Oracle Table Data Types
Oracle tables support the following data types:
-
Real - an approximate numeric data type.
-
Float - a data type where all platforms have values of the least specified minimum precision.
-
CLOB - a built-in data type that stores a Character Large Object as a column value in a row of a database table.
For all others, use the data types Float, Double, or CLOB and build them using a data type of “Other”.
Note –
The Oracle driver does not support the boolean and PL/SQL RECORD datatypes in the Function and Stored Procedure.
Long RAW for Prepared Statements and Stored Procedure support:
The following two parameters must be set prior to the Insert/Update/Delete statement.
setConcurrencyToReadOnly() setScrollTypeToForwardOnly() |
Using CLOBs
To use a CLOB in the Oracle Adapter, do the following:
-
In the Enterprise Designer, right-click on the project, select Import. From the submenu, select File. The Import File dialog box appears.
-
From
<Client_eDesigner>\usrdir\modules\ext\oracleadapter, create a copy of the ojdbc14.jar in the directory and rename it classes12.jar .
-
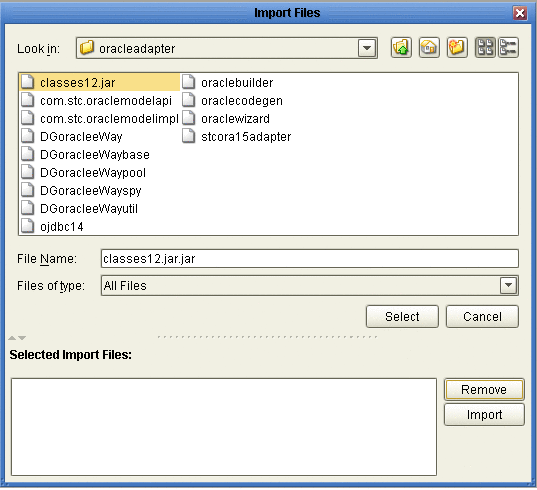
Navigate to the classes12.jar file,
<Client_eDesigner>\usrdir\modules\ext\oracleadapter\ classes12.jar using the Enterprise Designer’s Project File Import feature (see
-
Click Select.
-
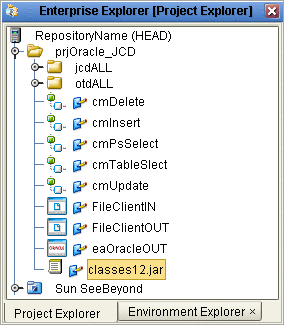
Click Import. The classes12.jar file appears, as shown in Using CLOBs.
-
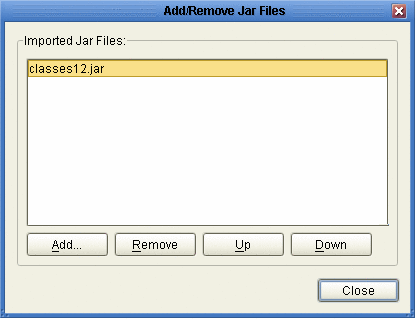
To load the classes12.jar file into your Java Collaboration, select the Import JAR File button. Click Add in the Add/Remove Jar Files window to add the Jar files (see Using CLOBs).
-
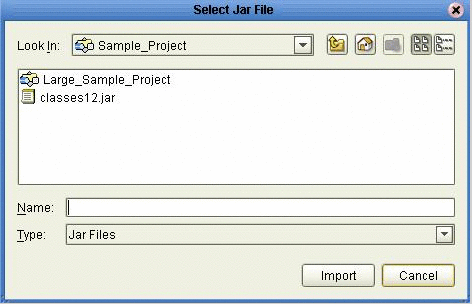
In the Select Jar File window, select the classes12.jar file and click Import (see Using CLOBs).
-
In the Add/Remove Jar Files window, click Close.
-
In the Business Rules Designer, call the CLOB method by clicking the Class Browser button. The Class Browser dialog box appears (see Using CLOBs).
