Sun Data Integrator
Extraction, transform, and load (ETL) is a data integration method that extracts data from various data sources, transforms the data into a common format, and then loads the data format into one or more target data sources. ETL processes bring together and combine data from multiple source systems into a data warehouse, enabling all users to work off a single, integrated set of data — a single version of the truth.
The following topics provide information about Sun Data Integrator and its components.
Sun Data Integrator Overview
Sun Data Integrator manages and orchestrates high-volume, high-performance data transformation from within the SOA tier. It is optimized for extracting, transforming, and loading bulk data between files and databases and provides connectivity to a vast range of heterogeneous and diversified data sources, including non-relational data sources. It is optimized for handling very large record sets. The Sun Data Integrator development and runtime environments are fully integrated into Open ESB, NetBeans Enterprise Pack, and Java CAPS.
You can use Sun Data Integrator to for many purposes. You might need to acquire a temporary subset of data for reports or other purposes, or you might need to acquire a more permanent data set in order to populate a data warehouse. You can also use Sun Data Integrator for database type conversions or to migrate data from one database or platform to another.
Sun Data Integrator applies the following ETL methodology:
-
Extract – The data is read from specified source databases or flat files and a specific subset of data is extracted. With Sun Data Integrator, the data can be filtered and joined from multiple, heterogeneous sources.
-
Transform – The extracted data is converted from its previous form into the proper form to be placed into a target database. Transformation occurs by using rules or lookup tables or by combining data from multiple sources.Sun Data Integrator applies the operators specified for the process to transform and cleanse data to the desired state.
-
Load – The transformed data is loaded into one or more target databases or data warehouses.
Sun Data Integrator Features
Sun Data Integrator provides your business with a powerful assortment of design-time features that you can use to create and configure ETL processes. The runtime features allow you to monitor the ETL processes and to review any data errors.
Sun Data Integrator provides the following features:
-
Stores all data transformation logic in one place and enables users, managers, and architects to understand, review, and modify the various interfaces.
-
Generates a schema based on the master index object structure in order to extract data from legacy systems and load it into a staging database for cleansing and analysis.
-
Can integrate with a wide variety of source data types, including HTML, XML and RSS.
-
Simplifies and standardizes ETL processes, requiring little database expertise to build high performance ETL processes.
-
Automatically discovers metadata, enabling you to design ETL processes faster.
-
Loads data warehouses faster by taking advantage of database bulk, no-logging tuning where applicable.
-
Supports creating automatic joins based on primary key and foreign key relationship, and create the code to ensure data integrity.
-
Takes advantage of the database engine by pushing much of the workload on to the target and source databases.
-
Supports extensive non-relational data formats.
-
Provides transform, filter, and sort features at the data source where appropriate.
-
Provides data cleansing operators to ensure data quality and a dictionary-driven system for complete parsing of names and addresses of individuals, organizations, products, and locations.
-
Provides the ability to normalize and denormalize data.
-
Converts data into a consistent, standardized form to enable loading to conformed target databases.
-
Provides build-in data integrity checks.
-
Allows you to define customized transformation rules, data type conversion rules, and null value handling.
-
Provides a robust error handler to ensure data quality, and a comprehensive system for reporting and responding to all ETL error events. Sun Data Integrator also provides automatic notification of significant failures.
-
Supports concurrent and parallel processing of multiple source data streams.
-
Supports full refresh and incremental extraction.
-
Supports data federation that enables you to use SQL as the scripting language to define ETL processes.
-
Supports near real-time click-stream data warehousing (in conjunction with the JDBC Binding Component (BC)).
-
Supports ERP/CRM data sources (in conjunction with various components from OpenESB or Java CAPS).
-
Is platform independent, and can be scaled to enterprise data warehousing applications.
-
Provides built-in transformation objects so you can easily specify complex transformations.
-
Supports scheduling of ETL session based on time or on the occurrence of a specific event.
-
Participates as a partner with BPEL business processes by exposing the ETL process as a web service.
-
Is able to extract data from outside a firewall in conjunction with the FTP BC and the HTTP BC.
-
Provides analysis of transformations that failed or were rejected and then allows for resubmitting them after the data is corrected.
Sun Data Integrator Architecture
The Sun Data Integrator design-time components allow you to specify the data source and target databases, map source fields and columns to target fields and columns, define custom processing, and test and validate the ETL collaboration. Design-time components include the NetBeans project system, a wizard to guide you through creating and configuring an ETL process, and a mapping editor where you can map source and target data and customize the transformation.
