Understanding the IEP Database
IEP uses a set of database tables to maintain information about the IEP Service Engine and deployed event processes. You can connect to the database through NetBeans, and then view the tables and their content through NetBeans windows. To view the IEP database tables, click the Services window of the NetBeans IDE. Expand the Databases node, the connection node, and the Tables node.
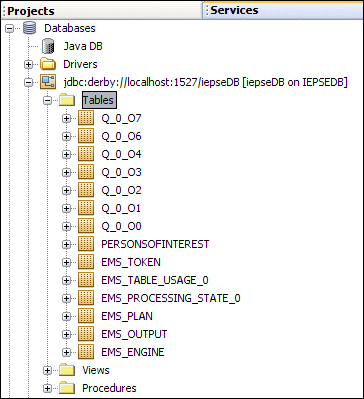
To view the contents of an IEP database table, right-click the table node and choose View Data. The SQL Editor appears and displays the appropriate SQL SELECT statement, which is performed on the table. The results of the query appear near the bottom of the SQL Editor.
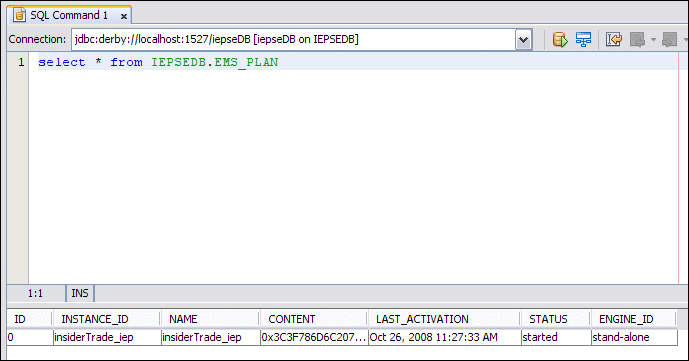
The following image shows the contents of the EMS_PLAN table.
You can use any of the following database servers for the IEP database:
Configuring the IEP Database to Use Oracle
By default, the IEP database is configured to use Java DB. Java DB is Sun's supported distribution of the open source Apache Derby database. After installation, you can configure the IEP database to use Oracle instead.
The first task is to create an IEP user in the Oracle database. You can run a provided SQL script that creates the IEP user and grants the appropriate privileges. The default version of the script contains the following SQL statements:
CREATE TABLESPACE "IEPSEDB_DB" DATAFILE 'IEPSEDB_DB1.dat' SIZE 2000M, 'IEPSEDB_DB2.dat' SIZE 2000M; CREATE USER IEPSEDB IDENTIFIED BY IEPSEDB DEFAULT TABLESPACE IEPSEDB_DB QUOTA UNLIMITED ON IEPSEDB_DB TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp QUOTA 0M ON system; GRANT CONNECT TO IEPSEDB; GRANT RESOURCE TO IEPSEDB; GRANT CREATE VIEW TO IEPSEDB; grant select on sys.dba_pending_transactions to IEPSEDB; grant select on sys.pending_trans$ to IEPSEDB; grant select on sys.dba_2pc_pending to IEPSEDB; grant execute on sys.dbms_system to IEPSEDB; grant select on SYS.dba_2pc_neighbors to IEPSEDB; grant force any transaction to IEPSEDB; |
You need to create two sets of connection pools and JDBC resources. A connection pool is a group of reusable connections for a particular database. The server maintains a pool of available connections to increase performance. A JDBC resource provides applications with a means of connecting to a database. Additional configuration of the service engine is also required.
To configure the IEP Service Engine to use Oracle, perform the following steps:
-
To Install the Oracle Database Driver in the Application Server
-
To Configure the IEP Service Engine to Use the JDBC Resources
-
To Restart the IEP Service Engine and Create the Database Tables
 To Create the IEP User in the Oracle Database
To Create the IEP User in the Oracle Database
-
In a web browser, enter the following URL: http://wiki.open-esb.java.net/Wiki.jsp?page=HowToRunIEPOnOracle.
-
Download the create_iepse_user.sql script.
-
Open the create_iepse_user.sql script and review the instructions.
-
The names of the tablespace, data files, user, and password include the string IEPSEDB. If you want to change this string to a different string, then replace all occurrences of IEPSEDB with the new string.
-
Connect to the Oracle database as a user with the SYSDBA privilege.
-
Run the create_iepse_user.sql script against the database.
 To Install the Oracle Database Driver in the
Application Server
To Install the Oracle Database Driver in the
Application Server
-
Go to the computer where the application server is installed.
