1.3 Sequence of Interactions
The following sequence describes the interactions between the various components in this deployment example. The interactions are illustrated and the numbered steps correspond to the numbers in the diagrams.
-
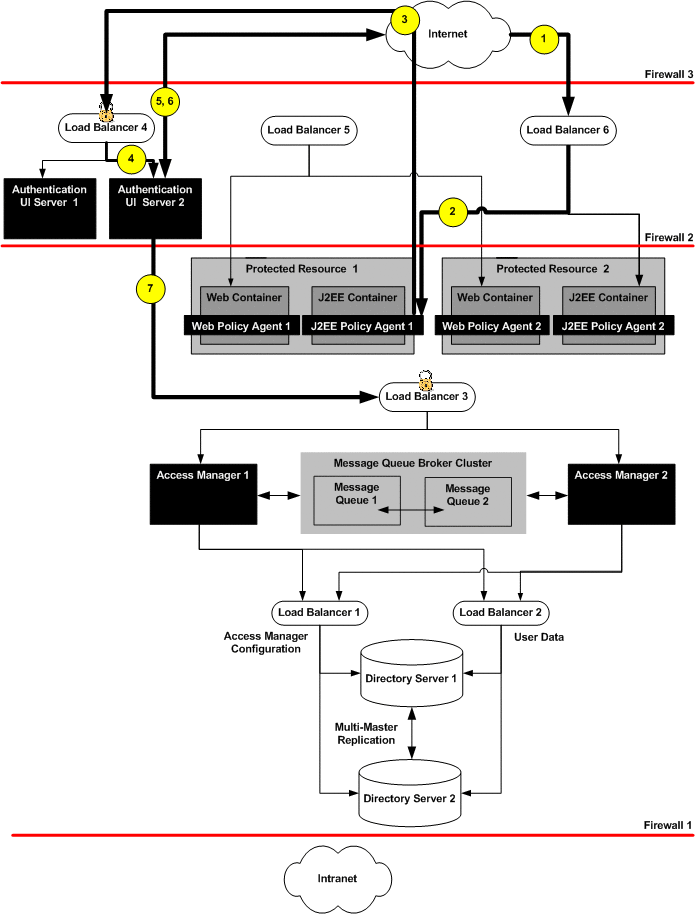
A user attempts to access a J2EE application hosted by Protected Resource 1 and Protected Resource 2.
-
Load Balancer 6 directs the user to Protected Resource 1.
-
The J2EE Policy Agent intercepts the request and checks for an Access Manager cookie. In this scenario, no cookie is found and the request is returned to the browser which then redirects it to Load Balancer 4, the load balancer for the Distributed Authentication User Interface.
-
Load Balancer 4 routes the user request to Distributed Authentication User Interface 2.
-
Distributed Authentication User Interface 2 displays a login page to the user.
-
The user enters credentials on the login page and they are returned to Distributed Authentication User Interface 2.
-
Distributed Authentication User Interface 2 passes the credentials to Load Balancer 3.
-
Load Balancer 3 routes the credentials to Access Manager 1 for validation.
-
Access Manager 1 sends a request for validation to Load Balancer 2 which specifically handles Directory Server requests for user data.
-
Load Balancer 2 routes the request to Directory Server 2 where validation takes place.