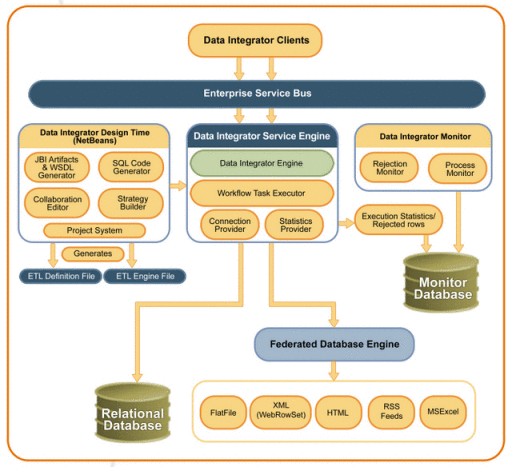
The runtime components include monitors to view the status of ETL processes and any rejected data. The Data Integrator Engine execute the ETL process. The following diagram shows the Sun Data Integrator components and their relationship to one another. Data Integrator clients could include technologies such as web services, Java EE or .Net applications, reporting tools, or MDM applications, such as Sun Master Index.
Figure 7 Data Integrator Architecture
Sun Data Integrator Development Phase
The development phase consists of standard tasks for specifying source and target databases and advanced tasks for further customizing the data transformation logic.
Standard Development Tasks
The following steps outline the basic procedure for developing an ETL process using Sun Data Integrator.
-
Connect to the source and target databases from the Services window in NetBeans.
-
Create a new Data Integrator Module project in NetBeans.
-
Using the Data Integrator Wizard, specify the source database and tables and the target database and tables.
-
Using either the Data Integrator Wizard or the ETL Collaboration Editor, specify join conditions and map the source fields or columns to the target fields or columns.
-
Specify the execution strategy.
-
Add the ETL service to a composite application.
-
Build and deploy the composite application.
Advanced Development Tasks
You can perform additional tasks during the development phase to customize your ETL application further.
-
Customized Data Transformation – Use data transformation operators to define advanced standardization and cleansing rules for the source data.
-
Master Index Staging – Create a staging database populated with the initial bulk data that will be loaded into a new master index application. The staging database is used by the master index Data Cleanser and Data Profiler prior to loading the data.
-
ETL Process Integration - Call an ETL collaboration from a BPEL business process, web service, Java client, or other application.
-
Extraction Scheduling - Configure a time or event that triggers a data extraction from the data source. You can extract data in batch mode or continuously based on database triggers.
-
Parallel Processing - Configure the ETL process to run on multiple threads for better performance and faster execution.
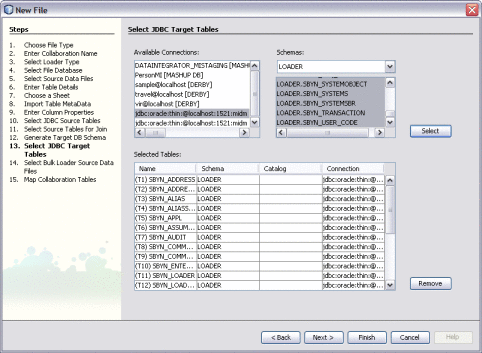
Data Integrator Wizard
The Data Integrator Wizard takes you through each step of the ETL setup process and, based on the information you specify, creates a collaboration that defines the configuration of the ETL process.
Figure 8 Select Target Table on the Data Integrator Wizard
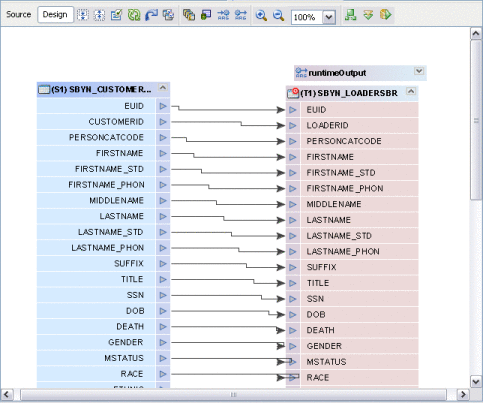
ETL Collaboration Editor
Once you define the data integration framework using the wizard, you use the ETL Collaboration Editor to further customize its configuration.
Figure 9 ETL Collaboration Editor
Sun Data Integrator Runtime Phase
Once all of the development tasks are complete and the system is running, you can perform any of these maintenance tasks.
-
Automatically connect to the predefined data sources and execute the ETL collaboration at specified times or when specific event occurs.
-
Monitor and manage activities and alerts in the application server logs
-
Modify the configuration of the ETL collaboration.
Monitoring and Maintenance
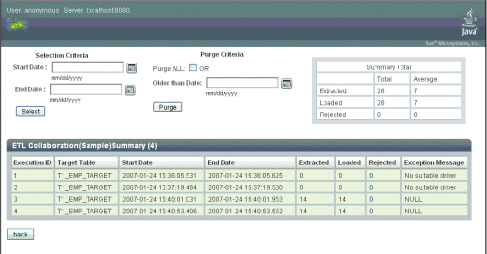
You can monitor ETL collaborations using the ETL Monitor, which is deployed on the application server Admin Console. The monitor allows you to specify a date range of events to monitor and also provides a purge function so you can remove outdated or obsolete events. For each event, the monitor displays the target table, start and end dates, the number of records extracted and loaded, the number of rejected records, and any exception messages. You can also view a summary, and drill down into the details of rejected records.
Figure 10 ETL Monitor on the Admin Console
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