-
Copy and paste the Oracle database driver (for example, ojdbc14.jar) to the glassfish-home/lib directory.
-
Restart the application server.
 To Create the Non-XA Connection Pool
To Create the Non-XA Connection Pool
-
Log in to the GlassFish Admin Console.
-
In the left navigation panel, expand Resources and JDBC, and then select Connection Pools.
-
Click New.
The New JDBC Connection Pool page appears.
-
Do the following:
-
Scroll down to the Additional Properties table, and then do the following:
-
Click Finish.
The connection pool is created.
-
Click the connection pool that you just created.
The Edit Connection Pool page appears.
-
Click Ping.
The Admin Console attempts to connect to the database. If the connection does not succeed, check to see whether the database is running and verify the database connectivity properties, such as the URL string.
 To Create the Non-XA JDBC Resource
To Create the Non-XA JDBC Resource
-
In the left navigation panel of the Admin Console, expand Resources and JDBC, and then select JDBC Resources.
-
Click New.
The New JDBC Resource page appears.
-
In the JNDI Name field, specify a unique name for the non-XA JDBC resource. By convention, the name begins with the jdbc/ string. For example:
jdbc/iepseOracleNonXA
You will use the JNDI name in a later procedure.
-
In the Pool Name field, select the non-XA connection pool that you created in the previous procedure.
-
Click OK.
The JDBC resource is created.
 To Create the XA Connection Pool
To Create the XA Connection Pool
-
In the left navigation panel of the Admin Console, expand Resources and JDBC, and then select Connection Pools.
-
Click New.
The New JDBC Connection Pool page appears.
-
For step 1 of the connection pool, do the following:
-
For step 2 of the connection pool, do the following:
-
Scroll down to the Connection Validation section.
-
Select the Enabled check box that appears to the right of the Allow Non Component Callers label.
-
Scroll down to the Additional Properties table.
-
In the User row, enter the user name of the IEP user (for example, IEPSEDB).
-
In the Password row, enter the password of the IEP user (for example, IEPSEDB).
-
In the URL row, enter the string for connecting to the database (for example, jdbc:oracle:thin:@myserver:1521:orcl).
-
-
Click Finish.
The connection pool is created.
-
Click the connection pool that you just created.
The Edit Connection Pool page appears.
-
Click Ping.
The Admin Console attempts to connect to the database. If the connection does not succeed, check to see whether the database is running, and verify the connectivity parameters, such as the URL string.
 To Create the XA JDBC Resource
To Create the XA JDBC Resource
-
In the left navigation panel of the Admin Console, expand Resources and JDBC, and then select JDBC Resources.
-
Click New.
The New JDBC Resource page appears.
-
In the JNDI Name field, specify a unique name for the XA JDBC resource. By convention, the name begins with the jdbc/ string. For example:
jdbc/iepseOracleXA
You use the JNDI name in a later procedure.
-
In the Pool Name drop-down menu, select the XA connection pool that you created.
-
Click OK.
The JDBC resource is created.
 To Enable Automatic Recovery of XA Transactions
To Enable Automatic Recovery of XA Transactions
-
In the left navigation panel of the Admin Console, expand Configuration and then select Transaction Service.
-
Select the Enabled check box that appears to the right of the On Restart label.
-
Click Save.
 To Configure the IEP Service Engine to Use
the JDBC Resources
To Configure the IEP Service Engine to Use
the JDBC Resources
-
Log in to the NetBeans IDE.
-
In the Services window, expand Servers > GlassFish V2 > JBI > Service Engines.
-
If the IEP Service Engine is not started, right-click sun-iep-engine and select Start.
-
Right-click sun-iep-engine and select Properties.
The Properties dialog box appears.
-
In the Non XA Data Source Name property, enter the non-XA JDBC resource that you created (for example, jdbc/iepseOracleNonXA).
-
In the XA Data Source Name property, enter the XA JDBC resource that you created (for example, jdbc/iepseOracleXA).
-
In the Database Schema Name property, enter the user name of the IEP user (for example, IEPSEDB).
In an Oracle database, the database schema name is identical to the user name.
-
Click OK.
 To Restart the IEP Service Engine and Create
the Database Tables
To Restart the IEP Service Engine and Create
the Database Tables
When you restart the IEP Service Engine, the database tables are automatically created in the database you specified through the connection pools and runtime properties.
-
If any Composite Application projects that contain event processes are currently deployed, undeploy the projects.
