Creating a BPEL Module Project
The proceeding sections describe the steps used to create a simple BPEL Module project. To demonstrate the procedures we are using the Synchronous sample project.
Accordingly, the typical procedure to follow when building a BPEL process is:
-
Creating a new BPEL Module Project using the New Project wizard. Creating the BPEL module project also includes:
-
Creating an XML Schema using the XSD Editor.
-
Creating the WSDL Documents using the New WSDL Editor.
-
Create the BPEL Processes using the BPEL Designer.
-
-
Creating a Composite Application Project.
When new projects are created using the sample projects that are included with GlassFish, the Composite Application projects are created automatically. When you create a project from scratch, you need to create the Composite Application project manually.
-
Add JBI Modules to the Composite Application project.
-
(Optional) Build the Composite Application project and make sure that the Application Server is started.
-
Build and Deploy the Composite Application Project to the BPEL Service Engine.
-
For sample processes, test cases are automatically created; for new projects, you need to create at least one test case.
-
Run one or all test cases.
-
(Optional) Debug the BPEL process.
Software Requirements and Installation
The following sections walk you through the Synchronous sample project to demonstrate the steps involved in creating and running a BPEL Module project.
It is assumed that you have installed the following:
-
GlassFish ESB Installation, which includes the following:
-
GlassFish v2 Update Release 2 (UR2)
-
NetBeans IDE 6.1 ML
-
Open ESB core components
-
Java Business Integration (JBI) service engines
-
Java Business Integration (JBI) binding components
-
Java Business Integration (JBI) component tooling
-
Note –
You must have the JDK (Java Development Kit) software installed and JAVA_HOME set prior to installing GlassFish ESB or the Installer will halt the installation. See Installing the JDK Software and Setting JAVA_HOME for details.
To get the latest installation of GlassFish ESB, see GlassFish ESB Downloads.
To download Shared Libraries, JAR files, or NetBeans-module files for BPEL SE, see BPEL Service Engine Downloads.
Starting GlassFish
The BPEL Service Engine starts together with GlassFish. Before deploying and performing test runs of a Composite Application project in the NetBeans IDE, make sure that the GlassFish Application Server is started.
 To check the Status of the GlassFish V2 Application
Server in the NetBeans IDE
To check the Status of the GlassFish V2 Application
Server in the NetBeans IDE
-
If the Services window is not visible, choose Window -> Services.
-
In the Services window, expand the Servers node.
The Servers node should contain a GlassFish V2 subnode. If the GlassFish V2 node does not appear, go to To Register the GlassFish V2 Application Server with the NetBeans IDE:
If a green arrow badge appears on the GlassFish V2 node, the server is running. If a green arrow badge does not appear, go to To Start the GlassFish V2 Application Server in the NetBeans IDE.
 To Register the GlassFish V2 Application Server with
the NetBeans IDE
To Register the GlassFish V2 Application Server with
the NetBeans IDE
-
If the Services window is not visible, choose Window -> Services.
-
In the Services window, right-click the Servers node and choose Add Server from the pop-up menu.
The Add Server Instance dialog box opens.
-
In the Choose Server page of the dialog box, select GlassFish V2 from the Server field.
The Add Server Instance dialog box opens.
-
(Optional) In the Name field, change the default name for the server.
The IDE uses this name to identify the server.
-
Click Next.
The Platform Location Folder page opens.
-
In the Platform Location field, click Browse and select the installation location of the application server.
-
Select the Register Local Default Domain radio button and click Next.
-
Enter the user name and password for the domain's administrator.
If you accepted the default values during the installation, the user name is admin and the password is adminadmin.
-
Click Finish.
 To Start the GlassFish V2 Application Server in the
NetBeans IDE
To Start the GlassFish V2 Application Server in the
NetBeans IDE
-
In the Services window, right-click the GlassFish V2 node and choose Start.
-
Wait for the following message to appear in the Output window:
Application server startup complete.
When the server is running, the IDE displays a green arrow badge on theGlassFish V2 node.
The BPEL Service Engine is represented as sun-bpel-engine in the Services window of the IDE, under the GlassFish V2 -> JBI nodes.
