Using Agent Builder to Create a Service That Uses the GDS
You can use Agent Builder to create the service that uses the GDS. Agent Builder is described in more detail in Chapter 9, SunPlex Agent Builder.
Creating and Configuring GDS-Based Scripts
 How to Start Agent Builder and Create the Scripts
How to Start Agent Builder and Create the Scripts
Steps
-
Become superuser or assume an equivalent role.
-
# /usr/cluster/bin/scdsbuilder
-
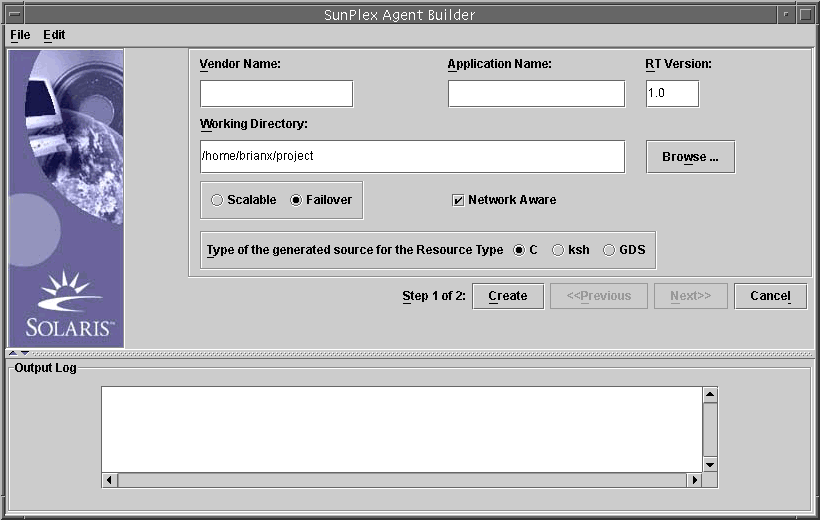
The Agent Builder Create screen appears.
-
Type the vendor name.
-
Type the application name.
Note –Starting with the Solaris 9 Operating System, the combination of vendor name and application name can exceed nine characters. However, if you are using an earlier version of the Solaris Operating System, the combination of vendor name and application name cannot exceed nine characters. This combination is used as the name of the package for the scripts.
-
Go to the working directory.
You can use the Browse drop-down menu to select the directory rather than typing the path.
-
Select whether the data service is scalable or failover.
You do not need to select Network Aware because that setting is the default when you create the GDS.
-
Select GDS.
-
(Optional) Change the RT version from the default value that is shown.
Note –You cannot use the following characters in the RT Version field: space, tab, slash (/), backslash (\), asterisk (*), question mark (?), comma (,), semicolon (;), left square bracket ([), or right square bracket (]).
-
Click Create.
Agent Builder creates the scripts. The results are displayed in the Output Log area.
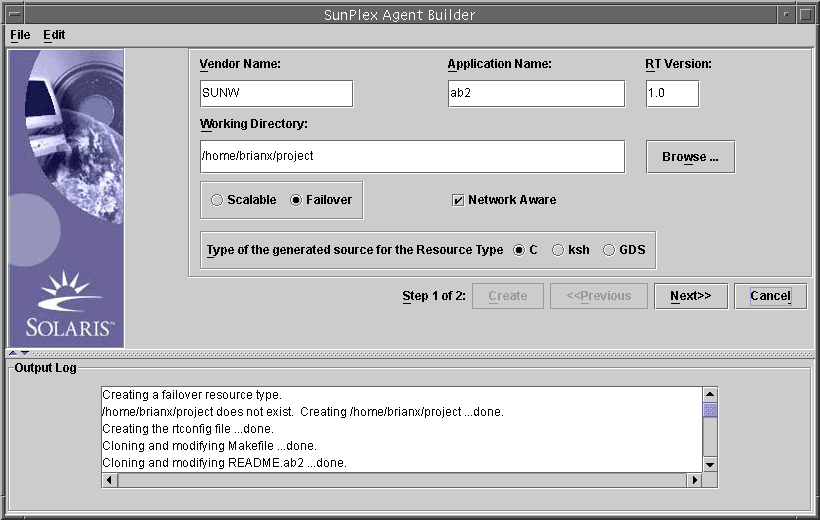
Note that the Create button is grayed out. You can now configure the scripts.
-
Click Next.
