Chapter 7 Installing and Configuring Portal Server 7.2 in High Availability Scenarios
In a high availability scenario, many Portal Server instances and Access Manager instances exist. An end user accesses any of the Portal Server instances. When a Session Fail Over occurs, the user automatically gets redirected to an available Portal Server instance. This chapter covers various high availability scenarios.
This chapter contains the following scenarios:
-
Installing Portal Server and Access Manager in a High Availability Scenario with Berkeley Database
-
Setting up SSL Termination Between Gateway and Portal Server at Load Balancer
Installing Portal Server and Access Manager in a High Availability Scenario with Berkeley Database
This section explains how to install Portal Server and Access Manager in a high availability scenario using Berkeley database. Berkeley database is installed when you install Access Manager. In a high availability scenario, Berkeley database is used to store session variables of the user.
In the procedures in this section, you do the following:
-
Install Directory Server, Application Server 9.1, Access Manager, and Portal Server on Node 1 and Node 2.
-
Install a Portal Server instance on Node 2. (The portal ID for Node 1 and Node 2 are the same.)
-
Install a Load Balancer on Node 3.
Figure 7–1 Portal Server With Berkely Database
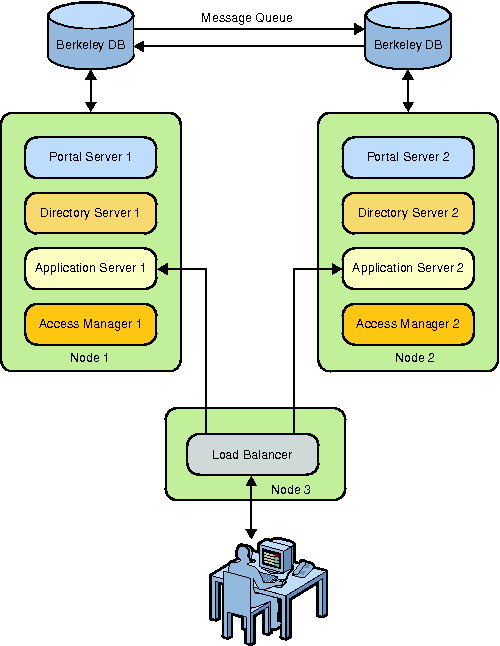
 To Install Portal Server and Access Manager in a High
Availability Scenario with Berkeley Database
To Install Portal Server and Access Manager in a High
Availability Scenario with Berkeley Database
These instructions require the following:
-
Directory Server on Node 1 is not in the multi master replication (MMR) mode. Only one instance of Directory Server exists.
-
Access Manager on Node 1 is installed in Legacy mode. The data can be stored only in Directory Server.
-
On Node 1, install Directory Server, Access Manager, and Application Server 9.1.
-
Verify whether Access Manager is installed properly by accessing Access Manager Console.
http://node1.domain-name:8080/amconsole
-
Login to amconsole on Node 1. In the Organization Aliases List, add the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of Node 2.
-
Click Service Configuration and click Platform in the right panel.
-
In the Platform Server List, add the following.
http://node2.domain-name:8080|02
-
On Node 2, run the Java ES installer to install Access Manager.
On the page that asks whether Directory Server is already provisioned with data, select Yes and proceed with installing Access Manager.
Note –Ensure that the password encryption key on Node 2 is the same as the password encryption key on Node 1. The password encryption key should be the same for the LDAP internal password on both of the nodes.
-
On Node 2, start Application Server 9.1 and verify whether Access Manager is installed properly by accessing Access Manager Console.
http://node2.domain-name:8080/amconsole
-
In a text editor, open the AMConfig.properties file on Node 1 and Node 2.
The file is located in the AccessManager_base/SUNWam/config directory.
 To Install the Load Balancer on Node 3
To Install the Load Balancer on Node 3
-
Install the Load Balancer plugin on Node 3 that is provided with Application Server 9.1. Select Web Server as a component to install with the Load Balancer plugin.
-
In a text editor, open the loadbalancer.xml file on Node 3.
This file is located in the WebServer_base/SUNWwbsvr7/https-Node3/config directory.
-
Edit the file so that the Load Balancer balances the load between the two Access Manager instances.
Edit the listeners with the appropriate values.
