Standard Inbound HL7 V2 Collaboration Overview over MLLPV2
In the MLLP V2 sample Projects, the inbound HL7 V2 Collaboration, jcdHL7Inbound, contains Message Libraries (previously called OTDs) for the HL7 Resource Adapter, JMS Data, HL7 ACK, JMS Journal, and JMS Error, as well as the Generic HL7 Event. The Collaboration works with its own internal code and the properties configuration files.
The following topics describe the business logic defined in the jcdHL7Inbound Collaboration for MLLP V2:
-
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 1
-
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 2
-
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 3
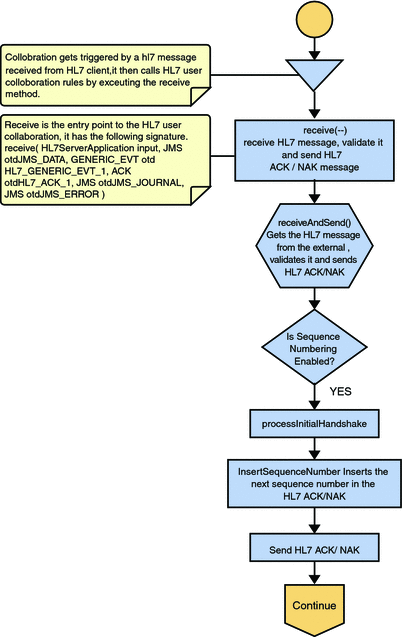
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 1
Once the message is received, the Collaboration determines whether the message needs to be validated. The HL7 V2 message is then validated making sure that the message structure is correct. Various fields in the MSH segment of the message are also validated, such as Version ID and Sending Facility. If these fields do not match the configuration, a NAK is returned.
If sequence numbering is enabled the Collaboration checks to see if the messages sequence number is valid. If the sequence number is not valid, the adapter sends a NAK.
The validated HL7 V2 message moves on to processInitialHandshake() and the sequence numbers are synchronized. The sequence number within the message is checked against the expected sequence number. If the numbers match, the Collaboration sends an ACK, if not it sends a NAK. The ACK or NAK includes information from various fields of the incoming MSA segment. The ACKs level of acknowledgement is set to A (acknowledgement is sent when the message is successfully received) or C (acknowledgement is sent after the message is successfully processed).
Figure 24 HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 1
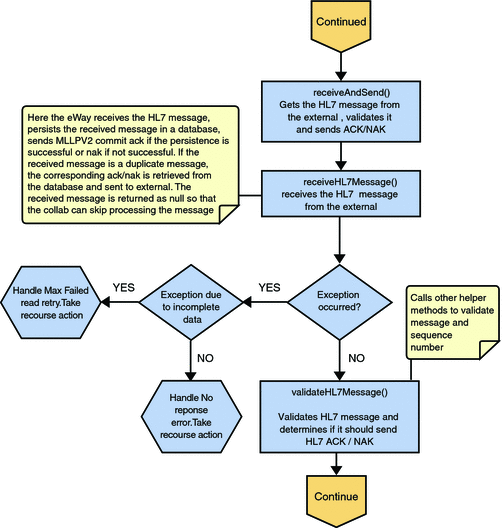
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 2
The Collaboration receives the HL7 V2 message from the external using receiveHL7message(). If an exception occurs due to incomplete data, and the adapter fails to read the data within the configured number of retries, the associated recourse action is taken. If the exception is due to no response, the associated recourse action is taken.
Figure 25 HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 2
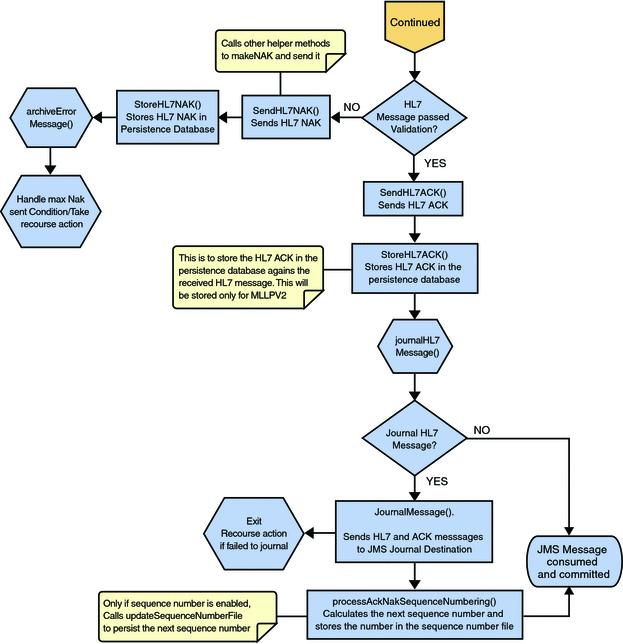
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 3
If no exception occurs, validateHL7Message() is called, which validates the message to determine whether to ACK or NAK the message. Other helper methods are also called to validate the HL7 message.
If the HL7 message does not pass validation, the Collaboration calls makeNak() and sendHL7Nak() to create and send the NAK to the external system. The HL7 message, with the NAK, is archived to the error queue. If the number of consecutive NAKs sent surpasses the maximum number of retries, the associated recourse action is taken.
If the HL7 message passes validation, the Collaboration calls makeAck() and sendHL7Ack() to create and send the ACK to the external system. The HL7 ACK/NAK messages are stored in the persistent database. This ACK/NAK is stored against the inbound HL7 message received.
After the ACK is sent, the HL7 message and the ACK are journaled to the JMS queue journal destination. If the message fails to journal the associated recourse action is taken.
If sequencing numbering is enabled, the processAckNakSequenceNumbering method calculates the next sequence number and stores the number in the sequence number file by calling the updateSequenceNumberFile method to persist the next sequence number.
Figure 26 HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 3
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