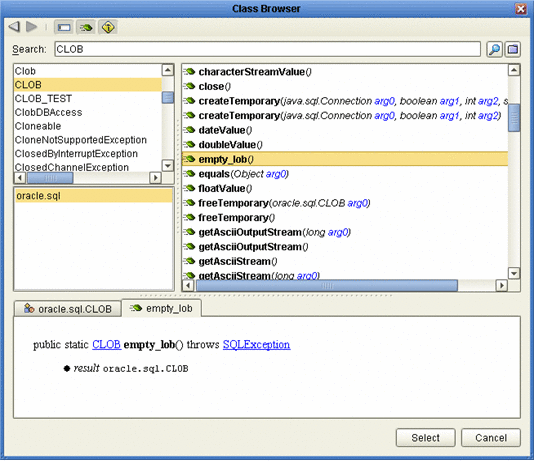
-
Select empty_lob from the list of CLOB variables and click Select.
-
Create a local variable by clicking the Local Variable button on the Business Rules toolbar. The Create Variable dialog box is displayed. (see Using CLOBs).
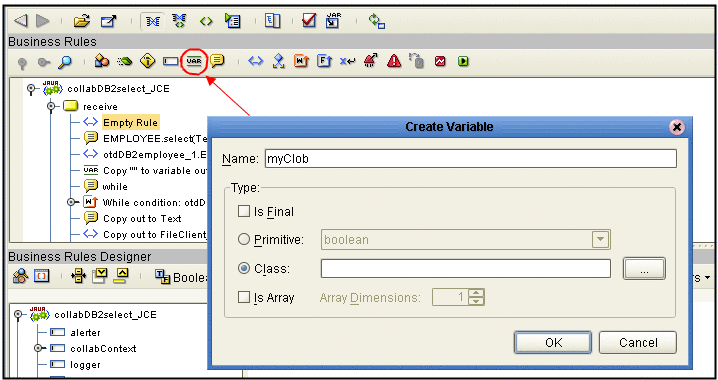
-
Name the variable myCLOB, select the Class type, and choose CLOB as the Class type.
-
Click OK to create the variable.
-
In the Business Rules Designer, drag the CLOB to the Local Variable using the Cast method. Click Yes when the incompatible Data Type warning appaers (see Using CLOBs).
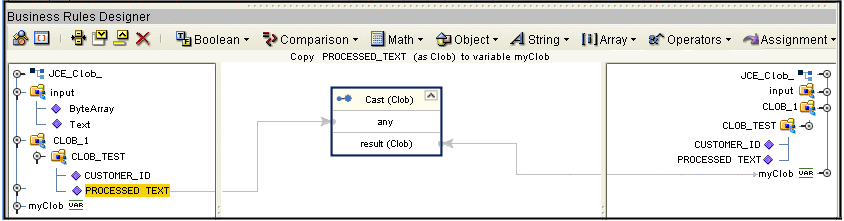
-
Use the CLOB putString method to assign 1 to Arg().
-
In the Java Collaboration Editor, the Java code resembles the following:
public void receive( com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage input,cLOB. CLOBOTD CLOB_1 ) throws Throwable { //@map:CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST.insert CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST().insert(); //@map:Copy java.math.BigDecimal.valueOf(100) to CUSTOMER_ID CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST().setCUSTOMER_ID( java.math.BigDecimal. valueOf( 100 ) ); //@map:Copy oracle.sql.CLOB.empty_lob to PROCESSED_TEXT CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST().setPROCESSED_TEXT( oracle.sql.CLOB.empty_lob() ); //@map:CLOB_TEST.insertRow CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST().insertRow(); //@map:CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST.select("customer_id = 100 for update") CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST().select( "customer_id = 100 for update" ); //If if (CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST().next()) { //@map:oracle.sql.CLOB myClob; oracle.sql.CLOB myClob; //@map:Copy cast PROCESSED_TEXT to oracle.sql.CLOB to myClob myClob = (oracle.sql.CLOB) CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST().getPROCESSED_TEXT(); //@map:myClob.putString(1,Text) myClob.putString( 1,input.getText() ); //@map:CLOB_TEST.updateRow CLOB_1.getCLOB_TEST().updateRow(); } }
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