A sample loadbalancer.xml which balances the load on Portal Server and Access Manager instances on Node 1 and Node 2 is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE loadbalancer PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems Inc.//DTD Sun ONE Application Server 9.1// EN" "sun-loadbalancer_1_1.dtd"> <loadbalancer> <cluster name="cluster1"> <!-- Configure the listeners as space seperated URLs like listeners="http://host:port https://host:port" For example: <instance name="instance1" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" listeners="http://localhost:80 https://localhost:443"/> --> <instance name="instance1" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" listeners="http://node1.domain-name:8080"/> <instance name="instance2" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" listeners="http://node2.domain-name:8080"/> <web-module context-root="/portal" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" error-url="sun-http-lberror.html" /> <web-module context-root="/psconsole" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" error-url="sun-http-lberror.html" /> <web-module context-root="/amserver" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" error-url="sun-http-lberror.html" /> <web-module context-root="/amconsole" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" error-url="sun-http-lberror.html" /> <web-module context-root="/ampassword" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" error-url="sun-http-lberror.html" /> <web-module context-root="/amcommon" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" error-url="sun-http-lberror.html" /> <web-module context-root="/" enabled="true" disable-timeout-in-minutes="60" error-url="sun-http-lberror.html" /> <health-checker url="/" interval-in-seconds="10" timeout-in-seconds="30" /> </cluster> <property name="reload-poll-interval-in-seconds" value="60"/> <property name="response-timeout-in-seconds" value="30"/> <property name="https-routing" value="true"/> <property name="require-monitor-data" value="false"/> <property name="active-healthcheck-enabled" value="false"/> <property name="number-healthcheck-retries" value="3"/> <property name="rewrite-location" value="true"/> </loadbalancer>
-
Start the Web Server.
-
On Node 1 and Node 2, start Access Manager, Directory Server, and Application Server 9.1.
 To Configure Session Failover with Message Queue and
Berkeley Database
To Configure Session Failover with Message Queue and
Berkeley Database
-
Edit the Application Server 9.1 domain.xml file on Node 1 and Node 2 to add locations of the jms.jar file and imq.jarfile.
<JAVA javahome="/usr/jdk/entsys-j2se" server-classpath="/usr/share/lib/imq.jar:/usr/share/lib/jms.jar: ....?
Note –When you create a Message Queue instance, do not use the default Message Queue instance that starts with Application Server 9.1 or the guest user for Message Queue.
-
Start Message Queue on Node 1 and Node 2.
/bin/imqbrokerd -tty -name mqins -port 7777 &
where mqins is the Message Queue instance name.
-
Add a user to this message queue.
imqusermgr add -u amsvrusr -p secret12 -i mqins -g admin
where amsvrusr is the name of the new user that is used instead of guest.
-
Inactivate the guest user.
imqusermgr update -u guest -i mqins -a false
-
Create an encrypted file for the message queue on Node 1 and Node 2.
./amsfopasswd -f /AccessManager_base/SUNWam/.password -e password-file
-
Edit the amsfo.conf file on both the nodes.
A list of sample entries in amsfo.conf file is displayed as follows:
AM_HOME_DIR=/opt/SUNWam AM_SFO_RESTART=true LUSTER_LIST=node1.domain-name:7777,node2.domain-name:7777 DATABASE_DIR="/tmp/amsession/sessiondb" DELETE_DATABASE=true LOG_DIR="/tmp/amsession/logs" START_BROKER=true BROKER_INSTANCE_NAME=amsfo BROKER_PORT=7777 BROKER_VM_ARGS="-Xms256m -Xmx512m" USER_NAME=amsvrusr PASSWORDFILE=$AM_HOME_DIR/.password AMSESSIONDB_ARGS="" lbServerPort=8080 lbServerProtocol=http lbServerHost=node3.domain-name SiteID=10
-
Configure amsfo.confon Node 1.
AccessManager_base/SUNWam/bin/amsfoconfig
After running the script, the following output is displayed:
Session Failover Configuration Setup script. ========================================================= ========================================================= Checking if the required files are present... ========================================================= Running with the following Settings. ------------------------------------------------- Environment file: /etc/opt/SUNWam/config/amProfile.conf Resource file: /opt/SUNWam/lib/amsfo.conf ------------------------------------------------- Using /opt/SUNWam/bin/amadmin Validating configuration information. Done... Please enter the LDAP Admin password: (nothing will be echoed): password1 Verify: password1 Please enter the JMQ Broker User password: (nothing will be echoed): password2 Verify: password2 Retrieving Platform Server list... Validating server entries. Done... Retrieving Site list... Validating site entries. Done... Validating host: http://amhost1.example.com:7001|02 Validating host: http://amhost2.example.com:7001|01 Done... Creating Platform Server XML File... Platform Server XML File created successfully. Creating Session Configuration XML File... Session Configuration XML File created successfully. Creating Organization Alias XML File... Organization Alias XML File created successfully. Loading Session Configuration schema File... Session Configuration schema loaded successfully. Loading Platform Server List File... Platform Server List server entries loaded successfully. Loading Organization Alias List File... Organization Alias List loaded successfully. Please refer to the log file /var/tmp/amsfoconfig.log for additional information. ############################################################### Session Failover Setup Script. Execution end time 10/05/05 13:34:44 ############################################################### -
Edit the amsessiondb script with the default path and directory of the following:
JAVA_HOME=/usr/jdk/entsys-j2se/ IMQ_JAR_PATH=/usr/share/lib JMS_JAR_PATH=/usr/share/lib BDB_JAR_PATH=/usr/share/db.jar BDB_SO_PATH=/usr/lib AM_HOME=/opt/SUNWam
-
Start and stop the Message Queue instance running on port 7777.
