Chapter 4 Sun Enterprise 10000 Release Notes
This chapter contains the Solaris operating environment on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server release notes, the Alternate Pathing (AP) release notes, and Dynamic Reconfiguration (DR), and the InterDomain Network (IDN).
Alternate Pathing
Alternate Pathing (AP) 2.2 is the first release of AP that is supported on Sun Enterprise 10000 domains running the Solaris 7 11/99 operating environment.
AP enables you to define and control alternate physical paths to peripheral devices, adding increased availability and a level of fault recovery to your server. If a physical path to a device becomes unavailable, an alternate path can be used. For more information, see the Sun Enterprise Server Alternate Pathing 2.2 User's Guide in the Solaris 7 11/99 on Sun Hardware Collection AnswerBook.
Note -
At the time of this printing, AP 2.2 is not compatible with any version of Sun Enterprise Volume Manager(TM) (SEVM).
Installation Issues
If you are upgrading from Solaris 2.5.1 or 2.6 to Solaris 7 11/99 and have AP 2.0 or 2.1 and Solstice(TM) DiskSuite(TM) 4.0 or 4.1 (SDS) on your system, you must upgrade to AP 2.2 and SDS 4.2. This section contains an overview of the entire process, which requires you to use several sections from different publications. You must ensure that you have the following publications before you start the upgrade:
-
Solaris 7 11/99 Release Notes Supplement for Sun Hardware (available in printed form in your Solaris 7 11/99 Media Kit)
-
Solaris 7 11/99 Sun Hardware Platform Guide, (available in printed form in your Solaris 7 11/99 Media Kit or in AnswerBook2 format on the Sun Hardware Supplements CD)
-
Sun Enterprise Server Alternate Pathing User's Guide (available in AnswerBook2 format on the Sun Hardware Supplements CD in your Solaris 7 11/99 Media Kit)
-
Solstice DiskSuite 4.2 User's Guide (available in AnswerBook2 format from http://docs.sun.com or from your SDS Media Kit)
-
Solstice DiskSuite 4.2 Installation and Product Notes (available in AnswerBook2 format from http://docs.sun.com or from your SDS Media Kit)
You must follow the sequence given here to successfully complete the upgrade.
In general, you will perform the following tasks:
-
Unconfigure SDS 4.0 or 4.1.
-
Remove AP 2.0 or 2.1.
-
Upgrade to Solaris 7 5/99.
-
Install AP 2.2.
-
Install and reconfigure SDS 4.2.
Specifically, you must perform the following tasks:
-
Read "Performing an Upgrade of AP" in "Alternate Pathing 2.2 on the Sun Enterprise 10000" in the Solaris 7 11/99 Sun Hardware Platform Guide.
-
Commit any uncommitted AP metadevices (see Step 1 in "To Upgrade AP" in "Alternate Pathing 2.2 on the Sun Enterprise 10000" in the Solaris 7 11/99 Sun Hardware Platform Guide).
-
Deconfigure SDS (see steps 1 through 8 in "How to Convert to DiskSuite 4.2 on SPARC Systems Running DiskSuite 4.0 or 4.1" in the Solstice DiskSuite 4.2 Installation and Product Notes).
 Caution -
Caution - Do not install Solaris 7 11/99 at this time.
-
Perform steps 3 through 5 in "To Upgrade AP" in "Alternate Pathing 2.2 on the Sun Enterprise 10000" in the Solaris 7 11/99 Sun Hardware Platform Guide).
Note -For this release, you must remove the SUNWapap package as part of Step 3a in "To Upgrade AP" in the Solaris 7 11/99 Sun Hardware Platform Guide.
-
Upgrade to Solaris 7 11/99 (see Step 6 in "To Upgrade AP" in "Alternate Pathing 2.2 on the Sun Enterprise 10000" in the Solaris 7 11/99 Sun Hardware Platform Guide).
-
Follow steps 6 through 9 in "To Upgrade AP" in "Alternate Pathing 2.2 on the Sun Enterprise 10000" in the Solaris 7 11/99 Sun Hardware Platform Guide).