Creating a new BPEL Module Project
The following sections use the Synchronous sample project, and provide step-by-step directions for creating a simple BPEL module project, using the Synchronous sample project.
 Create a BPEL Module project
Create a BPEL Module project
-
In the NetBeans IDE, choose File > New Project.
The New Projects wizard appears.
-
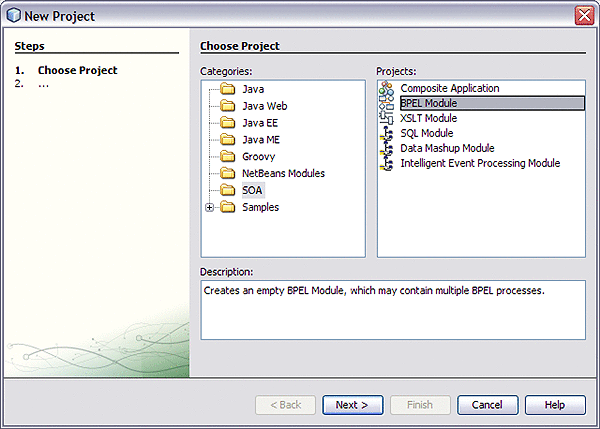
Under Categories, select Service Oriented Architecture.
-
Under Projects, select BPEL Moduleand click Next.
-
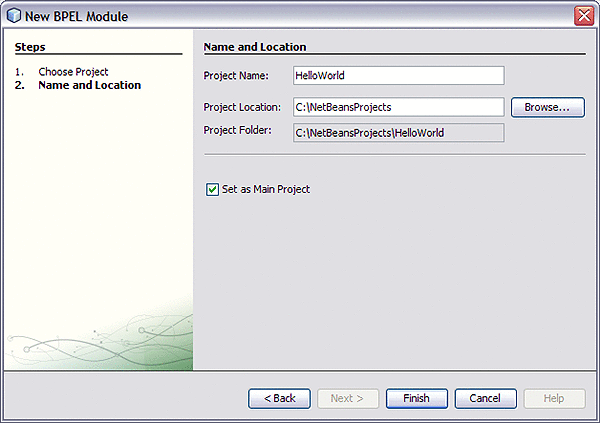
In the Name and Location page, enter the project name (for this example HelloWorld) and specify the project location or accept the defaults.
-
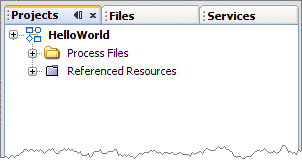
Click Finish.
The Projects window now contains a project node for the BPEL Module project.
Creating the XML Schema and the WSDL Document
-
Create a New BPEL Project
-
Create the XML Schema or XSD file
-
Create the WSDL Documents
-
Create the BPEL Process
Generally, the steps used to create a BPEL module project are:
The XSD file (XML Schema) helps to define the projects message structure or operations. Complex message structures are defined in the XSD file and imported into the WSDL Document. The WSDL Documents define the interfaces for the project. The BPEL Designer enables you to graphically design your BPEL business process.
To create the XML Schema and WSDL Document for this tutorial, following the directions provided in Creating a “Hello World” Composite Application. After you have created the XML Schema and WSDL, return here.
Creating a BPEL Process Using the BPEL Designer
Now that you have created your XML Schema and WSDL Document, you can create your BPEL process.
 Create the BPEL Process
Create the BPEL Process
-
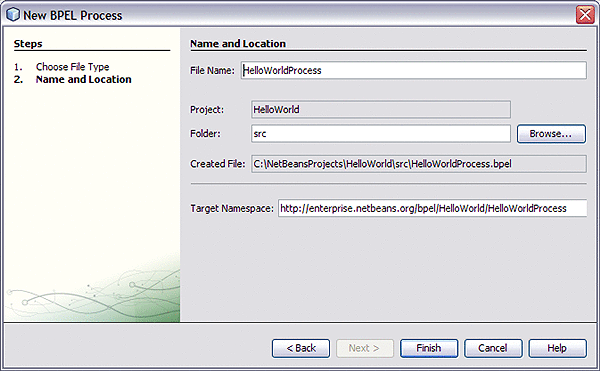
In the Projects window, expand your BPEL module project node, right-click the Process Files node, and choose New -> BPEL Process from the pop-up menu.
