10.2 Configuring the J2EE Policy Agents Load Balancer
Load Balancer 6 handles traffic for the J2EE policy agents, and is configured for simple persistence so that browser requests from the same IP address will always be directed to the same policy agent. From a performance perspective, each policy agent validates the user session and evaluates applicable policies. The results are subsequently cached by the individual policy agent to improve performance. If load balancer persistence is not set, each agent must build up its own cache, effectively doubling the workload on the Access Manager servers, and cutting overall system capacity in half. The problem becomes even more acute as the number of policy agents increases. Simple persistence guarantees that the requests from the same user session will always be sent to the same policy agent.
Tip –
In situations where each J2EE policy agent instance is protecting identical resources, some form of load balancer persistence is highly recommended for the performance reasons. The actual type of persistence may vary when a different load balancer is used, as long as it achieves the goal of sending the requests from the same user session to the same policy agent.
The following illustration shows the architecture of the policy agents and load balancers.
Figure 10–2 Policy Agents and Load Balancers
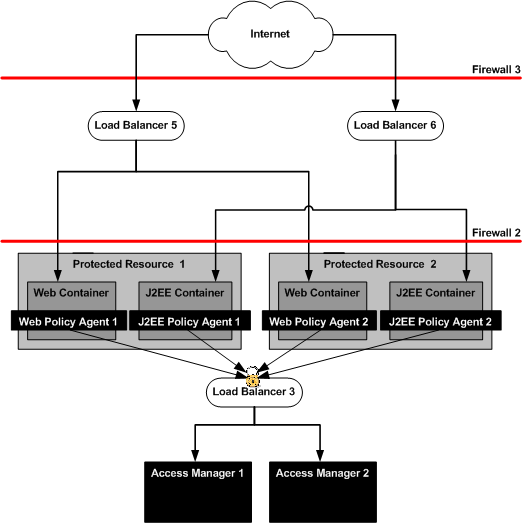
Note –
When firewalls are configured, Load Balancer 6 can be located in a less secure zone.
Use the following list of procedures as a checklist for configuring the J2EE policy agents' load balancer:
 To Configure the J2EE Policy Agents Load
Balancer
To Configure the J2EE Policy Agents Load
Balancer
Before You Begin
The load balancer hardware and software used for this deployment is BIG-IP® manufactured by F5 Networks. If you are using different load balancer software, see the documentation that comes with that product for detailed settings information.
-
Access https://is-f5.example.com, the Big IP load balancer login page, from a web browser.
-
Log in using the following information:
- User name:
-
username
- Password:
-
password
-
Click Configure your BIG-IP (R) using the Configuration Utility.
-
Create a Pool.
A pool contains all the backend server instances.
-
In the left pane, click Pools.
-
On the Pools tab, click Add.
-
In the Add Pool dialog, provide the following information:
- Pool Name
-
J2EEAgent-Pool
- Load Balancing Method
-
Round Robin
- Resources
-
Add the Application Server IP addresses and port numbers: ProtectedResource-1:1081 and ProtectedResource-2:1081.
-
Click Done.
-
In the List of Pools, click J2EEAgent-Pool.
-
Click the Persistence tab and provide the following information:
- Persistence Type:
-
Choose Active Http Cookie
Note –Active Http Cookie persistence uses an HTTP cookie stored on a client computer to allow the client to reconnect to the same server previously visited.
- Method:
-
Choose Insert
-
Click Apply.
-
-
Add a Virtual Server.
If you encounter JavaScript errors or otherwise cannot proceed to create a virtual server, try using Internet Explorer for this step.
-
In the left frame, click Virtual Servers.
-
On the Virtual Servers tab, click Add.
-
In the Add a Virtual Server dialog box, provide the following information:
- Address
-
Enter the IP address for LoadBalancer-6.example.com
- Services Port
-
91
- Pool
-
J2EEAgent-Pool
-
Continue to click Next until you reach the Pool Selection dialog box.
-
In the Pool Selection dialog box, assign the J2EEAgent-Pool pool.
-
Click Done.
-
-
Add Monitors.
-
Log out of the load balancer console.
 To Point the J2EE Policy Agents to Load Balancer
6
To Point the J2EE Policy Agents to Load Balancer
6
Modify the AMAgent.properties file to point Protected Resource 1 and Protected Resource 2 to Load Balancer 6.
-
As a root user, log in to the ProtectedResource–1 host machine.
-
Change to the config directory.
# cd /export/J2EEPA1/j2ee_agents/am_wl92_agent/agent_001/config
Tip –Backup AMAgent.properties before you modify it.
-
Make the following change to the AMAgent.properties file.
com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.mapping[LoadBalancer-6.example.com] = LoadBalancer-6.example.com
-
Save the file and close it.
-
Log out of the ProtectedResource–1 host machine.
-
As a root user, log in to the ProtectedResource–2 host machine.
-
Change to the config directory.
# cd /export/J2EEPA2/j2ee_agents/am_wl92_agent/agent_001/config
Tip –Backup AMAgent.properties before you modify it.
-
Make the following change to the AMAgent.properties file.
com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.mapping[LoadBalancer-6.example.com] = LoadBalancer-6.example.com
-
Save the file and close it.
-
Log out of the ProtectedResource–2 host machine.
 To Create Polices for the Agent Resources
To Create Polices for the Agent Resources
The policies you create here are used in To Verify the J2EE Policy Agent Load Balancer Configuration is Working Properly.