-
Install SDS 4.2, then restore it (see Step 10 in "To Upgrade AP" in "Alternate Pathing 2.2 on the Sun Enterprise 10000" in the Solaris 7 11/99 Sun Hardware Platform Guide and steps 10 through 16 in "How to Convert to DiskSuite 4.2 on SPARC Systems Running DiskSuite 4.0 or 4.1" in Chapter 1 of the Solstice DiskSuite 4.2 Installation and Product Notes).
General Issues
This section contains general issues that involve AP on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server. You should read this section before you attempt to install or configure AP.
Supported Devices
The following devices are supported by the AP software on Sun Enterprise servers:
-
SPARCstorage(TM) Arrays recognized by AP using the pln, soc, and ssd ports
-
Sun(TM) StorEdge(TM) A5000 recognized by AP using sf, soc, and ssd ports
-
SunFastEthernet(TM) 2.0 (hme)
-
SunFDDI(TM) 5.0 (nf) SAS (Single-Attach Station) and DAS (Dual-Attach Station)
-
SCSI-2/Buffered Ethernet FSBE/S and DSBE/S (le)
-
Quad Ethernet (qe)
-
Sun(TM) Quad FastEthernet(TM) (qfe)
-
Sun GigabitEthernet 2.0 (ge)
The following table lists which network devices are supported in which releases:
Table 4-1 Supported Network Devices|
|
AP 2.0 |
AP 2.1 |
AP 2.2 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Solaris 2.5.1 |
hme, le, nf, bf, hi, qe, qfe |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Solaris 2.6 (5/98) |
N/A |
ge, hme, le, nf, qe, qfe, vge |
N/A |
|
Solaris 7 11/99 |
N/A |
N/A |
ge,hme, le, nf, qe, qfe |
SunFDDI Devices
AP 2.2 validation tests were performed on SunFDDI (revision 6.0). If you install this device, you must use the revision level that was tested, unless a higher revision level exists. In addition, you must install all of the available patches for this device. Refer to http://www.sunsolve.sun.com for more information about the patches.
Sun StorEdge A3000
The Sun StorEdge A3000 supports failover capabilities that are similar to those provided by AP. Because of this, AP does not support the Sun StorEdge A3000. See that product's documentation for more information about its failover support.
Sun StorEdge A5000
AP supports the Sun StorEdge A5000 for this release.
Sun StorEdge A7000
AP 2.2 does not support the Sun StorEdge A7000 for this release.
Software Compatibility
The following figures show the possible combinations of SSP, AP, and Solaris software you can install on a Sun Enterprise server. Note that the Sun Enterprise 10000 can have any combination of domains with the operating environment and software listed on the right of the figures. The version of the Solaris operating environment on the SSP and the version on the domain do not need to match.
Note -
In the following figures, "base only" means no AP and no DR, unless otherwise noted. Mainly, "base only" refers to a domain that has only the Solaris operating environment installed. In addition, some of the scenarios below are possible only if you install a patch, or a set of patches, on the SSP or on the domain. For more information about what patch, or patches, refer to the patch descriptions at http://sunsolve.sun.com.