The New BPEL Process dialog box appears.
-
Enter a name for the process file name (HelloWorldProcess for this example), and click Finish.
The new BPEL file opens in the Design view of the BPEL Designer.
If the Palette and Properties windows are not displayed in your current view, click Windows -> Reset Windows on the NetBeans menu.
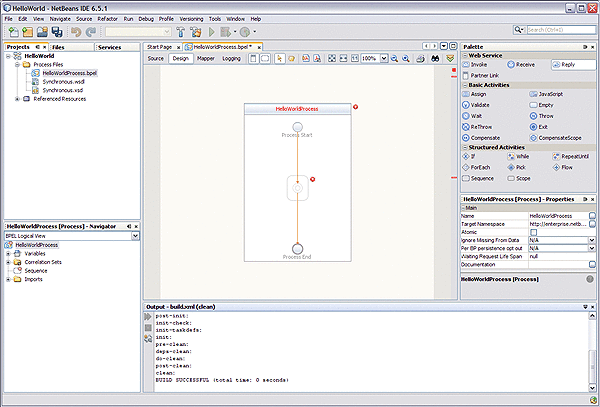
-
Add a partner link to the BPEL Process.
-
In the Projects window, expand your project's Process Files node and select the .wsdl file (Synchronous.wsdl for this example).
-
Drag the .wsdl file from the Projects window to the left side of the Design view canvas.
The IDE provides visual prompts to show you where you can drop the selection.
The BPEL Editor adds a partner link to the canvas.
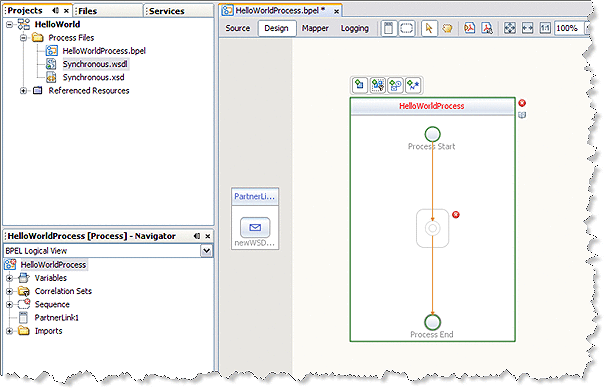
-
-
Add a Receive activity to the BPEL Process.
-
From the Web Service section of the Palette window, select the Receive activity.
-
Drag the Receive activity to the HelloWorldProcess process box in the Design view canvas, between the Process Start and the Process End activities.
The Receive1 activity is added to the process box.
-
Click the Receive1 activity's Edit icon.
The Receive1 Property Editor appears.
-
On the Main tab, change the value in the Name field to start.
-
From the Partner Link drop-down list, choose PartnerLink1.
The IDE populates the Operation field with NewWSDLOperation.
-
Click the Create button next to the Input Variable Field.
The New Input Variable dialog box appears. Click OK to accept the default values.
-
Click OK to close the Receive1 Property Editor.
The Design view displays the new connection between PartnerLink1 and the Start activity in the process box.
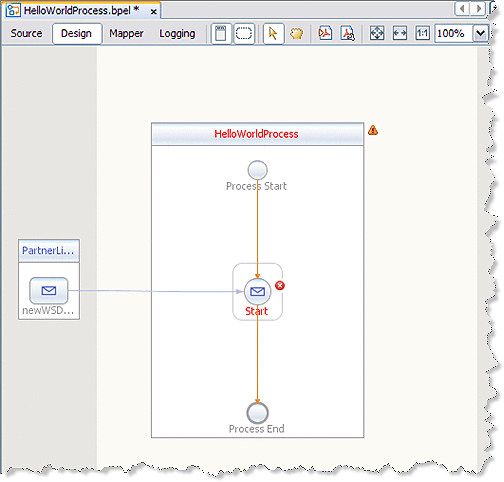
-
-
Add a Reply activity to the BPEL Process.
