Chapter 2 SPARC: Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB Versions Before 4.4)
This document describes the procedures to install and configure the data service called Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB).
This document contains two chapters.
-
This chapter contains information for the data service when it makes highly available those versions of the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) application before version 4.4 that are supported by the Sun Cluster product and by this data service.
-
Chapter 1, Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (Supporting HADB Versions as of 4.4) contains information for the data service when it makes highly available those versions of the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) application as of version 4.4 that are supported by the Sun Cluster product and by this data service.
This chapter contains the following sections.
-
Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Overview
-
Installing and Configuring the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Software
-
Creating a Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Database
-
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Packages
-
Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
-
Tuning the Fault Monitor for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Overview
This section describes how the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) data service enables the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) software for high availability.
The Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) is a data service with appropriate extension properties to configure a database that is mastered on multiple nodes at one time.
See Chapter 1, Planning for Sun Cluster Data Services, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for general information about data services.
The Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) software is packaged with the Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition installation. However, you can run Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) and Sun Java System Application Server on separate clusters if appropriate. This document describes how to install and configure the data service that enables you to use Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) in a cluster. First, enable Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) in your cluster to provide session and Enterprise Java Bean (EJB) persistence. See Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.2 High Availability Administration Guide for information about the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) software.
Implementation of the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) does not assume the existence of applications on which your architecture depends, such as databases and web servers. However, such applications can be configured to be highly available and might run on a different cluster.
Overview of the Installation and Configuration Process for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
The following table summarizes the tasks for installing and configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) and provides cross-references to detailed instructions for performing these tasks. Perform the tasks in the order that they are listed in the table.
Table 2–1 Tasks for Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)|
Task |
For Instructions |
|---|---|
|
Plan the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) | |
|
Install and configure the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) software |
Installing and Configuring the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Software |
|
Create a Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) database |
How to Create a Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Database |
|
Install the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) package |
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Packages |
|
Register and configure Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) as a data service mastered on multiple nodes at one time |
How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) |
|
Verify the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) | |
|
Maintain the HADB database | |
|
Tune the fault monitor for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) |
Tuning the Fault Monitor for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) |
Note –
If you run multiple data services in your Sun Cluster configuration, you can set up the data services in any order, with the following exception. If the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) data service depends on the Sun Cluster HA for DNS data service, you must set up DNS first. For details, see Sun Cluster Data Service for DNS Guide for Solaris OS. The DNS software is included in the Solaris software. If the cluster is to obtain the DNS service from another server, you should first configure the cluster to be a DNS client.
Planning the Installation and Configuration of Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
This section contains the information that you need to plan your installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB).
Store static files and data on the local file system of each cluster node. The Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) software is installed when you install the Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition software. See Sun Cluster Data Service for Sun Java System Application Server Guide for Solaris OS documentation for instructions. When the database is created, the configuration and data files are created by default on the local file system of each cluster node. For details, see the Sun Java System Application Server documentation.
Configuration Overview
Use the multiple masters configuration in this section to plan the installation and configuration of the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) data service. This data service might support additional configurations. However, you must contact your Enterprise Services representative for information about additional configurations.
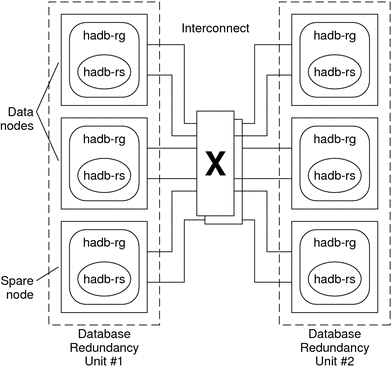
HADB configurations are defined by data nodes, or a collection of processes. Each node is a dedicated area of main memory with one or more secondary storage devices. These storage devices are not shared storage. Each HADB data node must have exclusive access to an area of main memory and several areas of disk space. HADB data nodes are active or spare.
The recommended minimum requirement for a cluster running the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) and the Sun Java System Application Server is four active data nodes plus two spare nodes. See Creating a Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Database for an example of how to create a Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) with four active nodes and two spare nodes by using the hadbm comand-line utility. For high availability, you configure the HADB data redundancy unit (DRU) to use the Sun Cluster interconnect. See the Sun Java System Application Server documentation for detailed information about DRUs. The HADB JDBC driver in the client application handles highly available access to the database.
