Portlet Filters
A portlet filter is a Java technology-based component that can be used to modify the content of the portlet request and portlet response before or after any life cycle method of the portlet. The concept of a portlet filter is same as that of a servlet filter. The only difference is that a servlet has only one request handling method, service() and therefore there is only one type of the servlet filter. A portlet on the other hand has four types of request handling methods and therefore there are four different types of portlet filters.
The portlet API defines the following interfaces for creating portlet filters:
-
javax.portlet.filter.ResourceFilter - For serveResource method
-
javax.portlet.filter.RenderFilter - For render method
-
javax.portlet.filter.ActionFilter - For processAction method
-
javax.portlet.filter.EventFilter - For processEvent method
Each of the above filter interface contains a single doFilter (*Request, *Response, FilterChain chain) method, which differs in the type of request and response object. For example, the doFilter() method in ActionFilter takes the code>ActionRequest and ActionResponse objects while the doFilter() method of RenderFilter takes instances of the RenderRequest and RenderResponse.
Each filter interface extends a common base interface called javax.portlet.filter.PortletFilter. This common base interface contains the following two methods:
-
init(javax.portlet.filter.FilterConfig filterConfig) - The init() method makes sure that every filter has access to a FilterConfig object from which it can obtain its initialization parameters, a reference to the PortletContext, which it can use, for example, to load resources needed for filtering tasks.
-
destroy() - Signifying the end of service of the filter.
The init() and destroy() methods of a portlet filter are called only once during their lifetime.
A single filter class can provide filter functionality for more than one life cycle method. Also, a single filter can provide filter functionality for more than one portlet. Multiple filters can be associated with one life cycle method of a portlet. The doFilter() method of a portlet filter might create customized request and response objects by using the *RequestWrapper and *ResponseWrapper classes and by passing these wrappers to the doFilter() method of the FilterChain object.
 To Write a Portlet Filter
To Write a Portlet Filter
-
Write a filter class.
A filter class should implement one or more of the above mentioned four interfaces and should provide a no argument public constructor. The filter class should also override the init() and destroy() methods of the javax.portlet.filter.PortletFilter interface.
public class HitCounterFilter implements RenderFilter { private FilterConfig filterConfig = null; public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws PortletException { this.filterConfig = filterConfig; } public void doFilter(RenderRequest renderRequest, RenderResponse renderResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, PortletException { . . . StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(sw); . . . writer.println(); writer.println("==============="); writer.println("The number of hits is: " +count); writer.println("==============="); . . . filterChain.doFilter(renderRequest, renderResponse); } public void destroy() { } } -
Add the following XML fragments in the portlet.xml files after you write the portlet filter class.
<portlet-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/ portlet-app_2_0.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/ portlet-app_2_0.xsd http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/portlet-app_2_0.xsd" id="myPortletApp" version="2.0"> <portlet> ... <filter> <filter-name>HitCounterRenderFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.filter .HitCounterFilter</filter-class> <lifecycle>RENDER_PHASE</lifecycle> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>HitCounterRenderFilter</filter-name> <portlet-name>HelloWorld</portlet-name> </filter-mapping> </portlet-app>
Sample Application
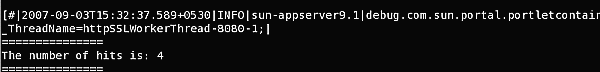
The following figure shows the number of times the sample portlet has been accessed is logged using a Filter. Access the portlet and check the application server log file. The log file shows the number of times the portlet has been accessed.
Figure 16–3 Sample Application for Portlet Filter
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