-
Select the Reply activity in the Web Service section of the Palette. Drag and drop the Reply to the prompt between the Start activity and the Process End activity in the process box on the design view canvas.
A Reply1 activity is added to the design view canvas.
-
Click the Reply1 activity's Edit icon.
The Reply1 Property Editor appears.
-
On the Main tab, change the value in the Name field to End.
-
From the Partner Link drop-down list, choose PartnerLink1.
The IDE populates the Operation field with NewWSDLOperation.
-
To create anew output variable, make sure that Normal Response is selected, and click the Create button next to the Input Variable Field.
The New Input Variable dialog box appears. Click OK to accept the default values.
-
Click OK to close the Reply1 Property Editor.
The Design view displays the new connection between the End activity in the process box and PartnerLink1.
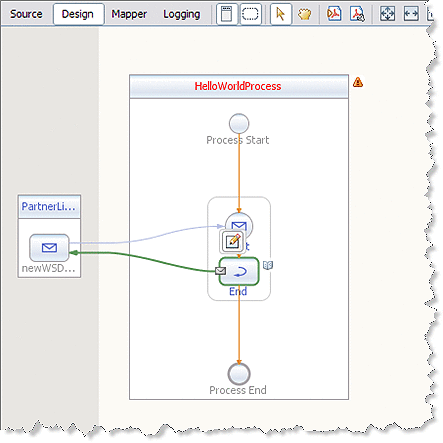
-
-
Add a Assign activity to the BPEL Process.
-
Select the Assign activity in the Basic Activities section of the Palette. Drag and drop the Assign to the prompt between the Start activity and the End activity in the process box on the design view canvas.
The Assign1 activity is added to the design view canvas.
-
Select the Assign1 activity and click the Mapper button on the editors toolbar.
The BPEL Mapper appears.
-
Map the paramA node under Variables -> NewWSDLOperationIn -> inputType in the Output pane of the BPEL Mapper, to the paramA node under Variables -> NewWSDLOperationOut -> resultType in the Input pane of the Mapper. To do this, select theparamA node under Variables -> NewWSDLOperationIn -> inputType in the Output pane, and drag your cursor to the paramA node under Variables -> NewWSDLOperationOut -> resultType in the Input pane.
This assignment copies the input statement into the output.
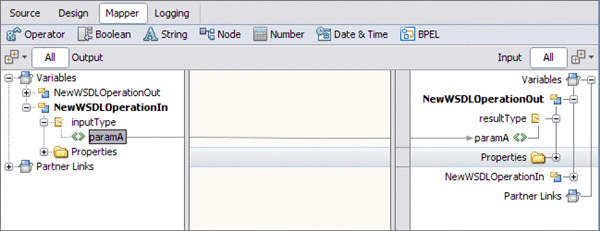
-
-
To save your changes click the Save All icon in the IDE menu bar.
Creating a Composite Application Project
A BPEL Module project is not directly deployable. You must first add a BPEL Module project, as a JBI module, to a Composite Application project. You can then deploy the Composite Application project. Deploying the project makes the service assembly available to the application server and enables its service units to run.
 Create a new Composite Application project
Create a new Composite Application project
-
Choose File > New Project (Ctrl-Shift-N).
-
In the Categories list choose Service Oriented Architecture, in the Projects list choose Composite Application, and click Next.
-
In the Name and Location page, change the project name to HelloWorldApplication, and specify the location of project files.
-
To set the new Composite Application the main project as main, leave the Set as Main Project checkbox selected, and click Finish.
-
To add the BPEL Module as a JBI module to the Composite Application project, right-click the new Composite Application and choose Add JBI Module from the pop-up menu.
The Select Project dialog box opens.
-
Select the HelloWorld project you created earlier and click Add Project JAR Files.
The Select Project dialog box closes and the HelloWorld.jar file is added to the JBI Modules node of the HelloWorldApplication Composite Application
Building and Deploying the Composite Application Project
Building a project compiles the BPEL source file and packages the BPEL file and web service artifacts, including WSDL and XSD files, into a JAR archive. Deploying the project compiles the files in the Composite Application project, packages the compiled BPEL and related web service artifacts (including WSDL and XSD files) into an archive, and deploys them to the Application Server.