The following figure illustrates the recommended minimum configuration for the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) and the Sun Java System Application Server.
Figure 2–1 Recommended Minimum Configuration
Configuration Planning Questions
Use the questions in this section to plan the installation and configuration of the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) data service. See Considerations for Installing and Configuring a Data Service in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for information that might apply to these questions. See also the worksheets in Appendix D, Data Service Configuration Worksheets and Examples, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
If you choose to use your HADB data service with another highly available application, resource dependencies might exist. See Appendix B, Standard Properties, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for a description of the Resource_dependencies property.
-
Will all history files, data and log devices, and the database configuration files reside on local file systems?
-
What are the Sun Cluster private interconnect hostnames that you will use?
Installing and Configuring the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Software
The Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) software is a Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE™) 1.3 compliant relational database. The Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) data service is designed to meet the needs of enterprise customers and run under the control of Sun Cluster software. The Sun Java System Application Server provides a transactional session-state persistence infrastructure that is highly available and highly scalable. Application Server uses the HADB to store session information. The HADB management client is the command-line interface (CLI) for the HADB. A full set of utilities are available for performing HADB configuration, runtime management, and monitoring.
Instructions for using these utilities are contained in the Sun Java System Application Server documentation, the hadbm man pages, and the asadmin command session-persistence man pages. The Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) software is co-packaged with the Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition. For information about installing and configuring HADB with Sun Java System Application Server, see Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.2 High Availability Administration Guide. For information about configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server, see Sun Cluster Data Service for Sun Java System Application Server Guide for Solaris OS.
Creating a Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Database
This section contains the procedure to configure and create the initial HADB database in a Sun Cluster environment. Consider the following restrictions before creating your database.
-
You must specify an even number of Sun Cluster hosts by using the --hosts option during database creation.
-
You must specify the Sun Cluster hosts by using the Sun Cluster private interconnect hostnames. An example of a private interconnect hostname is clusternode1-priv.
-
Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) mirror nodes must be located on different Sun Cluster nodes.
-
Do not use the --inetd option.
-
All history files, data and log devices, and the database configuration files must reside on local file systems.
-
If more than one Sun Cluster node is stopped, the entire database is shut down. You must either stop only one node at a time or stop all nodes. You can stop all nodes with the clresourcegroup offline command.
-
The HADB resource group must not be used with HA Storage Plus.
 How to Create a Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Database
How to Create a Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Database
Use the example in the following procedure to create, start, and verify the database.
-
Create the database. This command automatically starts the database.
# hadbm create \ -H clusternode1-priv,clusternode2-priv,clusternode3-priv, \ clusternode4-priv,clusternode5-priv,clusternode6-priv \ --devicesize=2048 \ -a 4 --set ManagementProtocol=rsh --dbpassword=secret12 \ -s 2 hadb
For details, see the Sun Java System Application Server documentation.
Note –You must specify the hosts by using the Sun Cluster private interconnect hostnames. To find these hostnames, run the clnode show command from the primary Sun Cluster node.
Note –If you are using the recommended SSH setup, you do not need to specify the ManagementProtocol property.
-
Verify that the database is running.
# hadbm status hadb --nodes
-
Stop the database.
# hadbm stop hadb
-
Create the session store and the JDBC connection pool.
For details, see the Sun Java System Application Server documentation.
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Packages
See Installing the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) Packages to install Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) package.
Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
This procedure describes how to use the Sun Cluster maintenance commands to register and configure the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) data service as a resource mastered on multiple nodes at one time.
Note –
See Tools for Data Service Resource Administration in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for details about additional options that enable you to register and configure the data service.
To perform this procedure, you need the following information about your configuration.
-
The name of the resource type for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (supporting HADB versions before 4.4), which is SUNW.hadb
-
The names of the cluster nodes that can master the data service
Setting Extension Properties for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
The sections that follow contain instructions for registering and configuring resources for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB). For information about the extension properties, see Appendix B, Properties for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB Versions Before 4.4). The Tunable entry indicates when you can update a property.
See Appendix B, Standard Properties, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for details about all of the Sun Cluster properties.