-
Access the Access Manager server, http://AccessManager-1.example.com:1080/amserver/UI/Login, from a web browser.
-
Log in to the Access Manager console as the administrator.
- Username
-
amadmin
- Password
-
4m4dmin1
-
Modify the referral policy for access to Load Balancer 6.
-
On the Access Control tab, click the top-level realm example.
-
Click the Policies tab.
-
Click the Referral URL Policy for users realm link.
-
On the Edit Policy page, under Rules, click New.
-
On the resulting page, select URL Policy Agent (with resource name) and click Next.
This selection is used to define policies that protect HTTP and HTTPS URLs.
-
On the resulting page, provide the following information:
- Name:
-
URL Rule for LoadBalancer-6
- Resource Name:
-
http://loadbalancer-6.example.com:91/*
Note –Make sure all letters are lowercase.
-
Click Finish.
-
On the resulting page, click Save.
The new rule is in the Rules list.
-
-
Create a policy in the users sub-realm.
-
On the Access Control tab, click the users link.
-
Click the Policies tab, and then New Policy.
-
In the Name field, enter URL Policy for LoadBalancer-6.
-
Under Rules, click New.
-
On the resulting page, accept the default URL Policy Agent (with resource name) and click Next.
-
On the resulting page, provide the following information:
- Name:
-
LoadBalancer-6.
- Parent Resource Name:
-
From the list, select, http://loadbalancer-6.example.com:91/*.
- Resource Name:
-
http://loadbalancer-6.example.com:91/* is automatically entered when you select the Parent Resource Name.
- GET
-
Mark the checkbox and select Allow.
- POST
-
Mark the checkbox and select Allow.
-
Click Finish.
-
On the New Policy page again, under Subjects, click New.
-
On the resulting page, verify that Access Manager Identity Subject is selected, and click Next.
-
On the resulting page, provide the following information:
- Name:
-
LoadBalancer-6_Groups
- Filter:
-
In the drop-down list, select Group and click Search.
The search returns a list of available groups.
-
Select Employee-Group and Manager-Group and click Add.
The Employee-Group and Manager-Group groups are in the Selected List.
-
Click Finish.
-
On the resulting page, click OK.
The policy you just created is now included in the list of Policies.
-
-
Log out of the Access Manager console and close the browser.
 To Verify the J2EE Policy Agent Load Balancer
Configuration is Working Properly
To Verify the J2EE Policy Agent Load Balancer
Configuration is Working Properly
-
Restart the Application Servers.
-
As a root user, log in to the ProtectedResource–1 host machine.
-
Change to the bin directory.
# cd /usr/local/bea/user_projects/domains/ProtectedResource-1/bin
-
Stop Application Server 1 managed instance.
# ./stopManagedWebLogic.sh ApplicationsServer-1 t3://localhost:7001
-
Stop the Application Server 1 administration server.
# ./stopWebLogic.sh
-
Start the Application Server 1 administration server.
# ./startWebLogic.sh &
-
Start Application Server 1 managed instance.
# ./startManagedWebLogic.sh ApplicationServer-1 t3://localhost:7001
-
Log out of the ProtectedResource–1 host machine.
-
As a root user, log in to the ProtectedResource–2 host machine.
-
Change to the bin directory.
# cd /usr/local/bea/user_projects/domains/ProtectedResource-2/bin
-
Stop the Application Server 2 managed instance.
# ./stopManagedWebLogic.sh ApplicationsServer-2 t3://localhost:7001
-
Stop the Application Server 2 administration server.
# ./stopWebLogic.sh
-
Start the Application Server 2 administration server.
# ./startWebLogic.sh &
-
Start the Application Server 2 managed instance.
# ./startManagedWebLogic.sh ApplicationServer-2 t3://localhost:7001
-
Log out of the ProtectedResource–2 host machine.
-
-
Access http://LoadBalancer-6.example.com:91/agentsample/index.html from a web browser.
The Sample Application welcome page is displayed.
-
Click the J2EE Declarative Security link.
-
On the resulting page click Invoke the Protected Servlet.
The policy agent redirects to the Access Manager login page.
-
Log in to the Access Manager console as testuser1.
- Username
-
testuser1
- Password
-
password
If you can successfully log in as testuser1 and the J2EE Policy Agent Sample Application page is displayed, this first part of the test succeeded and authentication is working as expected.
-
Click the J2EE Declarative Security link to return.
-
On the resulting page, click Invoke the Protected Servlet.
If the Successful Invocation message is displayed, this second part of the test has succeeded and the sample policy for the employee role has been enforced as expected.
-
Close the browser.
-
Open a new browser and access http://LoadBalancer-6.example.com:91/agentsample/index.html.
The Sample Application welcome page is displayed.
-
Click the J2EE Declarative Security link.
-
On the resulting page click Invoke the Protected Servlet.
The policy agent redirects to the Access Manager login page.
-
Log in to the Access Manager console as testuser2.
- Username
-
testuser2
- Password
-
password
If the Access to Requested Resource Denied message is displayed, this third part of the test succeeded and the sample policy for the manager role has been enforced as expected.
-
Click the J2EE Declarative Security link to return.
-
On the resulting page, click Invoke the Protected EJB via an Unprotected Servlet.
If the Successful Invocation message is displayed, the sample policy for the employee role has been enforced as expected.
-
Close the browser.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
