Tiered Architecture Applied to System Components
As shown in Figure 2–3, Java ES infrastructure service components provide the underlying infrastructure support for distributed software solutions. Some of these solutions include application-level services provided by Sun Java Communications Suite components and some Java ES components. These solutions use logical tier design approaches.
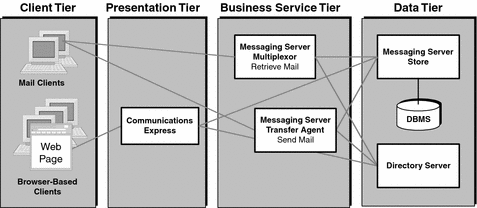
For example, the email communication services provided by Messaging Server are implemented using a number of logically distinct configurations of Messaging Server. These distinct configurations each provide a distinct set of services. When designing messaging solutions, these distinct configurations are represented as separate components that are situated in different logical tiers, as shown in the following figure where lines connecting components represent interactions.
Note –
The following figure is not meant to be a complete logical architecture. A number of Java ES components are omitted to simplify the illustration.
Figure 2–5 Messaging Server: Example of Tiered Architecture
Note –
Communications components are not part of Java ES but are often deployed with Java ES components and used within Java ES architectures. These communications components are part of the Sun Java Communications Suite and are referenced in this document for illustrative purposes only.
The logical separation of Messaging Server functions into different tiers allows the logically distinct configurations of Messaging Server to be deployed on different computers in a physical environment. The physical separation allows for flexibility in meeting quality of service requirements (see Dimension 3: Quality of Service). For example, it provides for different availability solutions for the different instances, and different security implementations for different Messaging Server functions.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