To set an extension property of a resource, include the following option in the clresource(1CL) command that creates or modifies the resource:
-p property=value |
- -p property
-
Identifies the extension property that you are setting.
- value
-
Specifies the value to which you are setting the extension property.
You can also use the procedures in Chapter 2, Administering Data Service Resources, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS to configure resources after the resources are created.
 How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
How to Register and Configure Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
Perform the following steps to complete your configuration.
-
On a cluster member, become superuser or assume a role that provides solaris.cluster.admin RBAC authorization.
-
Register the resource type for the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB).
# clresourcetype register SUNW.hadb
-
Create the resource group for the Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB).
# clresourcegroup create -n nodelist \ -p Maximum_primaries=nodes_in_rg \ -p Desired_primaries=nodes_in_rg resource_group
- -n nodelist
-
Specifies a comma-separated subset of cluster nodes to run Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB). If this option is omitted, all cluster nodes run Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB). Use the clnode list command to find the node list names.
- -p Maximum_primaries=nodes_in_rg
-
Specifies the maximum number of nodes on which the resource can start. You must specify the same number as the value of the Desired_primaries property.
- -p Desired_primaries=nodes_in_rg
-
Specifies the desired number of nodes on which the resource can start. You must specify the same number as the value of the Maximum_primaries property.
-
Create a resource for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB), either with or without auto-recovery.
-
If you do not require the auto-recovery feature, execute the following command.
# clresource create -g resource_group -t SUNW.hadb \ -p Confdir_list=config_directory_list \ -p HADB_ROOT=install_directory \ -p DB_name=database_name resource
- -g resource_group
-
Specifies that the resource is to be added to the resource group named resource_group.
- -t SUNW.hadb
-
Specifies the predefined resource type name.
- -p Confdir_list=config_directory_list
-
Specifies the path to the configuration directory.
- -p HADB_ROOT=install_directory
-
Specifies the installation directory.
- -p DB_name=database_name
-
Specifies the name of the HADB database.
The resource is created in the enabled state.
-
If you do want to use the auto-recovery feature, execute the following command.
# clresource create -g resource_group -t SUNW.hadb \ -p Confdir_list=config_directory_list \ -p HADB_ROOT=install_directory \ -p DB_name=database_name \ -p Auto_recovery=TRUE \ -p Auto_recovery_command=command \ -p DB_password_file=password_file resource
- -p Auto_recovery=TRUE
-
Specifies that you are using the auto-recovery feature.
- -p Auto_recovery_command=command
-
Specifies the command to execute after the database recovery. This extension property is optional, regardless of the value of the Auto_recovery property.
- -p DB_password_file=password_file
-
Specifies the file from which HADB reads the database password. See the Sun Java System Application Server documentation for the format and content of the password file.
The resource is created in the enabled state.
Note –The auto-recovery command and the database password file must both exist in the local file system on each node.
-
-
Bring the resource group online.
# clresourcegroup online resource_group
- resource_group
-
Specifies the name of the application resource group that is being enabled.
-
Verify that the resource group and HADB resource are online.
# cluster status # ps -ef
-
To verify that you have correctly installed and configured Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB), run the following command.
# hadbm status database_name --nodes
The output should indicate that the database that you specified is running.
Example 2–1 Creating a SUNW.hadb Resource With Auto-Recovery
This example shows the creation of a SUNW.hadb resource with auto-recovery.
In this example the resource has the following characteristics:
-
The resource is named hadb-rs.
-
The resource is a member of a resource group named hadb-rg.
-
The resource is an instance of the SUNW.hadb resource type. The registration of the resource type is not shown in this example.
-
The configuration directory is located at /etc/opt/SUNWhadb/dbdef/hadb.
-
The installation directory is located at /opt/SUNWappserver7/SUNWhadb/4.
-
The HADB database instance associated with this resource is named hadb.
-
Auto-recovery is on.
-
The full path to the command to execute after auto-recovery is /usr/local/etc/create-session-store.