 Build and deploy the Composite Application Project:
Build and deploy the Composite Application Project:
-
Right-click the Composite Application project's node, and choose Build from the pop-up menu.
When the build is complete the Output window reports Build Successful. If the Output window is not visible, choose Window -> Output -> Output.
-
Right-click the Composite Application project's node, and choose Deploy.
-
Deployment has succeeded when you see a Build successful message in the GlassFish tab of the Output window.
-
Open the Services window and expand Servers -> GlassFish V2 -> JBI -> Service Assemblies to see your new deployed Service Assembly.
If you do not see the deployed project, right-click the Service Assemblies node and choose Refresh.
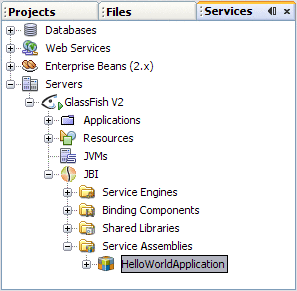
Testing the Composite Application
You can test your Composite Application project by adding test cases, binding to the operation, supplying input, and then using the tester.
 Test the HelloWorldApplication Composite Application
project
Test the HelloWorldApplication Composite Application
project
-
In the Projects window, expand the HelloWorldApplication project node, right-click the Test node, and choose New Test Case from the pop-up menu.
The New Test Case wizard opens.
-
Accept the default test case name, TestCase1, and click Next.
-
From the Select the WSDL Document page, expand the HelloWorld - Proecss Files node, select Synchronous.wsdl, and click Next.
-
From the Select the Operation to Test page, select the Operation1 and click Finish.
A new TestCase1 node is added under the project's Test node in the Projects window, containing two subnodes, Input and Output.
The Source Editor appears containing the Input file, Input.xml
Note –If the Source Editor does not contain a tab for Input.xml, double-click the Input node in the Projects window to open the file.
-
From the Input.xml tab of the Source Editor, do the following:
-
Locate the line:
<syn:paramA>?string?<syn:paramA>
-
Replace ?string? with Hello World, so that the line appears as follows:
<syn:paramA>Hello World<syn:paramA>
-
From the NetBeans IDE menu bar, click the Save All button.
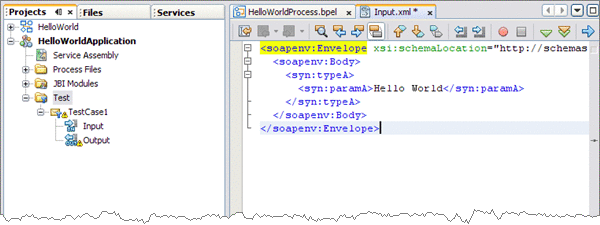
-
-
In the Projects window, double-click the Output node under Test -> TestCase1.
Output.xml is opened in the Source Editor. Initially, Output.xml is empty until the first test run populates the file.
-
In the Projects window, right-click the TestCase1 node and choose Run from the pop-up menu.
When the Overwrite Empty Output dialog box appears, click Yes to accept new output. The first test run populates the Output.xml file displayed in the Source Editor.
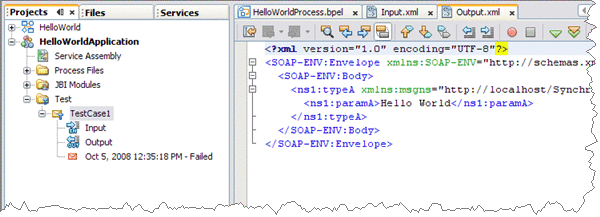
The test compares the output to the contents of the output file. Because the first run of the test has nothing to compare itself to, the first test fails. Subsequent test runs will compare their output with the contents of Output.xml and should succeed.
-
Run the test again.
The testcase is compared to the current output file and succeeds.
Summary
You just created the HelloWorld, synchronous sample project. This sample project is available in the NetBeans IDE's samples file under Project/Samples/SOA/Synchronous BPEL Process.
This tutorial above demonstrates how to:
-
Create a Bpel Module project
-
Use the BPEL Designer to create a BPEL process
-
Build and deploy a Composite Application project to GlassFish
-
Create and run test cases
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