AccessManager_base/SUNWam/bin/amsfo start
AccessManager_base/SUNWam/bin/amsfo stop
-
Restart Access Manager, Directory Server, Application Server 9.1, and Web Server on all the nodes.
-
Login to the amconsole through Load Balancer.
http://node3.domain-name:80/amconsole
-
Stop the Application Server 9.1 on Node 1.
The session is handled by Access Manager on Node 2.
 To Install Portal Server on Node 1
To Install Portal Server on Node 1
-
Invoke the Portal Server 7.2 GUI installer and install Portal Server on Node 1 in the Configure Now mode.
-
Access Portal Server to verify the installation.
http://node1.domain-name:8080/portal
-
Create a Portal Server instance on Node 2.
 To Create a Portal Server Instance on Node 2
To Create a Portal Server Instance on Node 2
-
Invoke the Portal Server 7.2 GUI installer on Node 2 and provide the same portal-id as node 1.
-
The Access Manager SDK will be automatically configured and the installer will detect the portal-id that exists and create an instance of portal.
Configuring HADB for Session Fail Over
High Availability Database (HADB) is a horizontally scalable database. It is designed to support data availability with load balancing, failover, and state recovery capabilities. HADB is used for session fail overs for portal server instances, which are clustered. This is also used for portlet session fail over.
The following is the topology that you need to follow when you cluster Portal Server:
-
Gateway (This comes with the SRA components of the portal) : https://gateway.com
-
LoadBalancer : https://loadbalancer.com/portal
-
Access Manager : https://accessmanager.com:8080/amconsole
-
Portal Server instance 1 and Administration Server : http://machine1.com:38080/portal
-
Portal Server instance 2 : http://machine2.com:38080/portal
where Portal Server instance 1 and instance 2 are clustered with Administration Server on 4848 port of machine 1. In the following procedure, HADB is installed on machine 1 and machine 2.
 To Configure HADB for Session Fail Over
To Configure HADB for Session Fail Over
Before You Begin
-
All machines should be in the same subnet.
-
Ensure that name resolution of all servers is correct on each server, either through the hosts file or DNS as required.
-
Ensure that the fully qualified hostname is the first entry after the IP address in the /etc/hosts file. Enter the other machine details also in hosts file.
For example, machine1.domainname should be present in hosts file of machine 2 and vice versa.
cat /etc/hosts file on machine1 : 127.0.0.1 localhost 172.12.144.23 machine1 machine1.com loghost 172.12.144.24 machine2 machine2.com
-
Repeat the above procedure for hosts file on machine 2.
-
Any previously installed Java Enterprise System components are removed from the system before starting the installation procedure.
-
Installation happens in a shared memory configuration.
-
Check the physical memory of the nodes.
prtconf | grep Mem
-
Calculate the value of the shminfo_shmmax parameter using the following formula.
shminfo_shmmax = ( Server's Physical Memory in MB / 256 MB ) * 10000000
For example, if the physical memory is 512 MB, the value of the shminfo_shmmax parameter is 20000000. For 1 GB, it is 40000000 and for 2 GB, it is 80000000.
-
Add the following parameters to the /etc/system configuration file.
set shmsys:shminfo_shmmax=0x40000000 set shmsys:shminfo_shmseg=20 set semsys:seminfo_semmni=16 set semsys:seminfo_semmns=128 set semsys:seminfo_semmnu=1000 set ip:dohwcksum=0
-
Check that hostname lookup and reverse lookup is functioning correctly.
-
Check the contents of the /etc/nsswitch.conf file hosts entry.
cat /etc/nsswitch.conf | grep hosts
-
Allow non-console root login by commenting out the CONSOLE=/dev/console entry in the /etc/default/login file.
cat /etc/default/login | grep "CONSOLE="
CONSOLE=/dev/console
-
If you need to enable remote root FTP, comment out the root entry in the /etc/ftpd/ftpusers file.
cat /etc/ftpd/ftpusers | grep root
-
Permit ssh root login. Set PermitRootLogin to yes in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, and restart the ssh daemon process.
cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep PermitRootLogin
PermitRootLogin yes
etc/init.d/sshd stop /etc/init.d/sshd start
-
Generate the ssh public and private key pair on each machine. In this procedure, on machine 1 and machine 2..
ssh-keygen -t dsa
Enter file in which to save the key(//.ssh/id_dsa): <Return> Enter passphrase(empty for no passphrase): <Return> Enter same passphrase again: <Return>
Note –When running the ssh-keygen utility program, do NOT enter a passphrase and press Return. Otherwise, whenever ssh is used by the Application Server 9.1, the passphrase will be prompted for — breaking the automated scripts.
-
Generate the keys on all Application Server 9.1 nodes before proceeding to the next step where the public key values are combined into the authorized_keys file.
