Dimension 1: Infrastructure Service Dependencies
The interacting software components of distributed enterprise applications require underlying infrastructure services that allow the distributed components to communicate with each other, coordinate their work, implement secure access, and so forth. This section explains the key role played by a number of Java ES components in providing these infrastructure services.
Infrastructure Service Levels
In designing a distributed software system, whether it consists mostly of custom-developed components or out-of-the-box Java ES components, you need to incorporate a number of infrastructure services. These services operate at many levels.
The infrastructure service dependencies of solution architecture are illustrated in Figure 2–2. The levels shown in this figure are an expanded view of the infrastructure service layer of Figure 1–1. The hierarchy of services in Figure 2–2 and the dependencies between them constitute an important dimension of a solution’s logical architecture. These infrastructure services provide the main rationale for Java ES system service components (see System Service Components).
In general, the services shown in the following figure divide into three broad groupings: low-level platform services, high-level application services, and a group of middleware services named for their location between the other two groupings.
Figure 2–2 Dimension 1: Infrastructure Service Levels
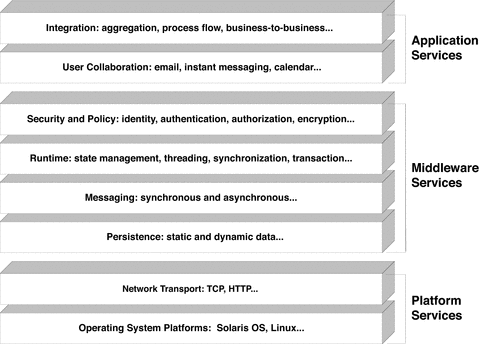
The following descriptions of the different infrastructure service levels refer to Java programming language artifacts, where relevant, and are listed from lowest to highest, as shown in Figure 2–2:
-
Operating system platforms. Provides the basic support for any process running on a computer. The operating system manages physical devices as well as memory, threads, and other resources necessary to support the Java Virtual Machine (JVMTM machine).
-
Network transport. Provides basic networking support for communication between distributed application components running on different computers. These services include support for protocols such as TCP and HTTP. Other higher-level communication protocols (see the messaging level) depend on these basic transport services.
-
Persistence. Provides support for accessing and storing both static data (such as user, directory, or configuration information) and dynamic application data (information that is frequently updated).
-
Messaging. Provides support for both synchronous and asynchronous communication between application components. Synchronous messaging is the real-time sending and receipt of messages and includes remote method invocation (RMI) between J2EE components and SOAP interactions with web services. Asynchronous messaging is communication in which the sending of a message does not depend on the readiness of the consumer to immediately receive it. Asynchronous messaging specifications, for example, Java Message Service (JMS) and ebXML, support guaranteed reliability and other messaging semantics.
-
Runtime. Provides support required by any distributed component model, such as the J2EE or CORBA models. In addition to the remote method invocation needed for tightly coupled distributed components, runtime services include component state (life cycle) management, thread pool management, synchronization (mutex locking), persistence services, distributed transaction monitoring, and distributed exception handling. In a J2EE environment, these runtime services are provided by EJB, web, and message-driven bean containers in an application server or web server.
-
Security and policy. Provides support for secure access to application resources. These services include support for policies that govern group or role-based access to distributed resources as well as single sign-on capabilities. Single sign-on allows a user’s authentication to one service in a distributed system to be automatically applied to other services (J2EE components, business services, and web services) in the system.
-
User collaboration. Provides services that play a key role in supporting direct communication between users and collaboration among users in enterprise and Internet environments. These services are application-level business services, normally provided by stand-alone servers such as an email server or a calendar server.
-
Integration. Provides the services that aggregate existing business services. Provides a common interface for accessing the services, as in a portal, or by integrating the services through a process engine that coordinates them within a production work flow. Integration can also take place as business-to-business interactions between different enterprises.
The service levels shown in Figure 2–2 reflect a dependence of the infrastructure services on one another, from the lowest-level operating system services to the highest-level application and integration services. Each service generally depends on services below it and supports services above it. Figure 2–2, however, does not represent a strict layering of infrastructure services. Higher-level services can directly interact with lower-level services without depending on intermediate levels. For example, some runtime services might depend directly on platform services without requiring any of the service levels in between. In addition, other service levels, such as a monitoring or management service, might also be included in this conceptual illustration.
Java ES Infrastructure Service Components
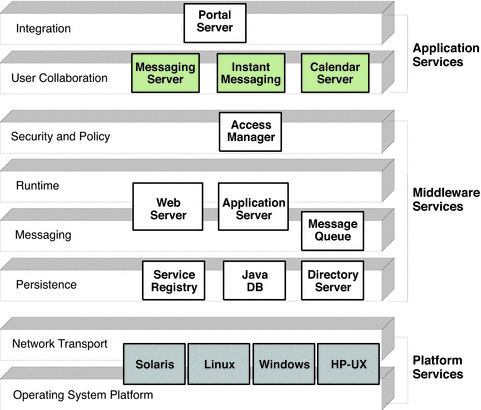
Java ES components implement the distributed infrastructure service levels shown in Figure 2–2. The positioning of system service components within the different levels is shown in the following figure.
Figure 2–3 Java ES System Service Components
Note –
The shaded boxes in the figure indicate components that are not included in Java ES. User collaboration components are not part of Java ES but are often deployed with Java ES components and used within Java ES architectures. These components are part of the Sun Java Communications Suite and are referenced in this document for illustrative purposes only. Also, operating system platforms are not formally part of Java ES, but are included to show the operating system platforms on which Java ES components are supported.
Java ES Infrastructure Service Dependencies
In general, each Java ES system service component shown in Figure 2–3 depends on components below it in the infrastructure and supports components above it. These dependency and support relationships are a key factor in designing logical architectures.
The following table shows the specific relationships between the Java ES system service components, listed from top to bottom, as shown in Figure 2–3.
Table 2–1 Relationships Between Java ES System Service Components
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
