Terminator
The Terminator property specifies whether or not the delimiter should appear for the last node of current level. For example, it determines whether data should look like "a,b,|" or "a,b|" assuming "," (comma) is the current level delimiter and "|" (pipe) is the parent level delimiter.
The delimiter that terminates the last child of the level in question is referred to as the terminator.
Table 12 Terminator Mode Options|
Option |
Rule |
|---|---|
|
never |
Specifies that the delimiter is not allowed to be a terminator in input and will not be emitted as terminator in output. |
|
allow |
Specifies that the delimiter is allowed to be a terminator in input but will not be emitted as terminator in output. |
|
cheer |
Specifies that the delimiter is allowed to be a terminator in input and will be emitted as terminator in output. |
|
force |
Specifies that the delimiter must appear as a terminator in input and will also be emitted as terminator in output. |
Consider the tree structure shown in the following figure, where the node a has a caret (^) as its delimiter, and its child nodes b and c have asterisks (*) as their delimiters.
Figure 12 Terminator Mode Property Example
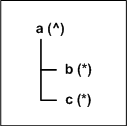
|
Option |
Input |
Output |
|---|---|---|
|
never |
c^ |
c^ |
|
allow |
c^ or c*^ |
c^ |
|
cheer |
c^ or c*^ |
c*^ |
|
force |
c*^ |
c*^ |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