-
Copy all the public key values to each server's authorized_keys file. Create the authorized_keys file on each server.
cd ~/.ssh cp id_dsa.pub authorized_keys
-
Run the above command on machine 2 also and copy the public key of machine 1 that is present in the authorized_keys file on machine 1 to the authorized_keys file on machine 2. Repeat the same process vice versa.
-
Disable IPv6 interface that is not supported by HADB. To do this on Solaris, remove the /etc/hostname6.__0 file, where __ is eir or hme.
-
Make Date and Time same on all the machines involved in the topology.
-
Restart both the machines using init 6 command.
-
Install Application Server 9.1 including HADB from the Portal Server 7.2 GUI installer on both machine 1 and machine 2.
-
Run MA on both machine 1 and machine 2.
cd /opt/SUNWhadb/4/bin ./ma
You can notice that running MA will not install all the HADB packages. So, on machine 1 and machine 2, navigate to the directory where you have unzipped the Application Server 9.1 installer. For example, /Application Server 9.1 unzip location/installer-ifr/package/.
-
Run the pkgadd -d . SUNWhadbe SUNWhadbi SUNWhadbv command.
Now the machine 1 has DAS and first Portal instance and machine 2 has second Portal instance.
-
Create cluster on machine 1.
./asadmin create-cluster --user admin pscluster
-
Create node agent on machine1.
./asadmin create-node-agent --host machine1.com --port 4848 --user admin machine1node
-
Create node agent on machine2.
./asadmin create-node-agent --host machine1 --port 4848 --user admin machine2node
Note –The -- should point to machine 1, since machine 1 is the Administration Server.
-
Create an Application Server 9.1 instance on machine 1.
./asadmin create-instance --user admin --cluster pscluster --nodeagent machine1node --systemproperties HTTP_LISTENER_PORT=38080 machine1instance
-
Create an Application Server 9.1 instance on machine 2.
./asadmin create-instance --user admin --cluster pscluster --host machine1.com --nodeagent machine2node --systemproperties HTTP_LISTENER_PORT=38080 machine2instance
-
Start both the node agents.
/opt/SUNWappserver/appserver/bin/asadmin start-node-agent machine1node
-
Run configure-ha-cluster.
./asadmin configure-ha-cluster --user admin --port 4848 --devicesize 256 --hosts machine1.com,machine2.com pscluster
Note –If configure-ha-cluster fails, then while re-installing the next time, run the ps -ef | grep ma command and kill all the ma processes and also the processes, which runs on port 15200. Restart the machines and try to run configure-ha-cluster again.
If configure-ha-cluster is successful, you can install Portal Server 7.2 to leverage its enhanced cluster capability.
Replacing Java DB With Oracle Database
Java DB is used as a default database for Portal Server. This section explains how to replace Java DB with the Oracle database. Using this, you can ensure high availability and scalability. This procedure is divided into the following tasks:
-
Setting Up General Requirements
-
Preparing Oracle
 To Prepare the Database
To Prepare the Database
-
Prepare the Database.
-
Establish appropriate privileges for the user accounts.
-
Configure Community Membership and Configuration.
-
Load the schema onto the database.
-
Edit the jdbc/communitymc JDBC resource to point to the new database.
Note –On some of the web containers, you might need to edit the corresponding JDBC connection pool instead of the JDBC resource.
-
Configure and install portlet applications.
-
Locate the portlet applications.
portal-data-dir/portals/portal-id/portletapps
-
Configure portlet applications to use the new database by editing tokens_xxx.properties.
-
Using the Administration Console or command-line tool provided by the web container, create a JDBC resource for the application using the values from the tokens_xxx.properties.
- Resource JNDI Name
-
jdbc/DB_JNDI_NAME
- Resource Type
-
javax.sql.DataSource
- Datasource Classname
-
DB_DATASOURCEA
- User
-
DB_USERU
- Password
-
DB_PASSWORDS
- URL
-
DB_URL
Note –Some of the web containers might require you to set up a connection pool prior to setting up the JDBC resource.
-
Undeploy existing portlets that use the Java DB Database as a datastore.
-
Deploy the newly configured portlet applications.
-
 To Prepare the Oracle Database
To Prepare the Oracle Database
-
Prepare Oracle.
-
Install Oracle 10g Release 2.
-
Create a database instance named portal (the SID is portal).
-
Login to Oracle Enterprise Manager (http://hostname:5500/em) as SYSTEM.
-
Create a tablespace communitymc_portal-id for example, communitymc_portal1.
Note –For Wiki, FileSharing, and Surveys portlets, the tablespace and user accounts are created during the deployment of the Oracle configured portlet.
-
Create a user account with the following information:
- Username:
-
portal
- Password:
-
portal
- Default Tablespace
-
communitymc_portal-id
- Assign roles
-
CONNECT and RESOURCE
-
-
Prepare the web container for the New Database
-
Locate the Oracle JDBC driver ojdbc14.jar.
$ORACLE_HOME/jdbc/lib/ojdbc14.jar
Alternatively, you can download the JDBC driver from the Oracle web site. Ensure that you download the version that is compatible with the Oracle RDBMS you use.