-
In the Services window, expand Servers > GlassFish V2 > JBI > Service Engines.
-
Right-click sun-iep-engine and select Stop.
-
Right-click sun-iep-engine and select Start.
-
If you undeployed any Composite Application projects, you can now redeploy the projects.
IEP Service Engine-Specific Database Tables
When you start the IEP Service Engine for the first time, the following tables are created in the IEP database. These tables apply to the IEP Service Engine as a whole.
Do not delete or alter these tables.
EMS_PLAN Table
The EMS_PLAN table maintains information about the event processes that are deployed to the IEP Service Engine. The EMS_PLAN table contains the following columns:
-
ID. An integer that uniquely identifies the event process.
-
NAME. The name of the event process.
-
CONTENT. The XML content of the event process. The value is displayed in binary format.
-
LAST_ACTIVATION. The last time the event process was started.
-
STATUS. The status of the event process definition. The valid values are started, stopped, deployed, and undeployed.
-
ENGINE_ID. The ID of the cluster node that is running the event process. If you are not running IEP in cluster mode, then the value is stand-alone.
EMS_OUTPUT Table
The EMS_OUTPUT table maintains information for event processes that have a Table Output operator. The EMS_OUTPUT table contains the following columns:
-
PLAN_INSTANCE_ID. The instance ID of the event process that has the Table Output operator.
-
OUTPUT_NAME. The name of the table.
-
OUTPUT_DESCRIPTION. The description of the table.
-
LAST_UPDATED. The last time the output table was updated.
EMS_ENGINE Table
The EMS_ENGINE table is used when you are running IEP in cluster mode. The EMS_ENGINE table contains the following columns:
-
ID. A value that uniquely identifies the IEP instance (instance1, instance2, and so on). If you are not running IEP in cluster mode, then the value is stand-alone.
-
INSTANCE_LOCATION. The IP address of the computer where the IEP instance is running.
-
LEASE_EXPIRATION. A timestamp that the cluster nodes use to determine which IEP instance is active.
EMS_TOKEN Table
The EMS_TOKEN table is used when you are running IEP in cluster mode. The EMS_TOKEN table contains the following columns:
-
ID. The unique identifier of a token that can be acquired and released by cluster nodes.
-
NAME. The name of a token that can be acquired and released by cluster nodes.
Event Process-Specific Database Tables
When you deploy an event process, the following tables are created in the IEP database. If you undeploy the event process, then the tables are deleted.
Do not delete or alter these tables.
EMS_PROCESSING_STATE_N Tables
The EMS_PROCESSING_STATE_N tables are used by the IEP Service Engine to maintain execution state for an event process. The EMS_PROCESSING_STATE_N tables contain the following columns:
-
PROCESSING_STATE. The execution state of the event process. The value is displayed in binary format.
-
PREV_TIMESTAMP_TO_CHECK. A timestamp that the IEP Service Engine uses to maintain execution state for the event process.
-
PREV_TIMESTAMP_TO_PROCESS. A timestamp that the IEP Service Engine uses to maintain execution state for the event process.
EMS_TABLE_USAGE_N Tables
The EMS_TABLE_USAGE_N tables are used in garbage collection. The EMS_TABLE_USAGE_N tables contain the following columns:
-
TABLE_NAME. The name of a table.
-
USER_ID. The ID of the operator that is using the table.
-
EMS_TIMESTAMP. A timestamp that is used in garbage collection.
Operator-Specific Database Tables
In the IEP Service Engine, one or more tables are created per operator. These tables are specific to operator behavior and functionality.
Do not delete or alter these tables.
The following table names illustrate how the names are formatted.
-
Q_0_O0
-
Q_0_O1
-
Q_1_O0
-
Q_1_O1
The first character of the table name is always Q.
The character after the first underscore is the ID of the event processor in the EMS_PLAN table.
The characters after the second underscore are the ID of the operator. You can view the operator ID in the IEP design view by selecting the operator and displaying the Properties window.
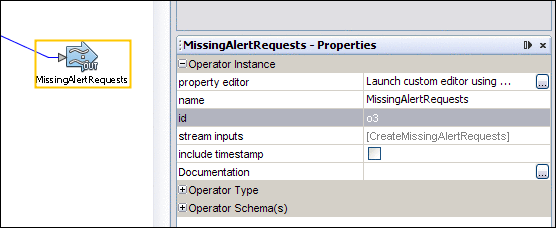
The operator ID is automatically generated. You cannot change the ID.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
