SunVTS Architecture
The SunVTS architecture is divided into three components: the SunVTS kernel, the user interface, and the collection of hardware tests. Figure 1-2 is a block diagram representing the SunVTS architecture.
Figure 1-2 SunVTS Architecture
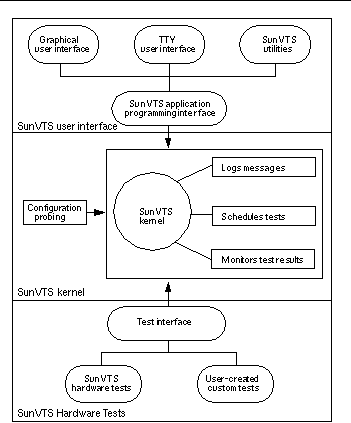
SunVTS Kernel
The following activities are scheduled and monitored by the kernel:
-
Probing and saving the test system's hardware configuration at startup
-
Logging messages reported from tests
-
Maintaining the status of all running tests
-
Monitorsingthe status requests and controls the commands from a user interface or other applications
-
Scheduling the tests that are enabled by the user
-
Runing as a background process (daemon)
There are two versions of the SunVTS kernel:
-
32-bit kernel: /opt/SUNWvts/bin/vtsk
-
64-bit kernel: /opt/SUNWvts/bin/sparcv9/vtsk
SunVTS User Interface
The SunVTS user interface is separate from the SunVTS kernel. The user interface communicates with the SunVTS kernel through an application programming interface (API). This gives SunVTS the ability to run the appropriate interface (CDE, OPEN LOOK, or TTY) based on the environment of the system. It also allows the user interface to run on a system other than the system under test.
SunVTS Hardware Tests
Many separate tests make up the collection of tests in the SunVTS application. Each test is a separate process from the SunVTS kernel.
When SunVTS is started, the SunVTS kernel automatically probes the system kernel to determine the installed hardware devices. Those devices are then displayed on the SunVTS control panel with the appropriate tests and test options. This provides a quick check of your hardware configuration, and no time is wasted trying to run tests that are not applicable to your configuration.
During testing, the hardware tests send the test status and messages to the SunVTS kernel through interprocess communication (IPC) protocols. The kernel passes the status to the user interface and logs the messages.
SunVTS has a shared object library that contains test-specific probing routines. At runtime, the SunVTS kernel dynamically links in and calls these probing routines to initialize its data structure with test-specific information. You can add new tests into the SunVTS environment without recompiling the SunVTS source code.
As of SunVTS 3.0, the SunVTS kernel and most tests support 32-bit and 64-bit operating environments. When the sunvts command is used to start SunVTS, the appropriate tests (32-bit or 64-bit versions) are presented in the SunVTS interface.
32-Bit and 64-Bit Tests
Because each test is a separate program, you can run individual tests directly from the command line. When this is done, care must be taken to run the appropriate test (32-bit or 64-bit) that corresponds to the operating system that is running (32-bit or 64-bit). This is done by running tests from specific directories as follows:
-
32-bit tests--/opt/SUNWvts/bin/testname
-
64-bit tests--/opt/SUNWvts/bin/sparcv9/testname
Note -
If you use the sunvts command to run SunVTS with a user interface (not from the command line), SunVTS will automatically allocate 32-bit or 64-bit tests based on the 32-bit or 64-bit Solaris operating environment that is running.
If you are not sure which version (32-bit or 64-bit) operating system is running, refer to the Solaris 7 System Administration manuals. On Solaris 7 the following command can be used to identify the application support of your system.
| # isainfo -v |
Note -
The isainfo command is not present on systems running Solaris 2.6 or earlier revisions.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
