SPARC: Sun Cluster Topologies for SPARC
A topology is the connection scheme that connects the cluster nodes to the storage platforms that are used in a Sun Cluster environment. Sun Cluster software supports any topology that adheres to the following guidelines.
-
A Sun Cluster environment that is composed of SPARC based systems supports a maximum of sixteen nodes in a cluster, regardless of the storage configurations that you implement.
-
A shared storage device can connect to as many nodes as the storage device supports.
-
Shared storage devices do not need to connect to all nodes of the cluster. However, these storage devices must connect to at least two nodes.
Sun Cluster software does not require you to configure a cluster by using specific topologies. The following topologies are described to provide the vocabulary to discuss a cluster's connection scheme. These topologies are typical connection schemes.
-
Clustered pair
-
Pair+N
-
N+1 (star)
-
N*N (scalable)
The following sections include sample diagrams of each topology.
SPARC: Clustered Pair Topology for SPARC
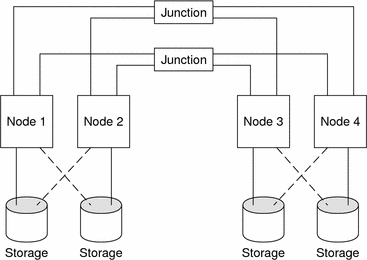
A clustered pair topology is two or more pairs of nodes that operate under a single cluster administrative framework. In this configuration, failover occurs only between a pair. However, all nodes are connected by the cluster interconnect and operate under Sun Cluster software control. You might use this topology to run a parallel database application on one pair and a failover or scalable application on another pair.
Using the cluster file system, you could also have a two-pair configuration. More than two nodes can run a scalable service or parallel database, even though all the nodes are not directly connected to the disks that store the application data.
The following figure illustrates a clustered pair configuration.
Figure 2–2 SPARC: Clustered Pair Topology
SPARC: Pair+N Topology for SPARC
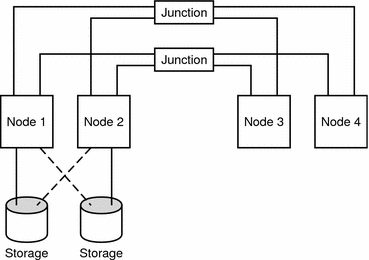
The pair+N topology includes a pair of nodes directly connected to shared storage and an additional set of nodes that use the cluster interconnect to access shared storage—they have no direct connection themselves.
The following figure illustrates a pair+N topology where two of the four nodes (Node 3 and Node 4) use the cluster interconnect to access the storage. This configuration can be expanded to include additional nodes that do not have direct access to the shared storage.
Figure 2–3 Pair+N Topology
SPARC: N+1 (Star) Topology for SPARC
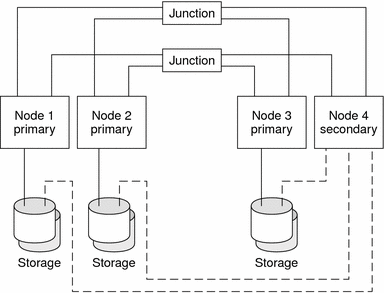
An N+1 topology includes some number of primary nodes and one secondary node. You do not have to configure the primary nodes and secondary node identically. The primary nodes actively provide application services. The secondary node need not be idle while waiting for a primary to fail.
The secondary node is the only node in the configuration that is physically connected to all the multihost storage.
If a failure occurs on a primary, Sun Cluster fails over the resources to the secondary, where the resources function until they are switched back (either automatically or manually) to the primary.
The secondary must always have enough excess CPU capacity to handle the load if one of the primaries fails.
The following figure illustrates an N+1 configuration.
Figure 2–4 SPARC: N+1 Topology
SPARC: N*N (Scalable) Topology for SPARC
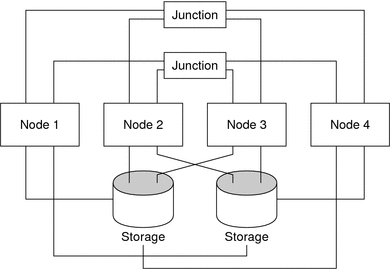
An N*N topology enables every shared storage device in the cluster to connect to every node in the cluster. This topology enables highly available applications to fail over from one node to another without service degradation. When failover occurs, the new node can access the storage device by using a local path instead of the private interconnect.
The following figure illustrates an N*N configuration.
Figure 2–5 SPARC: N*N Topology
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
