Events
Events enable portlets to communicate with each other by sending and receiving events. An event is a life cycle operation that occurs before the rendering phase. Events can be described as a loosely coupled, brokered means of communication between portlets. Events allow portlets to respond on actions or state changes not directly related to an interaction of the user with the portlet. A portlet can declare events in its deployment descriptor by using the event-definition element in the portlet application section.
In the portlet application section, each portlet specifies the events it would like to publish through the supported-publishing-event element and the events it would like to process through the supported-processing-event element. The supported-publishing-event and supported-processing-event elements must reference the event name defined in the portlet application section in a event-definition element.
The portlet creates events using the setEvent() method during action processing. This will be processed by the portlet container after the action processing has finished. To receive events, the portlet must implement the javax.Portlet.EventPortlet interface. The portlet container calls the processEvent() method for each event targeted to the portlet with an EventRequest and EventResponse object. The portlet can access the event that triggered the current process event call by using the EventRequest.getEvent() method. This method returns an object of type Event encapsulating the current event name and value.
Event names are represented as QNames to identify them uniquely. The event name can be retrieved by using the getQName() method that returns the complete QName of the event, or by using the getName() method that only returns the local part of the event name. The value of the event must be based on the type defined in the deployment descriptor.
 To Create Portlets That use the event Feature
To Create Portlets That use the event Feature
-
Declare the events in the portlet.xml file. To do this:
-
Set the event definition at the portlet application level. This specifies the event name and the object type.
Note –The object must be serializable and annotated with XML root element.
<portlet-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/portlet-app_2_0.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/portlet-app_2_0.xsd /opt/SUNWportal/dtd/portlet.xsd" version="2.0"> <portlet> <portlet-name>listportlet</portlet-name> <portlet-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.ListPortlet</portlet-class> .......<> </portlet> <portlet> <portlet-name>detailportlet</portlet-name> <portlet-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.DetailPortlet</portlet-class> .......<> </portlet><> <portlet> <portlet-name>weatherportlet</portlet-name> <portlet-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.WeatherPortlet</portlet-class> .......<> </portlet><> <portlet> <portlet-name>mapportlet</portlet-name> <portlet-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.MapPortlet</portlet-class> .......<> </supported-processing-event> </portlet> <event-definition> <qname xmlns:x="http:sun.com/tourevents"> x:Tour </qname> <value-type>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.Tour</value-type> </event-definition> </portlet-app> @XmlRootElement public class Tour implements Serializable { public Tour() { } private String name; private String description; private String guide; private String weathercode; private String mapcode; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; } public String getGuide() { return guide; } public void setGuide(String guide) { this.guide = guide; } public String getWeathercode() { return weathercode; } public void setWeathercode(String weathercode) { this.weathercode = weathercode; } public String getMapcode() { return mapcode; } public void setMapcode(String mapcode) { this.mapcode = mapcode; } } -
In the portlet section, specify the event name defined above for the portlets that you want to publish in this event.
<portlet-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/portlet-app_2_0.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/portlet-app_2_0.xsd /opt/SUNWportal/dtd/portlet.xsd" version="2.0"> <portlet> <portlet-name>listportlet</portlet-name> <portlet-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.ListPortlet</portlet-class> ... <supported-publishing-event> <qname xmlns:x="http:sun.com/tourevents"> x:Tour </qname> </supported-publishing-event> </portlet> ... </portlet-app>
-
In the portlet section, specify the event name defined above for the portlets that want to process in this event.
<portlet-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/portlet-app_2_0.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/portlet/portlet-app_2_0.xsd /opt/SUNWportal/dtd/portlet.xsd" version="2.0"> <portlet> ... <portlet-name>detailportlet</portlet-name> <portlet-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.DetailPortlet</portlet-class> ..... <supported-processing-event> <qname xmlns:x="http:sun.com/tourevents"> x:Tour </qname> </supported-processing-event> </portlet> <portlet> <portlet-name>weatherportlet</portlet-name> <portlet-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.WeatherPortlet</portlet-class> ..... <supported-processing-event> <qname xmlns:x="http:sun.com/tourevents"> x:Tour </qname> </supported-processing-event> </portlet> <portlet> <portlet-name>mapportlet</portlet-name> <portlet-class>com.sun.portal.portlet.touripc.MapPortlet</portlet-class> ..... <supported-processing-event> <qname xmlns:x="http:sun.com/tourevents"> x:Tour </qname> </supported-processing-event> </portlet> ...... </portlet-app>
-
-
Issue an event in the portlet that was specified as a supported-publishing-event event in the portlet.
