Chapter 12 Enabling Single Sign-On Between Sun Identity Manager and OpenSSO Enterprise
This chapter provides information about integrating Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 with Sun Identity Manager 8.0. This information is useful when you want to enable single sign-on between the two products, or when you want to use Identity Manager to provision users to OpenSSO Enterprise.
The following topics are contained in this chapter:
-
Considering the Deployment Assumptions, Dependencies, and Constraints
-
Setting Up and Configuring Single Sign-On Between Identity Manager and OpenSSO Enterprise
About Sun Identity Manager
Sun Identity Manager enables you to securely and efficiently manage and audit access to accounts and resources, and to distribute access management overhead. By mapping Identity Manager objects to the entities you manage such as users and resources, you significantly increase the efficiency of your operations. The Identity Manager solution enables you to:
-
Manage account access to a large variety of systems and resources.
-
Securely manage dynamic account information for each user's array of accounts.
-
Set up delegated rights to create and manage user account data.
-
Handle large numbers of enterprise resources, as well as an increasingly large number of extranet customers and partners.
-
Securely authorize user access to enterprise information systems.
Grant, manage, and revoke access privileges across internal and external organizations.
-
Keep data in sync by not keeping data.
Analyzing the Deployment Architecture
This deployment requires an OpenSSO Enterprise server, an Identity Manager server, and a Sun Policy Agent installed on the Identity Manager web container. The OpenSSO Enterprise server is configured with two data stores: the OpenSSO configuration data store, and the Sun Directory Server user data store. The user data store is configured in the OpenSSO Enterprise subrealm. The Identity Manager server is configured to use a MySQL server for both Identity Manager configuration and Identity Manager user data.
The following figure illustrates the main components of the deployment.
Figure 12–1 Deployment Architecture for Enabling Single Sign-On Between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager
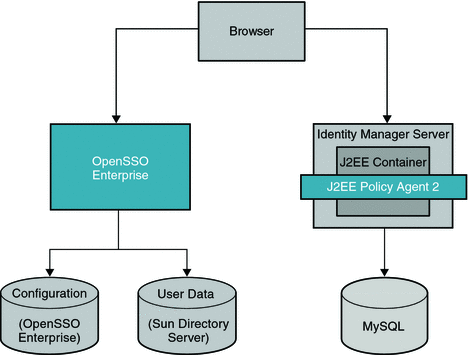
The Sun Policy Agent plays an important role in the single sign-on between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager. In addition to protecting the Identity Manager content pages, it helps map the OpenSSO Enterprise user ID to the Identity Manager user ID.
The following two figures illustrate a typical process flow.
Figure 12–2 Process Flow for Single Sign-On Between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager (Continued on next page)
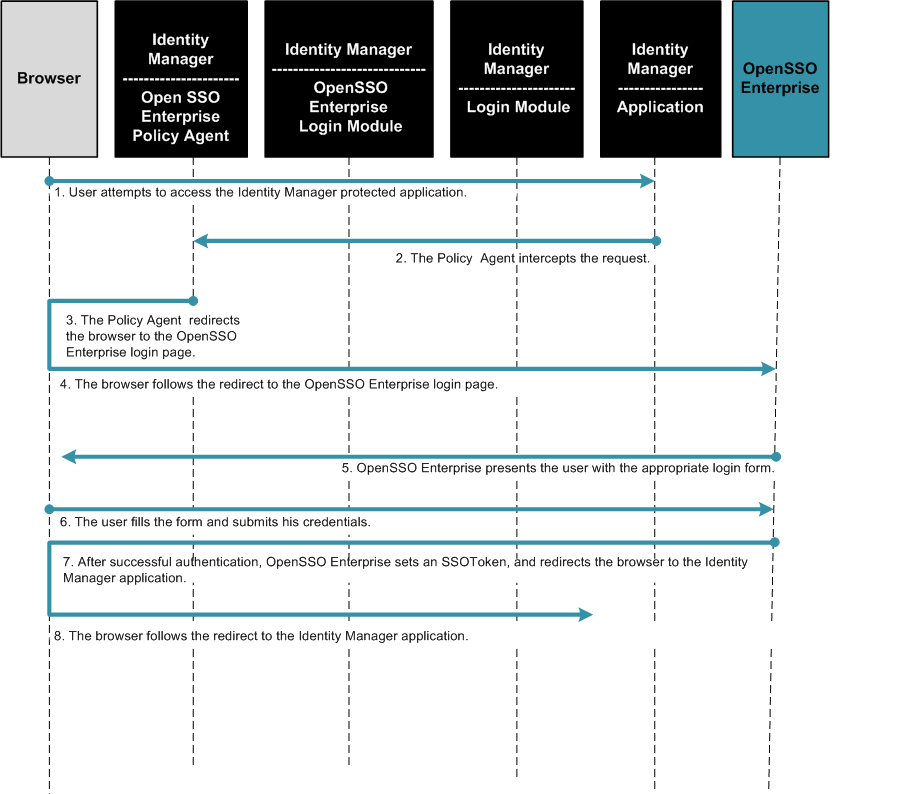
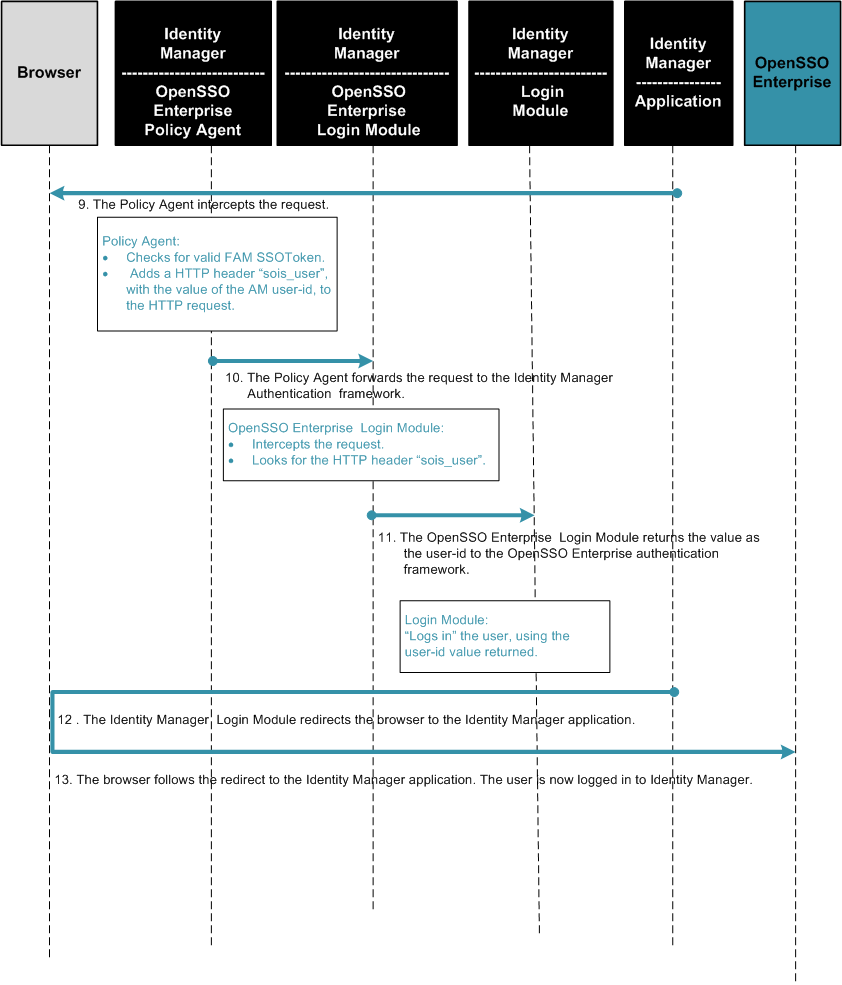
Figure 12–3 Process Flow for Single Sign-On Between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager (Continued)
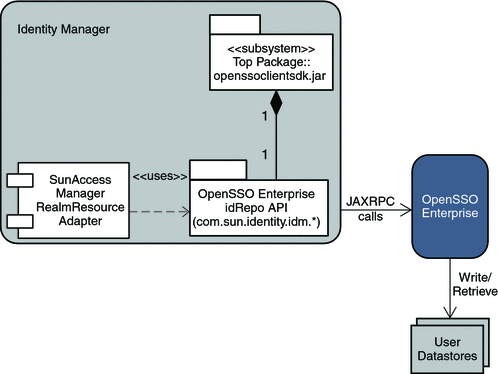
The following UML use case diagram illustrates the provisioning and retrieval of objects in Identity Manager.