-
Using the Administration Console or the CLI, add the JDBC driver ojdbc14.jar to the JVM classpath by adding the following JVM option: -Djdbc.drivers=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
-
For Web Server 7.0:
-
Login to Web Server 7 Administration Console.
-
Click the Configuration tab and select the respective configuration.
-
Click the java tab and add the location of the ojdbc14.jar to the classpath suffix.
-
Click the JVM Settings tab.
-
Replace any existing -Djdbc.drivers entry as below:
-Djdbc.drivers=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
-
If the -Djdbc.drivers entry does not exit, add the following:
-Djdbc.drivers=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
-
Click Save.
-
Click Deploy Pending and deploy the changes.
-
-
For Application Server 9.1
-
Login to Application Server 9.1 Administration Console.
-
Click Configurations > server-config (Admin Config) > JVM Settings > Path Settings > Path Settings.
-
Add the location of the ojdbc14.jar to the classpath suffix.
-
Click the JVM Settings tab.
-
Replace any existing -Djdbc.drivers entry as below:
-Djdbc.drivers=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
-
If the -Djdbc.drivers entry does not exit, add the following:
-Djdbc.drivers=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
-
Click Save.
-
-
-
-
Configure Community Membership and Configuration.
-
Edit the communitymc file database configuration file.
% vi portal-data-dir/portals/portal-id/config/portal.dbadmin db.driver=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver db.driver.classpath=JDBC-driver-path/ojdbc14.jar url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@oracle-host:oracle-port:portal
-
Remove or comment out the following property from the communitymc configuration file.
% vi portal-data-dir/portals/portal-id/config/communitymc.properties #javax.jdo.option.Mapping=derby
-
Load community schema onto the Oracle database.
% cd portal-data-dir/portals/portal-id/config % ant -Dportal.id=portal-id -f config.xml configure
-
Edit the JDBC and communitymc JDBC resource to point to Oracle.
-
For Application Server 9.1:
-
Login to the Application Server Administration Console.
-
Click Resources > JDBC > Connection Pools > communitymcPool
-
Set the Datasource classname to oracle.jdbc.pool.OracleDataSource
-
Set the following properties: user: portal and password: portal.
-
Delete the following derby properties: Database Name, Port Number, and Server Name.
-
Add the following property: url: jdbc:oracle:thin:@oracle-host:oracle-port:portal
-
Click Save.
-
-
-
-
Configure and install Portlet applications.
-
Run the filesharing script.
portal-data-dir/portals/portal-id/portletapps/filesharing
-
Configure tokens_ora.properties to load information when initially loading the schema.
- DB_ADMIN_DRIVER_CLASSPATH
-
$ORACLE_HOME/jdbc/lib/ojdbc14.jar
- DB_JNDI_NAME
-
OracleFileSharingDB
- DB_ADMIN_URL
-
jdbc:oracle:thin:@<ORACLE_ HOST>:<ORACLE_PORT>:portal
- DB_ADMIN_USER
-
<ORACLE_SYSTEM_USER>
- DB_ADMIN_PASSWORD
-
<ORACLE_SYSTEM_PASSWORD>
- DB_URL
-
jdbc:oracle:thin:@<ORACLE_ HOST>:<ORACLE_PORT>:portal
- DB_USER
-
portalfs
- DB_PASSWORD
-
portalfs
- DB_DRIVER_JAR
-
$ORACLE_HOME/jdbc/lib/ojdbc14.jar
- DB_TABLESPACE_NAME
-
Filesharingdb_<PORTAL_ID>
- DB_TABLESPACE_DATAFILE
-
filesharingdb_<PORTAL_ID>
- DB_TABLESPACE_INIT_SIZE
-
100M
-
Using the Administration Console or the command-line tool provided by the web container, create the JDBC resource using the values from the tokens_ora.properties.
-
For Application Server 9.1:
-
Create a new connection pool with the following properties:
- Name
-
OracleFilesharingDBPool
This value must match DB_JNDI_NAME in tokens_ora.properties.
- Resource Type
-
javax.sql.DataSource
- Datasource Class Name
-
oracle.jdbc.pool.OracleDataSource
This value must match DB_DATASOURCE in tokens_ora.properties.
-
In the Properties list, delete all the default properties and add the following:
- User
-
portalfs
This value must match DB_USER in tokens_ora.properties.
- Password
-
portalfs
This value must match DB_PASSWORD in tokens_ora.properties.
- URL
-
jdbc:oracle:thin:@<ORACLE_ HOST>:<ORACLE_PORT>:portal
This value must match DB_URL in tokens_ora.properties.
-
Create a JDBC resource with the following value:
- Resource JNDI Name
-
jdbc/OracleFilesharingDB
This value must match DB_JNDI_NAME in tokens_ora.properties.
- Connection Pool
-
OracleFilesharingDBPool
This value must match the pool that is created in the previous step.
-
Add the available target to the Selected list. Click OK.
