From Configuration Profiles to Application Settings
This section describes how the configuration data is processed to end up with user settings for a specific application running in a specific host.
Configuration Data Sources
Each user application receives configuration data from the following sources:
-
Default configuration data source: stores the default settings for an application. This configuration data source is deployed with the application and remains mostly unchanged throughout its lifetime. The query mechanisms and the format for this data source are defined by each application. Some applications use a "proprietary" method to store configuration data, while other applications use a shared subsystem for the configuration data, for example, GConf.
-
User configuration data source: stores user settings for an application. The query/update mechanisms and format for this data source are defined by each application.
-
Profile Configuration data source: this data source is provided by the Sun Desktop Manager 1.0. The configuration data is stored in the configuration repositories. The mechanisms to access that data are provided by the Configuration Agent and the Configuration Adapters.
The application settings for a user on a host are calculated in two steps. The profile configuration tree is constructed, and then the configuration data sources are combined.
Construction of the Profile Configuration Data
The profile configuration data holds the configuration profile for a user application that runs on a specific host.
The organizational units of an organization, along with the users, are stored in the configuration repository hierarchically. The same applies to the domain components.
Configuration profiles are assigned to elements in the hierarchies. Configuration profiles that are assigned to an element are inherited by the children of that element.
The configuration data of an application depends on the user who runs the application and the host where the application runs.
The configuration settings that affect a user depend on the configuration profiles that are assigned to the elements in the path from the user element to the root of the tree. These profiles must be merged together to build the set of configuration settings for the user.
Since it is possible to define profiles based on the host where the application of the user is running, the profiles assigned to the host, or to any of the elements that are in the path from the host to the root of the tree should also be merged together with the configuration profiles that affects the user.
Figure 1–2 Configuration Process
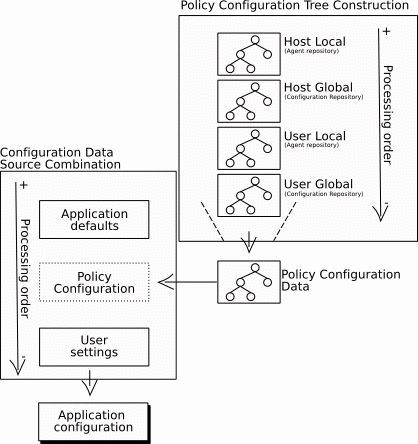
The following rules are used to construct the profile configuration:
-
Order of processing: The order in which profiles are merged is important. The Host Local set of configuration profiles are processed first, followed by the Host Global set, the User Local set, and then the User Global set.
If there is more than one configuration profile in a set, the priority number that is associated with a profile determines the precessing order for the profile, that is, the lowest number is processed first.
-
Properties and Values: A property is an element in the configuration that can be defined, for example, "background color". A value is the value that you assign to a property, for example, the value for the property "background color" is "white".
If a new property is introduced by one profile, the property and its value are added to the merged configuration tree.
If a property has a value that is marked as enforced, the new value is stored in the merged tree. New values for the property that occur in other profiles are ignored.
If a property already has a value when a new value is defined in a profile that is being processed, the new value is assigned to the property.
Configuration Data Source Combination
The configuration data provided by the three different configuration data sources must be combined to produce a single set of settings for the user application to use at runtime.
-
The configuration data provided by the default configuration provider is read and a configuration tree is constructed.
-
A profile configuration data is constructed based on the user and host of the client application.
-
The user settings are read and a configuration tree is constructed.
-
The three trees are combined into one to get the configuration settings that the application will use. The rules followed in this process are the same that where used to construct the profile configuration data.
The resulting tree will be used by the application adapters to provide the configuration settings.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