Figure 4-1 SSP 3.0, AP 2.0, and Solaris 2.5.1 on the Sun Enterprise 10000
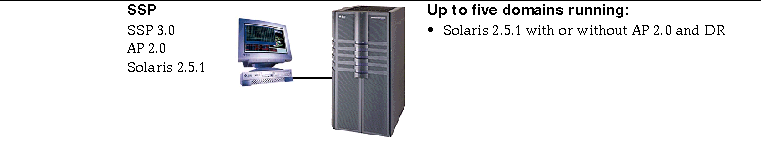
Figure 4-2 SSP 3.1, AP 2.1, Solaris 2.5.1, Solaris 2.6 3/98, Solaris 2.6 5/98, and Solaris 7 on the Sun Enterprise 10000
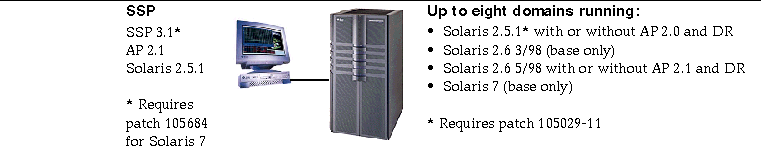
Figure 4-3 SSP 3.1, AP 2.2, AP 2.1, Solaris 2.5.1, Solaris 2.6 3/98, Solaris 2.6 5/98, Solaris 7, Solaris 7 3/99, Solaris 7 5/99, and Solaris 7 11/99 on the Sun Enterprise 10000
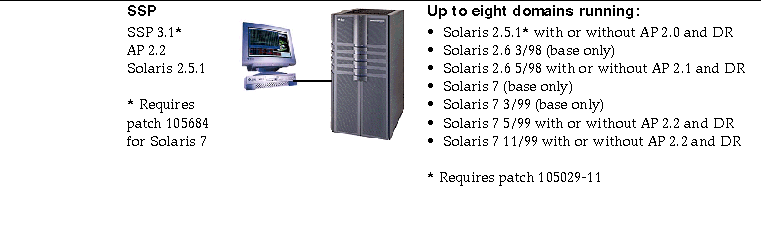
Known Bugs
There are no known bugs in this release of AP.
Fixed Bugs
This section contains the synopses and Sun BugID number of the more important bugs that have been fixed since the AP 2.1 release (Solaris 2.6 5/98). This list does not include all of the fixed bugs.
4126743 - AP disk autofailover hangs on simultaneous multi-pathgroup failures (this bug was fixed by BugID 4136249).
4126897 - Domain panics when there are no AP database and metadevice entry in /etc/vfstab.
4136249 - I/O's to SEVM RAID volumes hang after AP autofailover.
4141438 - mhme interface hangs under heavy use of network.
4143514 - FDDI with AP hangs with heavy use of network.
4147674 - AP causes ifconfig to hang on a mutex.
4153152 - apconfig works as an ordinary user.
4161396 - AP 2.x needs capability to work with GEM.
4163270 - netstat of network ap network meta interface shows no tallies.
4166620 - snoop of AP meta network interface stops snooping after switch.
4170818 - If you run the $<callouts nadb macro, or fm2's "callout ts" command, you see thousands of qenable timeouts in the timeshare callout table.
4180055 - Accessing an AP'd metadisk with a failed active alternate panics.
4180702 - Messages from swap.c are not internationalized.
4183581 - apboot disk causes coredump when disk is the same as the current boot disk.
4185154 - GigabitEnthernet stress test hangs.
4188418 - It is possible for a hard disk error to go undetected by Veritas [SEVM].
4195441 - AP2.0 ap_daemon doesn't communicate with AP2.2.
4226867 - ap_reboot_host fails for photon in mixed AP versions.
4228731 - Non-existent network interfaces not marked as detached after reboot.
Dynamic Reconfiguration
Release notes and other technical information in this section apply only to the Solaris 7 11/99 version of Sun Enterprise 10000 Dynamic Reconfiguration (DR).
General Issues
This section contains general issues that involve DR on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server. You should read this section before you attempt to install or configure DR.
dr-max-mem Utility
The way dr-max-mem is used has changed since the Solaris 2.5.1 release. Please see the appropriate section of the Solaris 7 11/99 version of the Sun Enterprise 10000 Dynamic Reconfiguration User's Guide for a detailed description of this important OBP variable.
DR and Bound User Processes
For Solaris 7 11/99, DR no longer automatically unbinds user processes from CPUs that are being detached. Users are now required to perform this operation themselves before initiating a DR Detach sequence. The DR Drain operation will fail if CPUs are found with bound processes.
Nonpageable Memory Location
For Solaris 7 11/99, the location of nonpageable memory (that is, OBP and kernel memory), the kernel cage, resides in the highest physical address space, which generally is on the highest-numbered system board in the domain. The direction of growth of this area is from highest to lowest physical addresses. Exceptions to this rule do exist. Always use drshow(1M) to verify a board's memory state.