-
-
-
Undeploy existing portlets that use Java DB Database as a datastore.
/opt/SUNWportal/bin/psadmin undeploy-portlet -u \ uid=amadmin,ou=people,dc=acme,dc=com -f password-file \ -p portal-id -i portal-instance-id
-
Deploy the newly configured file sharing portlet.
cd portal-data-dir/portals/portal-id/portletapps/filesharing ant -Dapp.version=ora
This ant command performs several tasks including regenerating the war image, loading up the schema onto the database, and deploying the newly built portlet. If the ant command fails and you want to unload schema, use the following command:
ant -Dapp.version=ora unconfig_backend
Note –During deployment provide the Access Manager Administrator password.
If the ant -Dapp.version=ora command fails with the following error, “Error: Password file does not exist or is not readable,” run ant deploy from command line to deploy the portlet.
-
Repeat this procedure for the other portlet applications, such as Surveys and Wiki.
-
Installing Portal Server on Application Server 9.1 Cluster
This section explains how to install Portal Server 7.2 in an Application Server 9.1 cluster environment. In a cluster environment, a primary node exists where Portal Server is installed. A cluster is created in the primary node. One or more secondary nodes exist where instances of Portal Server are created. The user accesses the portal through a load balancer. In such an environment, if any of the servers installed on any node goes down, the load balancer automatically redirects the user to the other available Portal Server instances.
Note –
If Portal Server is installed on a clustered environment, any deployment or undeployment of container specific files should be done on the primary instance, where DAS is installed.
Figure 7–2 Portal Server on Application Server 9.1 Cluster
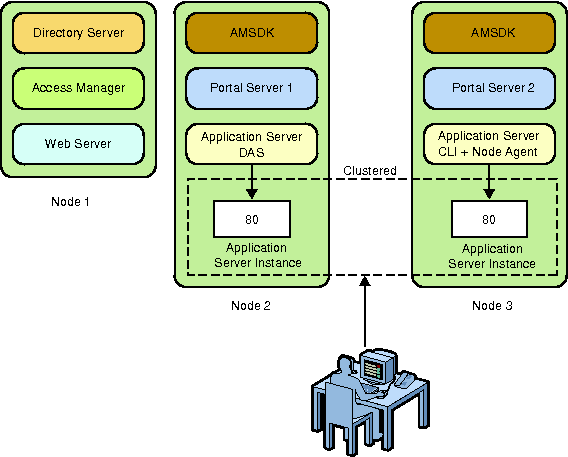
 To Install Portal Server on Application Server 9.1
Cluster
To Install Portal Server on Application Server 9.1
Cluster
The instructions provided in the task are for setting up a cluster configuration that contains only two instances.
-
Install Web Server 7.0 using Java ES 5 or Java ES 5 Update 1 installer.
-
Install Application Server 9.1 and Load Balancer plugin. Start DAS after installation.
ApplicationServer-install-dir/appserver/bin/asadmin start-domain --user admin --passwordfile password-file domain1
-
Install Access Manager and Directory Server on port 8080.
-
Start Directory Server.
DirectoryServer-install-dir/opt/SUNWdsee/ds6/bin/start /var/opt/SUNWdsee/dsdsins1
-
Start Application Server 9.1.
ApplicationServer-install-dir/appserver/bin/asadmin start-domain --user admin --passwordfile password-file domain1
-
Verify whether you are able to access, Access Manager Administration Console.
http://machine-name.domain-name.com:8080/amconsole
-
Start Web Server Administration Server and the default instance running on running on port 80.
-
Create Application Server 9.1 cluster, pscluster.
ApplicationServer-install-dir/appserver/bin/asadmin create-cluster --user admin --passwordfile password-file pscluster
-
Create node agent for Node 1.
ApplicationServer-install-dir/appserver/bin/asadmin create-node-agent --user admin --passwordfile password-file node1-nodeagent
-
Add an Application Server 9.1 instance named node1-7788 to the cluster.
ApplicationServer-install-dir/appserver/bin/asadmin create-instance --user admin --passwordfile password-file --cluster pscluster --nodeagent node1-nodeagent --systemproperties HTTP_LISTENER_PORT=7788 node1-7788
-
Start the local node agent.
ApplicationServer-install-dir/appserver/bin/asadmin start-node-agent --user admin --passwordfile password-file node1-nodeagent
-
Using Portal Server 7.2 GUI installer, install Portal Server 7.2 in the Configure Now mode.
-
Provide the cluster name in the installer and the port on which, portal instance is running properly.
-
Run the following command.
PortalServer-install-dir/SUNWportal/bin/psconfig --config example14.xml
-
After configuring, restart the cluster: pscluster.
-
Verify whether the portal desktop displays properly.
http://node1:7788/portal/dt
 To Add a Portal Server Instance to a Cluster
To Add a Portal Server Instance to a Cluster
-
Create a node agent that points to the DAS on Node 1.