Figure 12–4 Provisioning and Retrieving Objects in Identity Manager
Considering the Deployment Assumptions, Dependencies, and Constraints
Before you can enable single sign-on between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager, you must resolve the following issues.
Assumptions
-
OpenSSO Enterprise must already be installed.
-
OpenSSO Enterprise must be installed in the Realm mode of operation.
-
OpenSSO Enterprise must be configured with Sun OpenDS as the embedded configuration data store.
-
OpenSSO Enterprise must contain a sub-realm named idm configured with Sun Directory Server user data store.
-
The Directory Server user data store must also have the OpenSSO Enterprise schema loaded in it.
Dependencies
-
If you require roles to be provisioned on Identity Manager to OpenSSO Enterprise, and you are using the Sun Access Manager Resource Adapter, then the OpenSSO Enterprise user data store must have the OpenSSO Enterprise schema loaded in it.
If the OpenSSO Enterprise data store plug-in for a generic LDAPv3 data store has no OpenSSO Enterprise schema in it, the data store plug-in does not support the management of either managed roles or filtered roles through it. The OpenSSO Enterprise data store plug-in is designed to work this way. It is important to note here that you do not have to provision roles in order to achieve single sign-on.
-
Because OpenSSO Enterprise is installed in the Realm mode of operation, the Identity Manager resource adapter for Realm mode, SunAccessManagerRealmResourceAdapter, must be configured on Identity Manager.
In earlier versions of OpenSSO Enterprise, previously known as Access Manager, the product was installed in the Legacy mode of operation. In Legacy mode, a different Identity Manager resource adapter, SunAccessManagerResourceAdapter, must be configured on Identity Manager. Both types of adapters have the same functionality with one difference. The SunAccessManagerResourceAdapter uses the legacy Access Manager AMSDK API, while the SunAccessManagerRealmResourceAdapter uses the OpenSSO Enterprise idRepo API. The idrepo APIs are the next-generation OpenSSO client APIs, and will eventually replace the legacy AMSDKAPI.
Constraints
When testing the Sun Access Manager Resource Adapter, before the Policy Agent has been installed, the client-side AMConfig.properties file must be configured with amadmin or a user that has privileges to read the OpenSSO Enterprise configuration data, for the property com.sun.identity.agents.app.username. If a different type of user is used in this configuration, the configuration of the Sun Access Manager Resource Adapter fails. This change is required only until the Policy Agent is installed. After the Policy Agent has been installed, the AMConfig.properties file is not required and can be deleted from the filesystem.
Although this document describes the use case where Identity Manager and OpenSSO Enterprise are configured for both single sign-on and provisioning, it is possible to configure the deployment for either single sign-on or provisioning only. If single sign-on between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager is not required, then the OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent does not need to be installed and configured. You can ignore the steps that involve configuring the OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent.
Understanding Typical Business Use Cases
The most common use case for this deployment is when a company uses OpenSSO Enterprise with OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agents to protect business applications, including Identity Manager applications. The main objective is to streamline the login process for end-users who are already logged in to OpenSSO Enterprise. For example, if a user is already logged in to OpenSSO Enterprise, the user should experience a seamless transition into any Identity Manager application without having to log in to Identity Manager. A secondary objective is to provide a measure of controlled access to all Identity Manager applications.
