Dependency Cycles
The Logical Domains Manager does not permit you to create domain relationships that create a dependency cycle. A dependency cycle is a relationship between two or more domains that lead to a situation where a slave domain depends on itself, or a master domain depends on one of its slave domains.
The Logical Domains Manager determines whether a dependency cycle exists before adding a dependency. The Logical Domains Manager starts at the slave domain and searches along all paths that are specified by the master array until the end of the path is reached. Any dependency cycles found along the way are reported as errors.
The following example shows how a dependency cycle might be created. The first command creates a slave domain called mohawk that specifies its master domain as primary. So, mohawk depends on primary in the following dependency chain:
Figure 11–1 Single Domain Dependency

The second command creates a slave domain called primary that specifies its master domain as counter. So, mohawk depends on primary, which depends on counter in the following dependency chain:
Figure 11–2 Multiple Domain Dependency

The third command attempts to create a dependency between the counter and mohawk domains, which would produce the following dependency cycle:
Figure 11–3 Domain Dependency Cycle
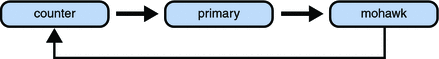
The ldm set-domain command will fail with the following error message:
# ldm add-domain master=primary mohawk # ldm set-domain master=counter primary # ldm set-domain master=mohawk counter Dependency cycle detected: LDom "counter" indicates "primary" as its master |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