-
The HADB password file is /usr/local/etc/hadb-password-file.
clresource create -g hadb-rg -t SUNW.hadb \ -p Confdir_list=/etc/opt/SUNWhadb/dbdef/hadb \ -p HADB_ROOT=/opt/SUNWappserver7/SUNWhadb/4 \ -p DB_name=hadb \ -p Auto_recovery=true \ -p Auto_recovery_command=/usr/local/etc/create-session-store \ -p DB_password_file=/usr/local/etc/hadb-password-file hadb-rs |
Verifying the Installation and Configuration of Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
This section contains the procedure to verify that you installed and configured your data service correctly.
 How to Verify the Installation and Configuration for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
How to Verify the Installation and Configuration for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
-
Ensure that the HADB is started under the control of Sun Cluster software.
# clresourcegroup online -M resource_group
-
Verify that the resource group and HADB resource are online.
# cluster status # ps -ef
-
Verify that you have correctly installed and configured Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB).
# hadbm status database_name --nodes
The output should indicate that the database that you specified is running.
Maintaining the HADB Database
This section explains how to maintain the HADB database within the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) data service.
 How to Maintain the HADB Database
How to Maintain the HADB Database
When you want to run HADB maintenance commands that initiate a rolling restart of the HADB nodes, the HADB resource probe in the fault monitor must be disabled before the maintenance commands are executed and then enabled after the commands and the rolling restart have been completed.
-
Disable the fault monitor.
# clresource unmonitor resource
-
Run the commands that might initiate a rolling restart.
The hadbm subcommands that might result in a rolling restart include set, restart, and addnodes.
-
Reenable the fault monitor.
# clresource monitor resource
Alternative Method of Maintaining the Database
Alternatively, the HADB resource can be disabled and HADB started outside Sun Cluster control while maintenance commands are being performed.
Tuning the Fault Monitor for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB)
The fault monitor for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB) is contained in the resource that represents Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB). You create this resource when you register and configure Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB). For more information, see Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Application Server EE (HADB).
System properties and extension properties of this resource control the behavior of the fault monitor. The default values of these properties determine the preset behavior of the fault monitor. The preset behavior should be suitable for most Sun Cluster installations. Therefore, you should tune the fault monitor only if you need to modify this preset behavior.
For more information, see the following sections.
Operations by the Fault Monitor During a Probe
The start method of the HADB resource starts HADB nodes that are configured to run on the local Sun Cluster node if they are not running. The method then attempts to start the HADB database. If a failure occurs, the database is started later in the probe.
The fault monitor probe periodically checks the status of the HADB database and the HADB nodes. The probe restarts failed HADB nodes. The probe also starts the HADB database if the HADB resource is not ready to start the database during the start method. For each iteration of this procedure, the probe executes the following steps:
-
The probe retrieves the current status of the HADB database and the HADB nodes by executing the hadbm status and hadbm status --nodes commands.
-
If the database is not running, the probe checks that the HADB stopstate file corresponding to that database exists on the local Sun Cluster node. The hadbm start command references the stopstate file for role assignment of nodes when it starts the database.
-
If the stopstate file exists, the HADB resource examines it to determine if the database can be started.
-
If the database can be started, the probe starts the database and sets the resource status to Online.
-
If the database cannot be started, the probe sets the resource status to Online Degraded.
-
-
If the database is running, the probe starts the HADB nodes configured to run on the local Sun Cluster node.
-
If the database and the local HADB nodes are running, the probe sets the resource status to Online if it was Online Degraded.
-
If all the Sun Cluster nodes in the HADB resource group have the HADB resource running in the Online Degraded state longer than Stop_timeout seconds, the HADB resource concludes that the database cannot be started. For a description of the Stop_timeout property, see the method_timeout resource property in Appendix B, Standard Properties, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
-
If the Auto_recovery extension property is set to TRUE, the HADB resource attempts to recover the database.
-
If recovery of the database is attempted, the probe executes the following steps:
-
Issues the hadbm clear --fast command on one of the Sun Cluster nodes in the resource group's node list. This command clears the database contents and reinitializes and restarts the database.
-
If the hadbm clear command succeeds, the command specified in Auto_recovery_command is issued on the same Sun Cluster node that issued the hadbm clear command. The command would normally be a script that contains the asadmin create-session-store command. The command can also perform other actions. For example, it might send mail to the Application Server administrator.
-
If both steps succeed, the probe sets the state of the resource to Online.
-
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