Another typical use case for this deployment is provisioning. The company uses Identity Manager to provision users into various business systems such as human resources or accounting systems. This can also include provisioning users into the company's business systems that are protected by OpenSSO Enterprise.
Setting Up and Configuring Single Sign-On Between Identity Manager and OpenSSO Enterprise
The following components are used in this deployment:
-
Sun Solaris Operating System 10
-
Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0
-
Sun Java Identity Manager 8.0
-
Sun Java Web Server 7.0
-
Sun Java Application Server 9.1
-
Sun Java Directory Server 6.1
-
MySQL 5.1
-
MySQL Connector 5.0
-
Sun Java AM Policy Agent 3.0 (for Sun Java Application Server 9.1) (Optional)
-
Netbeans IDE 6.0.1
See the Chapter 1, Integrating Sun Identity Manager , in Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 Integration Guide for detailed installation steps. The following is a summary of high-level procedures you must complete to enable single sign-on between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager:
-
Installing And Configuring MYSQL
-
Install MySQL.
-
Complete post-installation tasks.
-
-
Installing And Configuring Identity Manager Application Server
-
Install Application Server.
-
Install Identity Manager on Application Server.
-
Complete post-installation configuration on Application Server.
-
-
Create an OpenSSO Enterprise Realm Administrator in OpenSSO Enterprise.
-
Create an OpenSSO Enterprise Realm Resource Object in Identity Manager.
-
Provision identities from Identity Manager to OpenSSO Enterprise.
-
Provision a test user from Identity Manager into OpenSSO Enterprise.
-
Provision a test role from Identity Manager into OpenSSO Enterprise.
-
Provision an Admin-User from Identity Manager into OpenSSO Enterprise
-
Provision an Admin-Role from Identity Manager into OpenSSO Enterprise.
-
-
Install and Configure the OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent on Identity Manager.
-
Complete pre-installation tasks for the OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent.
-
Install the OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent on the Identity Manager server.
-
Configure the OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent on the OpenSSO Enterprise Server.
-
Disable OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent protection of the Identity Manager server.
-
Configure the OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent on the Identity Manager server.
-
-
Configure Identity Manager for single sign-on.
-
Configure Identity Manager Login Module Groups.
-
Configure the Identity Manager User Login Interface.
-
Configure the Identity Manager Admin Login Interface.
-
-
Test single sign-on from OpenSSO Enterprise to Identity Manager.
-
Re-Enable OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent protection of the Identity Manager server.
-
Test end-user single sign-on between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager.
-
Test Admin-User single sign between OpenSSO Enterprise and Identity Manager.
-
Evaluating Benefits and Tradeoffs
As you design your deployment architecture, be sure to consider the benefits, tradeoffs. The following lists may help you determine if enabling single sign-on between Identity Manager and OpenSSO Enterprise is appropriate to meet your business needs.
Benefits
-
If you use an OpenSSO Enterprise user store that has the OpenSSO Enterprise schema loaded into it, you can provision managed-roles or filtered-roles into OpenSSO Enterprise.
-
If you configure OpenSSO Enterprise with a generic LDAP user datastore that does not have the OpenSSO Enterprise schema loaded into it, then you could configure an LDAP Resource Adapter instance instead of the Sun Access Manager Resource Adapter on Identity Manager. The LDAP Resource Adapter on Identity Manager is a generic adapter that can be used to provision or manage objects in any LDAP resource. This would potentially reduce the number of different types of Resource Adapters, that an Identity Manager administrator would have to maintain.
Tradeoffs
If the OpenSSO Enterprise user store does not have the OpenSSO Enterprise schema loaded into it, OpenSSO Enterprise would use the generic LDAPv3 plug-in for this datastore. The creation of managed-roles and filtered-roles is not supported on such a datastore.
Finding More Information
-
Sun Identity Manager 8.0 product documentation
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