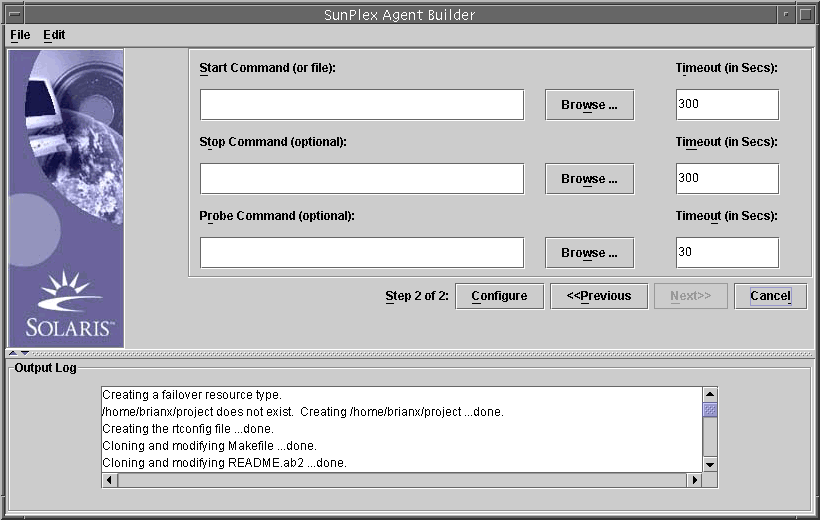
The Configure screen appears.
 How to Configure the Scripts
How to Configure the Scripts
After creating the scripts, you need to configure the new service.
Steps
-
Type the location of the start command, or click Browse to locate the start command.
You can specify property variables. Property variables are described in Using Property Variables.
-
(Optional) Type the location of the stop command, or click Browse to locate the stop command.
You can specify property variables. Property variables are described in Using Property Variables.
-
(Optional) Type the location of the probe command, or click Browse to locate the probe command.
You can specify property variables. Property variables are described in Using Property Variables.
-
(Optional) Specify new timeout values for the start, stop, and probe commands.
-
Click Configure.
Agent Builder configures the scripts.
Note –Agent Builder concatenates the vendor name and the application name to create the package name.
A package for scripts is created and placed in the following directory:
working-dir/vendor-name-application/pkg
For example, /export/wdir/NETapp/pkg.
-
On each node of the cluster, become superuser or assume an equivalent role.
-
On each node of the cluster, install the completed package.
-
For the Solaris 10 OS in a zones environment, as global administrator in the global zone, type the following commands:
# cd /export/wdir/NETapp/pkg # pkgadd -G -d . NETapp
The package that you specified is added to the global zone, provided that the contents of the package do not affect any area of the global zone that is shared with a non-global zone.
The following files are installed by pkgadd:
/opt/NETapp /opt/NETapp/README.app /opt/NETapp/man /opt/NETapp/man/man1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/removeapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/startapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/stopapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/app_config.1m /opt/NETapp/util /opt/NETapp/util/removeapp /opt/NETapp/util/startapp /opt/NETapp/util/stopapp /opt/NETapp/util/app_config
-
For any other version of the Solaris OS or the Solaris 10 OS in a non-zones environment, type the following commands:
# cd /export/wdir/NETapp/pkg # pkgadd -d . NETapp
The following files are installed by pkgadd:
/opt/NETapp /opt/NETapp/README.app /opt/NETapp/man /opt/NETapp/man/man1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/removeapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/startapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/stopapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/app_config.1m /opt/NETapp/util /opt/NETapp/util/removeapp /opt/NETapp/util/startapp /opt/NETapp/util/stopapp /opt/NETapp/util/app_config
Note –The man pages and script names correspond to the application name that you typed previously on the Create screen, preceded by the script name (for example, startapp).
-
-
On one node of the cluster, configure the resources and start the application.
# /opt/NETapp/util/startapp -h logicalhostname -p port-and-protocol-list
The arguments to the startapp script vary according to the type of resource: failover or scalable.
Note –To determine the command line that you need to type, check the customized man page, or run the startapp script without any arguments to display a usage statement.
To view the man pages, you need to specify the path to the man page. For example, to view the startapp(1M) man page, type:
# man -M /opt/NETapp/man startapp
To display a usage statement, type:
# /opt/NETapp/util/startapp The resource name of LogicalHostname or SharedAddress must be specified. For failover services: Usage: startapp -h logicalhostname -p port-and-protocol-list [-n ipmpgroup-adapter-list] For scalable services: Usage: startapp -h shared-address-name -p port-and-protocol-list [-l load-balancing-policy] [-n ipmpgroup/adapter-list] [-w load-balancing-weights]
Output From Agent Builder
Agent Builder generates three scripts and a configuration file based on input that you provide when you create the package. The configuration file specifies the names of the resource group and the resource type.
The scripts are as follows:
-
Start script. Configures the resources and starts the application that is under RGM control.
-
Stop script. Stops the application and takes down resources and resource groups.
-
Remove script. Removes the resources and resource groups that are created by the start script.
These scripts have the same interface and behavior as the utility scripts that are generated by Agent Builder for non-GDS-based data services. The scripts are put in a Solaris package that you can reuse across multiple clusters.
You can customize the configuration file to provide your own names for resource groups or other arguments that are normally given as arguments to the scrgadm command. If you do not customize the scripts, Agent Builder provides default values for the scrgadm arguments.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
