Mapping Examples
These examples illustrate several mapping scenarios:
Assign Activity Scenario
Assume that you want a BPEL process to copy data received from a partner. Do the following tasks:
-
Add an Assign activity after the Receive activity.
-
Use the BPEL Mapper to define one or more copy assignments. To open the BPEL Mapper, double-click the Assign activity on the diagram or select the Mapper tab on the toolbar.
The following example shows a copy assignment that does not use any XPath functions. The itinerary part of the ItineraryIn variable is copied to the itinerary part of the ItineraryOut variable. Notice that the left pane and the right pane contain the same tree component.

The following example shows a copy assignment that uses the concat XPath function. The input variable paramA is concatenated to the end of the string literal Parameter A: and copied to the output variable paramA.

If Activity Scenario
Assume that you want to execute a series of steps only if a certain condition is true. Do the following tasks:
-
Add an If activity to the BPEL process.
-
Use the BPEL Mapper to define the Boolean condition. To open the BPEL Mapper, double-click the If activity on the diagram or select the Mapper tab on the toolbar.
-
Add the steps inside the If activity.
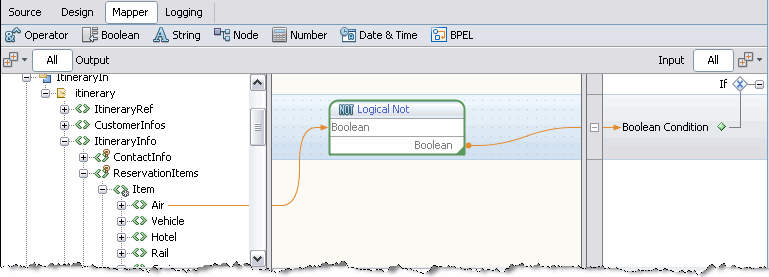
The following example shows a mapping for the condition. The mapping uses the Not XPath function, which is available from the Boolean node on the menu bar. If the itinerary has an airline reservation, then the Not XPath function returns true. The result is mapped to the Result node in the right pane.
Predicate Scenario
Assume that you want a BPEL process to copy itinerary data from itineraries of customers with no more than two in their party. The input records include a variable that specifies the number of passengers in the customer's party. Do the following tasks:
-
In the left pane of the BPEL Mapper window, right-click the repeating node that is marked with an asterisk (*) and choose New Predicate.
The Predicate Editor window appears.
-
Add the Less XPath function to the middle pane.
-
Add the number literal XPath function to the middle pane. Set the value to 3.
-
Map the variable node to the first argument of the Less XPath function.
-
Map the result of the number literal XPath function to the second argument of the Less XPath function.
-
Map the result of the Less Than XPath function to the Result node in the right pane.
-
Click OK.
The following example shows how the mapping appears in the Predicate window. Once you click OK, you can use the predicate node in a copy assignment.

If the BPEL process received the following XML, then the predicate would select the first Air tag.
<Air>
<NumberInParty>2</NumberInParty>
</Air>
<Air>
<NumberInParty>4</NumberInParty>
</Air>
<Air>
<NumberInParty>6</NumberInParty>
</Air>
|
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