Kernel Cage Location
For Solaris 7 11/99, the location of the kernel cage changed from the lowest numbered system board(s) to the highest numbered board(s). However, some customers require the kernel cage to be located on the lowest numbered system board. If you have this requirement, you can apply Patch 105873-08, as a minimum level, on the SSP to change the location of the cage. Refer to the Patch README file for instructions on how to install the patch. You can obtain the patch from http://sunsolve.corp.sun.com or from your local service provider.
DR and Tape Drives
For Solaris 7 11/99, the st driver, which has been considered DR unsafe in the past, is now DR safe. The driver now waits for existing I/O requests to complete before the drive is suspended.
DR and SunFDDI
If your Sun Enterprise 10000 server contains any SunFDDI(TM) SBus Adapter 5.0 interfaces and you plan to use DR, you must install Sun Patch 104572-05, or the highest revision level available. You can obtain this patch at the following Web site:
-
http://sunsolve.corp.sun.com
DR and the Sun StorEdge A3000
Dynamic Reconfiguration of Sun(TM) StorEdge(TM) A3000 arrays on the Sun Enterprise 10000 running Solaris 2.6 requires RAID Manager 6.01.00, or later, for correct operation.
DR and the Sun StorEdge A5000
DR will be supported on systems configured with Sun StorEdge A5000 devices and the latest StorEdge A5000 patch. Contact your service provider for more information on how to obtain the patch.
For I/O boards connected to the A5000, you must ensure that the FC-AL disk firmware version is ST19171FC 0413 or newer version. For more information, refer to the following Web site:
-
http://sunsolve2.Sun.COM/sunsolve/Enterprise-dr/
DR and pln and soc Drivers
If you are using pln and/or soc drivers on your server, you must ensure that the parameters are properly set in the /etc/system file. The file should include the following two entries, exactly as the appear in the example.
set pln:pln_enable_detach_suspend=1
set soc:soc_enable_detach_suspend=1
Known Bugs
This section contains the known bugs in the Sun Enterprise 10000 DR feature of the Solaris 7 11/99 release.
DR Abort Detach May Not Resume All Detached Disks (4010910)
If a DR detach operation fails to detach an sd device and the controller has sd devices that have already been detached, the abort-detach operation does not resume (that is, re-attach) those devices that share the same controller instance and that have already been detached. This situation rarely occurs. The most likely time for it to happen is if the disk drive firmware is locked up.
Workaround: None
dr_daemon Does Not Find Veritas Device Usage (4011123)
Veritas software usage of disks is not displayed by DR applications in their device-usage displays.
Workaround: None
disks(1M) Command Preens Controller Entries and Corrupts the Sun StorEdge A3000 Device Tree (4096048)
The Solaris disks(1M) command preens or deletes symbolic link entries when disk devices are no longer present in an Enterprise 10000 domain. If you have dynamically reconfigured the devices so that they are no longer present, the Symbios-managed device tree and the Solaris-managed device tree can become inconsistent.
Workaround: You must obtain the proper patch from SunSolve or from your service representative. This patch contains fixes that ensure persistent node names under the Solaris operating environment when StorEdge A3000 devices are dynamically reconfigured out of a given Enterprise 10000 domain. The patch ensures that when the same array is brought back into the domain, it inherits the same node name it originally had, thereby maintaining data availability without having to modify system mount points or user application configurations. You must ensure that you do not perform reconfiguration reboot operations (boot -r) in a domain when A3000 devices are present on the system boards.
DR Operation Fails Due to an Incompatibility with the DMP Feature in SEVM (4215683)
DR and the DMP feature in Sun Enterprise Volume Manager (SEVM) are not compatible. If any disks are under DMP control, they cannot be detached.
Workaround: None
Cannot Drain and/or Detach Sun Enterprise Server System Boards that Host QFE Cards (4231845)
The configuration of a boot server for Solaris 2.5.1-based x86 clients results in the execution of rpld daemons. These daemons maintain an active (open) reference to all network devices, whether or not such devices are in use. These active references prevent DR operations from detaching these devices.