/opt/SUNWappserver/appserver/bin/asadmin create-node-agent --user admin --passwordfile password-file --host Node 1 --port 4848 node2-nodeagent
-
Create an instance for the cluster.
/opt/SUNWappserver/appserver/bin/asadmin create-instance --user admin --passwordfile password-file --cluster pscluster --nodeagent node1-nodeagent --systemproperties HTTP_LISTENER_PORT=8877 node2-8877
-
Start the node agent.
/opt/SUNWappserver/appserver/bin/asadmin start-node-agent --user admin --passwordfile as_password hostBnodeagent
-
Invoke the Portal Server 7.2 GUI installer and provide details about this instance. Provide the same portal-id as Node1. The installer will automatically create a portal instance on this Node.
 To Install Load Balancer on Node 2
To Install Load Balancer on Node 2
-
Setting up Load Balancer for pscluster and copy over the loadbalancer.xml file.
asadmin create-http-lb-config -u admin portal_lb asadmin create-http-lb-ref -u admin --config portal_lb pscluster asadmin enable-http-lb-application -u admin --name portal pscluster asadmin create-http-health-checker -u admin pscluster asadmin export-http-lb-config -u admin --config portal_lb loadbalancer.xml
-
Modify theloadbalancer.xml file. Change enabled to “true” for all entries.
-
Copy the loadbalancer.xml file to the Web Server 7.0 instance configuration directory.
-
Restart DAS and cluster.
-
Stop and start Web Server 7.0 instance.
-
Ensure that portal is accessible through Load Balancer.
 To Display the Default WSRP Portlets in the WSRP tab
of Portal Desktop
To Display the Default WSRP Portlets in the WSRP tab
of Portal Desktop
When you configure Portal Server on Application Server 9.1 cluster, the default portlets are not displayed on the WSRP tab of the desktop. Do the following to get portlets displayed on the WSRP tab.
-
Create a producer with the portlets that you want to add to the WSRP tab.
-
Configure a consumer with the producer.
-
Add the consumer to the WSRPSamplesTabPanel container.
Note –You can also do the following to display the defaults portlets on the WSRP tab:
-
Create a producer with Bookmark, JSP Remote, Notepad, and Weather portlets.
-
Configure a consumer with the producer.
-
Copy the producer entity ID after configuring the producer.
-
Go to Manage Channels and Container.
-
Under Developer Sample, select the WSRPSamplesTabPanel container.
This container displays Bookmark, JSP Remote, Notepad, and Weather portlets.
-
Select the portlet and paste the producer entity ID to the Producer Entity ID field.
-
 To Configure Portlet Session Failover on Application
Server 9.1
To Configure Portlet Session Failover on Application
Server 9.1
Before You Begin
The portal instances should be clustered and HADB should be installed.
-
Undeploy the portal.war from the Application Server 9.1 DAS (Administration Server), and add the <distributable/> tag in the WEB-INF/web.xml of portal.war. Refer to the sample web.xml file displayed below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN " "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd"> <web-app> <display-name>Sun Java Enterprise System Portal Server Desktop Web Application</ display-name> <description>Provides a user customizable interface for content that is aggregat ed from Portlet applications</description> <distributable/> <context-param> <param-name>desktop.configContextClassName</param-name> <param-value>com.sun.portal.desktop.context.PropertiesConfigContext</param-value>
-
Add the same <distributable/> tag to the web.xml of the portlet.war which is used for storing session variable.
-
Ensure that the Availability option is selected for both portal.war and the portlet.war files.
Setting up SSL Termination Between Gateway and Portal Server at Load Balancer
SSL Termination between Gateway and Portal Server at Load Balancer means that SSL traffic between Gateway and the Portal Server is terminated at the Load Balancer. SSL communication has an overhead of encrypting and decrypting that affects performance.
 To Set up SSL Termination Between Gateway and Portal
Server at Load Balancer
To Set up SSL Termination Between Gateway and Portal
Server at Load Balancer
Assume there are two instances of Portal Server: PS1 and PS2 on Node 1 and Node 2 respectively. Gateway is on Node 3 and Load Balancer is on Node 4 — between Gateway and Portal Server instances. Access Manager (AM) instances are on Portal Server (PS) instances. Assume there are two instances for Access Manager and Portal Server: Gateway —> Load Balancer —> Portal Server instances (PS 1, PS 2....and so on).
-
On Node 1, install Portal Server, Access Manager, and Directory Server.
Use Java ES 5 or Java ES Update 1 installer for installing Access Manager and Directory Server. Use Portal Server 7.2 GUI installer for installing Portal Server 7.2.
-
Start the web container and Directory Server and ensure that Portal Server is accessible, to check whether everything is installed properly on Node 1.
-
On Node 3, install Gateway and Access Manager SDK and point to Portal Server on Node 1. Ensure that you can login to Portal Server through Gateway on Node 1.
Now, you have setup a single Gateway and Portal Server without a Load Balancer.
-
On Node 2, install Application Server 9.1 to create Access Manager and Portal Server instances.
