Saturation Algorithm for Load Balancing
In the saturation algorithm, requests are distributed to data sources according to a combination of the weight of the data source and the number of available connections.
All requests of a certain type are distributed to the data source with the highest weight, until its saturation level is reached. Once this level is reached, requests are distributed between this data source and the data source with the next highest weight. The saturation level is obtained by multiplying the weight of the data source by the total number of connections.
The following figure illustrates how Directory Proxy Server distributes requests to a pool of data sources with 10 connections and different weights. The number of available connections multiplied by the weight is shown in brackets.
Figure 16–2 Distribution of Requests According to the Saturation Algorithm for Load Balancing
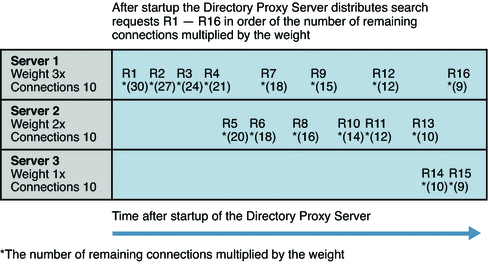
If your deployment includes data sources with greatly different capacity, you can use the saturation algorithm to distribute requests according to the capacity of the data source.
For an example of how configure the saturation algorithm, see To Configure the Saturation Algorithm for Load Balancing in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.2 Administration Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