Workaround: Remove or rename the /rplboot directory, then shut down and restart NFS with these commands:
# sh /etc/init.d/nfs.server stop
# sh /etc/init.d/nfs.server start
StorEdge A3000 Daemon Cannot Be Suspended (4100212)
The presence of StorEdge A3000 daemons (rdaemon) prevent a DR Detach operation from completing if the operating environment must be quiesced (that is, suspended and resumed) to detach non-pageable memory.
Workaround: Temporarily disable the daemon before the DR operation, then restart the daemon after the DR operation by using the following command:
# sh /etc/rc2.d/S90amon stop
# sh /etc/rc2.d/S90amon start
Unable to Drain Sysboards in Solaris 7 and dr_daemon Segmentation Faults (4229238)
After numerous iterations through a failure handling condition within the DR daemon, the daemon can encounter a segmentation violation (that is, a core dump). Note that this condition occurs during an error handling flow (that is, a DR operation failure).
Workaround: Restart the DR applications on the SSP.
Bugs Fixed
The following important bugs have been fixed since the last release of DR. This list does not include minor bugs, nor does it include those bugs that were fixed in patches.
4083412 - socal and sf need to support DETACH/SUSPEND/RESUME
4090750 - DR panics during detach when dr-max-mem set is high.
4067860 - SUNWcsr on upgrading from Solaris 2.5.1 8/97 to Solaris 2.6 5/98 creates duplicate majors in name_to_major.
4131197 - dr_daemon core dumps with Solaris 2.6 5/98 release.
4133607 - DR operations with mem_board_interleave_ok cause problems.
4134357 - availrmem is not being reduced during Sun Enterprise 10000 memory detach.
4135366 - Sun StorEdge A3000 patch has been changed.
4136544 - Getting "flusher thread" hang during DR drain with official -20 KU patch.
InterDomain Networks
InterDomain Networks (IDNs) are internal, high-speed, hardware connections that enable dynamic system domains (referred to as domains in this chapter) on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server to communicate with each other as though they are communicating over a standard network. For more information, refer to the Sun Enterprise 10000 InterDomain Networks User Guide in the SSP 3.2 AnswerBook2TM collection.
General Issues
This section contains general issues about the IDN feature. Read this section before you attempt to configure an IDN.
Software Support
To use IDNs, the SSP must be running SSP version 3.2.
idn.conf(4) File
IDNs are initialized on the domain by using the idn.conf(4) file. Each domain must have an idn.conf(4) file to be a member of an IDN. This file is used to instantiate each instance of the driver and to initialize multiple parameters that can affect the performance and behavior of the IDN. You must ensure that the values of the parameters are within the allowed ranges of the values. Refer to the Sun Enterprise 10000 InterDomain Networks User Guide in the SSP 3.2 AnswerBook2TM collection for more information about the idn.conf(4) parameters.
Values outside of the allowed range can result in panics occurring on the domain after the domain is rebooted. If the domain panics, the event detector daemon detects the panic and reboots the domain, causing the domain to panic again. Thus, the domain cannot be rebooted if the idn.conf(4) file contains an incorrect value. Sun Microsystems suggests that any /etc/hostname.idnX file be removed to prevent automatic loading of the IDN driver upon reboot.
OpenBootTM PROM
Be aware of the following issues with the idn-smr-size variable and with breaking to the OpenBoot PROM (OBP) prompt on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server.
idn-smr-size Variable
The OBP variable for the IDN feature, idn-smr-size, is present in Solaris 2.6. If Solaris 2.6 is installed on a domain, do not set the value to any other value other than zero (the default value). The IDN feature is not supported in the Solaris 2.6 operating environment.
OBP Environment
Before you break to the OBP prompt, unlink the domain from its IDN by using the domain_unlink(1M) command. Do not break to OBP while the domain is linked to an IDN.
Known Bugs
The following is a list of bugs that are known to exist in this release of the IDN feature.
VerExec Error Occurs When a Solaris 2.6 Domain Is Rebooted From OBP (4254715)
Errors that are related to the IDN feature can occur on domains running the Solaris 2.6 operating environment. Some messages can be safely ignored; however, some messages are related to setting the OBP variable idn-smr-size to a value other than zero.