public void processAction(ActionRequest request, ActionResponse response) throws PortletException, java.io.IOException { Tour selectedTour = new Tour(); String name = request.getParameter("name"); String desc = request.getParameter("desc"); String guide = request.getParameter("guide"); String wc = request.getParameter("wc"); String mc = request.getParameter("mc"); selectedTour.setName(name); selectedTour.setDescription(desc); selectedTour.setGuide(guide); selectedTour.setWeathercode(wc); selectedTour.setMapcode(mc); QName qname = new QName("http:sun.com/tourevents", "Tour"); response.setEvent(qname, selectedTour); ......... } } -
Process the event in the portlet that has been specified as a supported-processing-event event in the portlet.
public class MapPortlet extends GenericPortlet { ......... public void processEvent(EventRequest request, EventResponse response) { Event event = request.getEvent(); logger.severe("MapPortlet got event"); if(event.getName().equals("Tour")){ Tour payload = (Tour)event.getValue(); response.setRenderParameter("TourName", payload.getName()); response.setRenderParameter("TourMap", payload.getMapcode()); } } ......... } public class DetailPortlet extends GenericPortlet{ ......... public void processEvent(EventRequest request, EventResponse response) { Event event = request.getEvent(); if(event.getName().equals("Tour")){ Tour payload = (Tour)event.getValue(); response.setRenderParameter("TourName", payload.getName()); response.setRenderParameter("TourGuide", payload.getGuide()); response.setRenderParameter("TourDesc", payload.getDescription()); } } ......... } public class WeatherPortlet extends GenericPortlet { ......... public void processEvent(EventRequest request, EventResponse response) { Event event = request.getEvent(); if(event.getName().equals("Tour")){ Tour payload = (Tour)event.getValue(); response.setRenderParameter("TourName", payload.getName()); response.setRenderParameter("TourCode", payload.getWeathercode()); } } ......... }
Sample Application
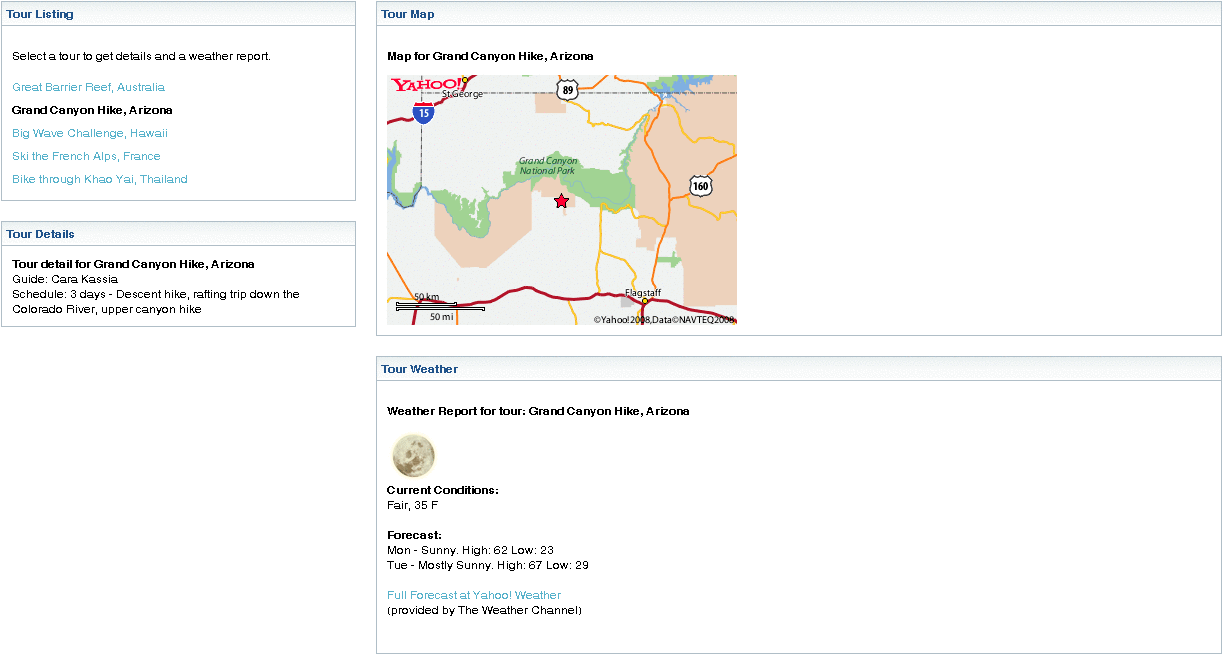
The following figure shows the Tour Listing, Tour Details, Tour Map, and Tour Weather Portlets that participate in the event. Clicking on any Tour Listing, triggers an event. This event is processed by the Tour Details, Tour Map, and Tour Weather Portlets to show the relevant information.
Figure 16–1 Sample Application for Eventing
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
