaboration (Java) to send an HTTP get request to an HTTP server.
- post
-
The method called in the Collaboration (Java) to send an HTTP post request to an HTTP server.
- getRequest
-
The method called in the Collaboration (Java) for other “request” related helper methods, such as to set the URL, to add properties, and so on.
- getResult
-
The method called in the Collaboration (Java) for other “respond” related helper methods, such as, to obtain the respond code, respond result, text result, and so on.
For more information on methods available in the HTTP OTDs, see the HTTPS Adapter’s Javadoc.
HTTPS Server OTD
The HTTPS Server input OTD has two nodes, Request and Response. The Request node contains the data that the HTTPS Server adapter receives from an HTTP client, while the Response node is used to set the HTTP response data that will be sent back to the HTTP client.
Figure 1–1 Input Server OTD
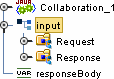
Figure 1–2 Input Server Request Node
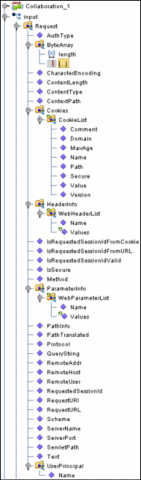
Figure 1–3 Input Server Response Node
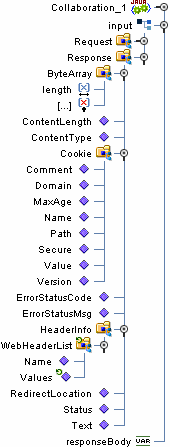
Working With the Server OTD
Use the OTDs Request and Response nodes to build the logic in your HTTPS Collaborations. The HTTP response is not sent back to the HTTP client until sendResponse() method is called on the HTTP server input OTD.
Figure 1–4 sendResponse() Method
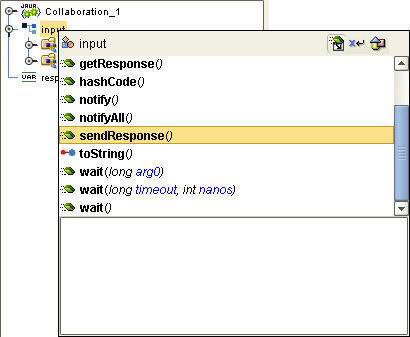
It is critical that you use this method to send the response back to the client. Otherwise, the client will wait indefinitely for the response. HTTP requires that a response be sent to the client whether the response is a valid application response or an application error response.
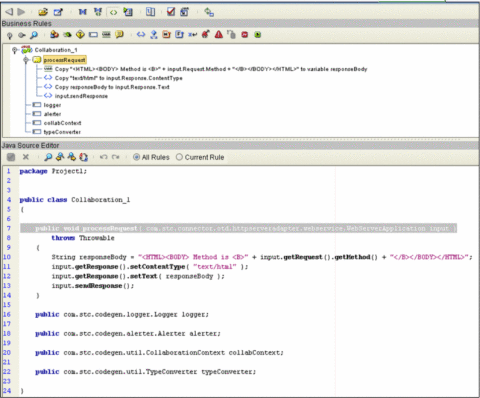
Collaboration Example
The following example shows a simple Java Collaboration that retrieves the HTTP method from the Request node through the Method property. This creates an HTML response indicating the HTTP method. This method is retrieved from the request, sets the ContentType property as “text/html” on the Response node. It then sets the Text property with the HTML response, and then calls the sendResponse() method. This is called on the HTTP server input OTD to send the constructed response to the HTTP client.
Figure 1–5 sendResponse() Example
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