Workaround: The Solaris 2.6 operating environment does not support the IDN feature. Do not change the default value of idn-smr-size on domains that are running the Solaris 2.6 operating environment.
IDN Driver Can Panic if idn_slab_mintotal Is Set to a Value Other Than Zero (4273317)
Parameter values set outside of the allowed range can result in panics occurring on the domain. You must ensure that you use a value that is within the allowed range of values.
The following is a list of parameters that can cause a panic if the value set in the idn.conf(4) file is outside of the allowed range.
-
idn_slab_mintotal
-
idn_slab_bufcount
-
idn_smr_bufsize
Workaround: No workaround exists for this bug. The domain will continue to panic because of the incorrect values in the idn.conf(4) file any time the IDN driver is loaded. You must ensure that you use values that are within the allowed range.
Setting idn_protocol_nservers Value to the Minimum Value of One Causes Panic (4275051)
Setting the idn.conf(4) parameter idn_protocol_nservers to one can cause the domain to panic. The idn.conf(4) parameters are initialized when the domain is rebooted and the IDN driver is loaded. If the domain panics, the event detector daemon reboots the domain, and the domain panics again, causing an unrecoverable error.
Workaround: Do not set this parameter to one. If this error occurs, reboot the domain to single-user mode and remove the /etc/hostname.idnX file to prevent the IDN driver from being automatically loaded at reboot.
Remote Domain Reporting Master Domain Without CPU ID (4275420)
Certain combinations of CPU IDs and domain IDs in a domain responding to a connect request can cause incorrect information being sent in the connect request.
Workaround: None
IDN Driver Does Not Implement MIB-II Kernel Statistics (4276084)
The IDN driver does not implement MIB-II kernel statistics for this release. Thus, network management tools that display MIB-II kernel statistics will not be able to display statistics about IDNs.
Workaround: No workaround exists for this bug. It will not be fixed in this release.
Setting idn_msgwait_nego to the Minimum Value (1 Second) Can Cause IDN Operations to Fail (4277617)
Setting the idn.conf(4) parameter idn_msgwait_nego to 1 second can cause IDN operations to fail. The idn.conf(4) parameters are initialized when the domain is rebooted. If this error occurs, you must reset the value and reboot the domain before you can execute IDN operations.
Workaround: Do not set this parameter to one. This bug will not be fixed in this release.
Patches
This section contains a list of patches that should be applied before you attempt to set up an IDN.
108317-01
Description: IDN driver can will panic if property (idn_slab_mintotal) set out of range
Bugs fixed: 4273317, 4275051, 4275420
Note -
You must go to the SunSolve web site to obtain this patch.
Documentation Errata
This section contains descriptions of errors in the publications that were found after the release of the IDN feature.
domain_link(1M) and domain_unlink(1M)
The domain_link(1M) and domain_unlink(1M) man pages should have included a note that instructs users to use the proper domain name for the SUNW_HOSTNAME variable when they are linking or unlinking domains. The domain must support the IDN feature. The IDN user guide includes this information.
IDN Parameter Values
Some of the parameter values given in "Configuring InterDomain Networks" in the Sun Enterprise 10000 InterDomain Networks User Guide are incorrect. The following table contains the proper values.
Table 4-2 Corrections to IDN Parameter Values|
Parameter |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
idn_awolmsg_interval |
0 |
3600 |
60 |
|
idn_hiwat |
1024 |
1048576 |
262144 |
|
idn_lowat |
1 |
524288 |
1 |
|
idn_msgwait_cfg |
1 |
300 |
40 |
|
idn_msgwait_cmd |
1 |
300 |
40 |
|
idn_msgwait_con |
1 |
300 |
20 |
|
idn_msgwait_nego |
1 |
300 |
20 |
|
idn_netsvr_spin_count |
0 |
10000 |
500 |
|
idn_netsvr_wait_min |
0 |
3000 |
40 |
idn.conf(4) File Parameters
Some of the parameter descriptions in "Configuring InterDomain Networks" in the Sun Enterprise 10000 InterDomain Networks User Guide state that the parameter can be changed at any time or that the domain must be unlinked from the IDN before the parameter can be changed. This information is incorrect. All idn.conf(4) file parameters can be changed while the domain is linked to the IDN; however, the domain must be rebooted before the values take affect.