-
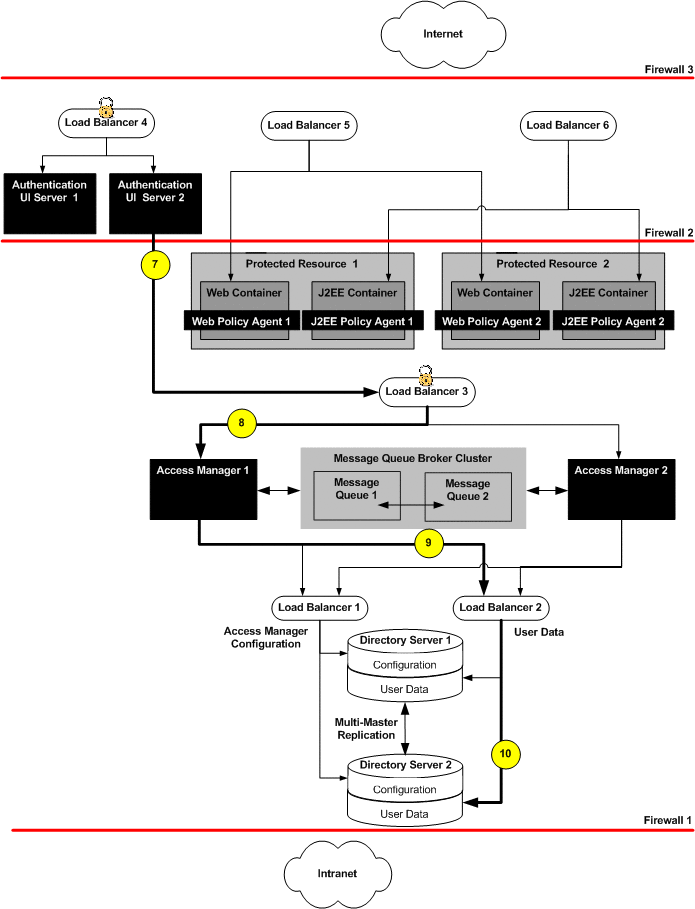
After successful authentication, Access Manager 1 sends the response back to the J2EE Policy Agent. The J2EE Policy Agent receives the request and checks for the Access Manger cookie.
-
When a cookie is found, the J2EE Policy Agent sends a session validation request to the Access Manager Load Balancer 3.
-
The Access Manager load balancer forwards the request to the Access Manager 1 where the session originated. Cookie-based persistency enables proper routing.
-
Access Manager 1 sends a response back to the J2EE Policy Agent.
-
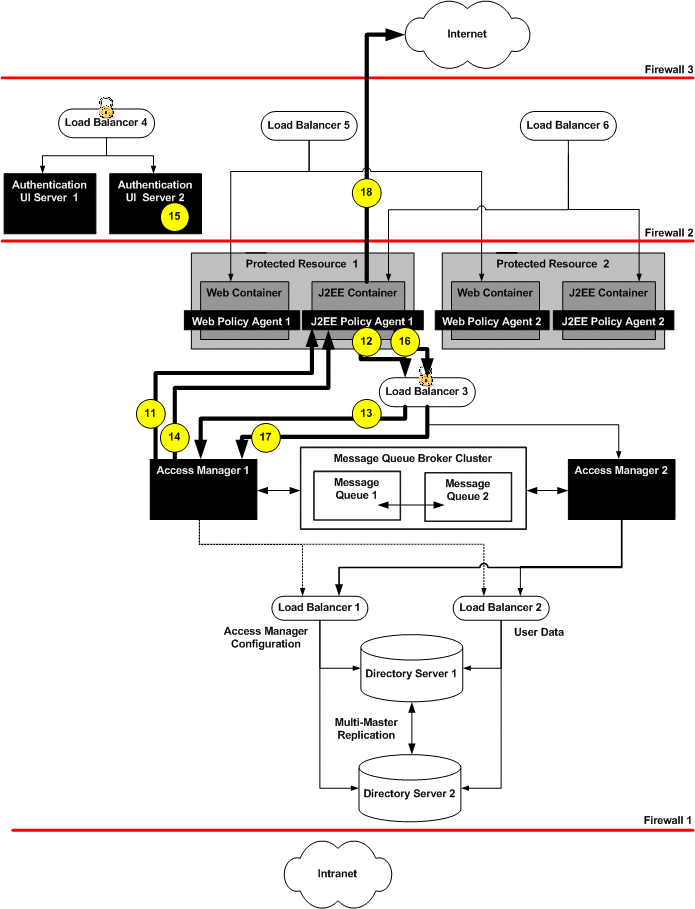
If the session is not valid, the J2EE Policy Agent would redirect the user to the Distributed Authentication User Interface.
-
If the session is valid, the J2EE Policy Agent receives the response back and sends a policy request to the Access Manager Load Balancer 3.
-
The policy request is directed to Access Manager 1 which conducts the policy evaluation.
-
Based on the policy evaluation, the J2EE Policy Agent either allows access to the resource or denies access to the resource. In this scenario, the user is allowed access to the Application Server.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
