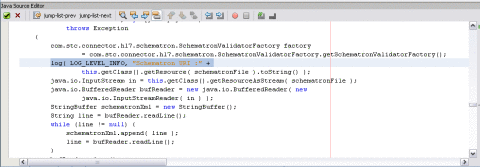
Validating With Schematron Method
The Schematron method invokes the Schematron API. It reads the schematron files from classpath and constructs a DOM source. The DOM source passes it to obtain the SchematronValidator object. The object invokes the validate() method to pass the hl7payload.
validateWithSchematron() method
private com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.
ValidationOutput validateWithSchematron( String
schematronFile, byte[] hl7payload )
throws Exception
{
com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.SchematronValidatorFactory
factory =
com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.SchematronValidatorFactory.
getSchematronValidatorFactory();
log( LOG_LEVEL_INFO, "Schematron URI :" +
this.getClass().getResource( schematronFile ).toString() );
java.io.InputStream in = this.getClass().
getResourceAsStream( schematronFile );
java.io.BufferedReader bufReader = new java.io.
BufferedReader( new
java.io.InputStreamReader( in ) );
StringBuffer schematronXml = new StringBuffer();
String line = bufReader.readLine();
while (line != null) {
schematronXml.append( line );
line = bufReader.readLine();
}
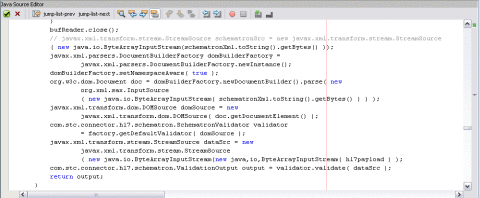
|
bufReader.close(); |
javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory domBuilderFactory = javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory. newInstance(); domBuilderFactory.setNamespaceAware( true ); org.w3c.dom.Document doc = domBuilderFactory. newDocumentBuilder().parse( new org.xml.sax.InputSource( new java.io.ByteArrayInputStream ( schematronXml.toString().getBytes() ) ) ); javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource domSource = new javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource( doc. getDocumentElement() ); com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.SchematronValidator validator = factory.getDefaultValidator( domSource ); javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamSource dataSrc = new javax.xml. transform.stream.StreamSource( new java.io.ByteArrayInputStream( hl7payload ) ); com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.ValidationOutput output = validator.validate( dataSrc ); return output; } |
The illustrations are as shown.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