The value of the idn_smr_bufsize parameter must be a power of two.
The idn.conf(4) file parameter table includes the idn_modunloadable parameter. This parameter is an ndd(1M) parameter. It is not an idn.conf(4) parameter.
The description of the idn.conf(4) parameter idn_smr_size is incorrect. The description should state that the size of the shared memory region (SMR) is limited by the value of the OBP variable idn-smr-size. The size of the SMR is determined by the minimum value of the idn-smr-size variable and by the minimum value of the idn_smr_size parameter. If idn-smr-size is set to zero, the OBP variable overrides the value of the idn.conf(4) parameter.
Solaris Operating Environment
This section contains general issues, known bugs, patches, and notes about the Solaris 7 11/99 release on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server.
General Issues
Upgrades from Solaris 2.3 or Solaris 2.4 to Solaris 7 11/99 are not supported.
Note -
Before beginning the fresh install or upgrade procedures for the Solaris operating environment on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server, you must install the SSP patches described in the Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP Installation Guide and Release Notes, unless you have upgraded the SSP operating environment to SSP 3.1.1 or SSP 3.2.
Solaris 7 11/99 and Boot-Disk Partition Sizes
If you are upgrading the operating environment from Solaris 2.6 to Solaris 7 11/99 and if you used the partition layout suggested in the SMCC Hardware Platform Guide Solaris 2.6, the partitions may not be large enough for the upgrade. For instance, the /usr partition must be at least 653 megabytes. If /usr is smaller than the size needed to perform the upgrade, suninstall uses the dynamic space reallocation (DSR) mode to reallocate the space of the disk partitions.
DSR may calculate a partition layout which is not acceptable for some systems. For instance, DSR may select partitions that appear to DSR as being unused (non-UFS partitions which may contain raw data or other types of file systems). If DSR selects a used partition, data loss may occur. Therefore, you must know the current status of the partitions DSR wants to use before you allow DSR to continue with the reallocation of the disk partitions.
After DSR presents an acceptable layout and you choose to proceed with the reallocation, DSR will adjust the affected file systems, and the upgrade will continue. However, if you cannot constrain the layout so that it is acceptable for your needs, then you may need to manually repartition the boot device, or you may have to perform a fresh install.
Solaris 7 11/99 and Driver Variables
For Solaris 7 11/99, you must enable the soc and pln drivers in /etc/system before you attempt to detach a system board that hosts these drivers. Use the following syntax to enable the drivers:
set pln:pln_enable_detach_suspend=1
set pln:pln_enable_detach_suspend=1
SunFDDI
SunFDDI(TM) is not supported on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server.
SunATM 4.0 Update 1
SunATM(TM) 4.0 Update 1 is not supported on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server.
Known Bugs
This section contains the bugs known to exist in the Solaris 7 11/99 release.
4231845 - Cannot Detach System Board if the in.rarpd Daemon is Running and /rplboot Exists
For Solaris 7 11/99 Beta, the qec and qe drivers are not compatible with DR or AP 2.2.
Workaround: None
Fixed Bugs
This section lists important bugs that have been fixed. Minor bugs are not included. Each entry includes a 7-digit BugID assigned by Sun to aid in bug-tracking and a one-line description of the bug.
4110199 - /etc/init.d/cvc Implementation, Packaging Inconsistent
Documentation Errata
This section contains errors in the documentation that pertains to the Solaris operating environment on the Sun Enterprise 10000 server.
OBP Variables
Before you perform the boot net command from the OBP prompt (ok), you must verify that the local-mac-address? variable is set to false, which is the factory default. If it is set to true, you must ensure that this value is an appropriate local configuration.
If local-mac-address? is set to true, it may prevent the domain from successfully booting over the network.
In a netcon(1M) window, you can use the following command at the OBP prompt to display the values of the OBP variables:
ok printenv
To Set the local-mac-address? Variable
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
