Overview of Portal Server
This section provides a brief description of the Portal Server. See Sun Java System Portal Server 7.1 Technical Overview for a complete product architecture description.
What Is a Portal?
A portal is a doorway or entry point to a set of resources that an enterprise wants to make available to the portal’s users. For some consumer portals, the set of resources includes the entire World-Wide Web. For most enterprise portals, the set of resources includes information, applications, and other resources that are specific to the relationship between the user and the enterprise.
The primary purpose of the Sun Java System Portal Server is to give end users a portal Desktop, which provides access to resources and applications. In addition, a search engine infrastructure enables intranet content to be organized and accessed from the portal Desktop.
Portal Server Architecture
This section describes the Portal Server architecture. In Figure 1–1, the Portal Server components consist of:
-
Services such as search (made up of the search engine and robot), discussions, and subscriptions
-
Content delivery and presentation on the Desktop
The Java Development KitTM (JDK) provides the Java run-time environment for all Java software in Portal Server and its underlying components.
The Sun Java System Web Server, or the Sun Java System Application Server, or the BEA WebLogic Server, or the IBM WebSphere Application Server provides the web container. The application server provides the Portal Server with a robust, highly scalable web container for the Portal Server web applications. It also provides the Portal Server with compatibility for other applications written to use application server and for developers that want to use the additional enterprise services that are provided by these application servers.
The Directory Server provides the user profile data repository. The Access Manager provides support for core services such as profile, session, authentication, and logging. It also provides single-sign-on services, policy management, debug utility, and client support interfaces for the Portal Server. Use the Access Manager administration console for user administration.
The Portal Server Search Engine provides the search capability. It includes basic and advanced search and browse channels for the Desktop. It uses a robot to create resource descriptions for documents that are available in the intranet, and stores these resource descriptions in an indexed database. Search includes Java and C APIs for submitting resource descriptions and for searching the database. Search also includes an administration console module for editing Search service data and for configuring the search engine and the robot. The console also lets you edit the contents of the Search database.
The Desktop provides the primary end-user interface for the Portal Server and a mechanism for extensible content aggregation through the Container Provider Interface (PAPI). The Desktop includes a variety of providers that provide a container hierarchy and the basic building blocks for building some types of channels. The Desktop implements a display profile data storage mechanism on top of an Access Manager service for storing content provider and channel data.
Figure 1–1 Portal Software Architecture
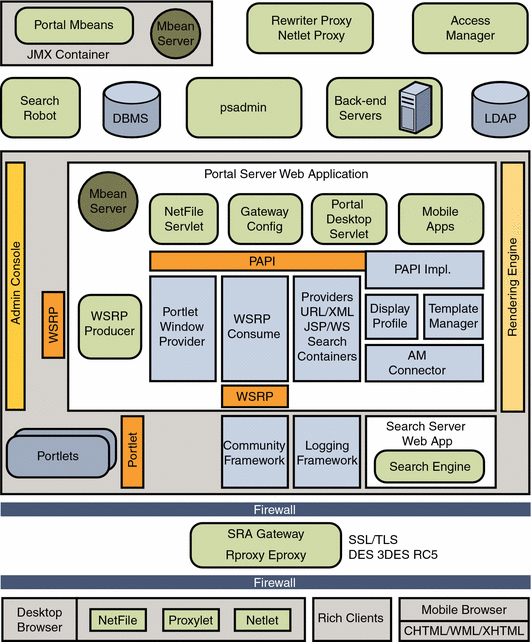
Portal Desktop
The Portal desktop is a logical component, which consists of the Desktop servlet, Provider API and SPI, various channels, and other support APIs and utilities.
Sample Desktop and Desktop Hierarchy
The sample desktops use an aggregation of a variety of separate web applications (channels) within a common framework. The common framework provides multiple levels and styles of aggregation, presented to end users through a container metaphor.
Providers and Channels
In the Desktop, leaf channels are the basic unit of content, displaying a specific type of information. To the end user, a channel is a distinct unit of content in the Desktop, usually (but not always) set off with a border and header row of icons that enables users to configure the channel to their preference. A provider is a Java class responsible for converting the content, from a file or an application or service, into a presentable format for a channel.
Portlets and Web Service for Remote Portlets
Portlets and Web Service for Remote Portlets (WSRP) are available with Portal Server. Portlets are web components specifically designed to be aggregated in the context of a composite page. Java Specification Request (JSR) 168 specifies how portlets interact, how their life cycles are managed, and provides details of their semantics.
WSRP is a specification that defines a web service interface to access and interact with interactive presentation-oriented web service. WSRP is a standard to access and get the content using the portlets deployed in remote server using web services.
Portal Server Software Desktop
The Desktop provides a mechanism for extending and aggregating content through the Provider Application Programming Interface (PAPI). The PAPI is a Java API that enables you to construct the basic building blocks for creating channels. Usually, though not always, channels contain content. You can also have channels of channels; that is, a container channel that aggregates other channels. A channel can also be the entire Desktop page. The container channels define the layout of the Desktop.
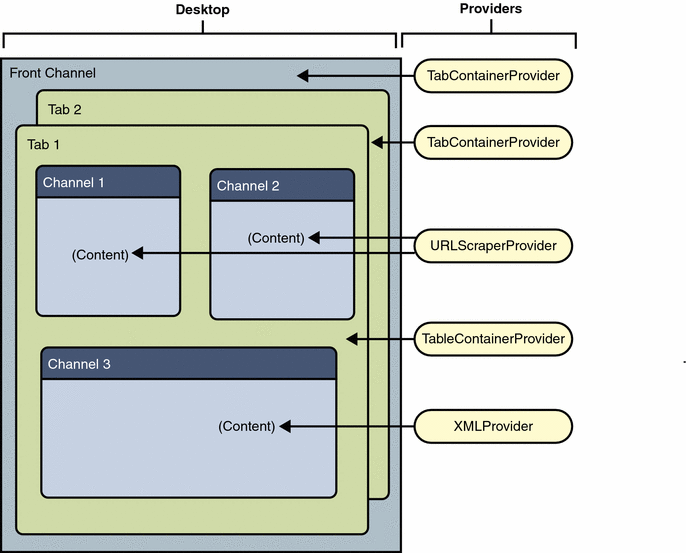
The figure below shows a simple representation of a portal Desktop and its providers and containers. In this figure, the Desktop front page is a tab container with two tabs. Each tab contains a table container with various channels.
Notice how one provider, in this case, URLScraperProvider, is serving more than one channel. Providers can have a one-to-many relationship with channels.
Figure 1–2 Desktop Hierarchy and Building Block Providers
Search Engine
The Portal Server Search Engine is a taxonomy and database service designed to support basic and advanced search and browse channels for the Desktop. The search engine uses a robot to create resource descriptions (RDs) for documents that are available in the intranet, and stores these resource descriptions in an indexed database. Resource descriptions can also be imported from another server or from a backup Search (Summary Object Interchange Format) file. The search engine includes Java and C APIs for submitting resource descriptions and for searching the database. The search engine database can also be used for storing other arbitrary content such as a shared content cache for other content providers.
Access Manager Software Services
Portal applications and resources use Access Manager to provide services such as authentication, single-sign-on, profile, and session management. See the Access Manager documentation for more information.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