-
Login to Access Manager (on Node 1) Administration Console, through a web browser. In the Organization Aliases listbox on the right side with entries Node1.domain.com and domain, add the Node2.domain.com entry.
-
Click Service Configuration -> Platform. In the Platform Server List, add the http://Node2.domain.com:port entry.
-
On Node 2, install Access Manager. Point to Directory Server on Node 1. Restart Application Server 9.1 on Node 2 and ensure that the Access Manager Administration Console is accessible.
-
Create a Portal Server instance on Node 2.
-
Install Portal Server 2 in the Configure Later mode.
-
Modify the Webcontainer.properties.SJSAS9.1 and run the following command.
./psadmin create-instance -u amadmin -f ps-password -p portal-id -w /opt/SUNWportal/template/Webcontainer.properties.SJSAS91
-
Restart Application Server 9.1 and access the newly created Portal Server instance.
-
-
Install Load Balancer on Node 4. This can be a software or a hardware load balancer. Ensure that you can load balance Access Manager and Portal Server URIs through this SSL instance of Load Balancer.
-
Access Portal Server Administration Console on Node 1 or Node 2.
-
Go to Secure Remote Access -> default. In the Portal Servers list box, remove the existing entry. Add the https://Node4.domain.com:port/portal entry in the list box.
-
In the URLs to which User Session Cookie is Forwarded list box, add the following URLs and save:
http://Node1.domain.com:port http://Node1.domain.com:port/portal http://Node2.domain.com:port http://Node2.domain.com:port/portal https://Node4.domain.com:port https://Node4.domain.com:port/portal
-
Click the Security Tab. In the Non-Authenticated URL list, add the following URLs to the existing URLs:
http://Node2.domains.com:port/amserver/css http://Node2.domain.com:port/amserver/login_images, http://Node2.domain.com:port/amserver/js http://Node2.domain.com:port/amconsole/console/js http://Node2.domain.com:port/amconsole/console/images http://Node2.domain.com:port/amconsole/console/css http://Node2.domain.com:port/amserver/images https://Node4.domains.com:port/amserver/css https://Node4.domain.com:port/amserver/login_images, https://Node4.domain.com:port/amserver/js https://Node4.domain.com:port/amconsole/console/js https://Node4.domain.com:port/amconsole/console/images https://Node4.domain.com:port/amconsole/console/css https://Node4.domain.com:port/amserver/images
-
-
On Node 1 and Node 2, run the following command to populate Non-Authenticated URL list under the default Gateway profile:
./psadmin provision-sra -u amadmin -f ps_password -p portal-id --gateway-profile default --enable ./psadmin provision-sra -u madmin -f ps_password --loadbalancer-url https://Node4.domain.com:port/portal --console --console-url https://Node4.domain.com:port/psconsole -gateway-profile default ----enable
-
On Node 1, open the /etc/opt/SUNWam/config/AMConfig.properties file and do following:
-
Add the following line: com.sun.identity.server.fqdnMap[Node4.domain.com]=Node4.domain.com
-
Edit the line: com.sun.identity.loginurl=https://Node4.domain.com:port/amserver/UI/Login
-
com.iplanet.am.jssproxy.trustAllServerCerts=true
-
-
On Node 1 and Node 2, add a Certificate Authority Root CA certificate to JVM keystore:
cd /usr/jdk/entsys-j2se/jre/lib security /usr/jdk/entsys-j2se/jre/bin/keytool -keystore cacerts -keyalg RSA import -trustcacerts -alias "Node1.domain.com" -storepass changeit -file path-to-rootca-certificate
-
On Node 1 and Node 2, run the following command.
psadmin set-attribute -u amadmin -f ps-password p portal1 -m desktop -a AccessURL "https://Node4.domain.com:port"
-
On Node 2, repeat the above step. Restart Application Server 9.1 and Common Agent Container.
-
Install server certificate and Root CA certificate on Gateway Node from the same Certificate Authority from where Load Balancer was assigned certificate.
-
Point the Gateway to Load Balancer instead of Portal Server and Access Manager on Node 1. Do the following on the Gateway Node.
-
In the platform.conf.default file, change gateway.ignoreServerList to true.
-
In the platform.conf.default file, change gateway.dsame.agent to https\://Node4.domain.com\:port/portal/RemoteConfigServlet.
-
In the AMConfig-default.properties and AMConfig.properties files, change the Access Manager related information as follows:
com.iplanet.am.server.host=Node4.domain.com com.iplanet.am.server.port=load-balancer-port com.iplanet.am.console.protocol=https com.iplanet.am.console.host=Node4.domain.com com.iplanet.am.console.port=load-balancer-port com.iplanet.am.profile.host=Node4.domain.com com.iplanet.am.profile.port=load-balancer-port com.iplanet.am.naming.url=https://Node4.domain.com:load-balancer-port/amserver/namingservice com.iplanet.am.notification.url=https://Node4.domain.com:load-balancer-port/amserver/notificationservice
-
-
Restart the Gateway and access it.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
